Arts and literature
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(October 2012) |
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in Norway | ||||
Events in the year 1176 in Norway .
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(October 2012) |
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(October 2012) |
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(October 2012) |

The Kalmar Union was a personal union that from 1397 to 1523 joined under a single monarch the three kingdoms of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway, together with Norway's overseas dependencies. The union was not quite continuous; there were several short interruptions. Legally, the countries remained separate sovereign states, but with their domestic and foreign policies being directed by a common monarch.

Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe whose territory comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula; the remote island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard are also part of the Kingdom of Norway. The Antarctic Peter I Island and the sub-Antarctic Bouvet Island are dependent territories and thus not considered part of the kingdom. Norway also lays claim to a section of Antarctica known as Queen Maud Land.
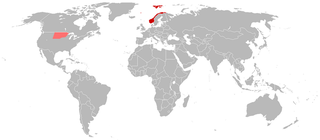
Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken mainly in Norway, where it is the official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties, and some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are hardly mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Era.

Oslo is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. Founded in the year 1040 as Ánslo, and established as a kaupstad or trading place in 1048 by Harald Hardrada, the city was elevated to a bishopric in 1070 and a capital under Haakon V of Norway around 1300. Personal unions with Denmark from 1397 to 1523 and again from 1536 to 1814 reduced its influence, and with Sweden from 1814 to 1905 it functioned as a co-official capital. After being destroyed by a fire in 1624, during the reign of King Christian IV, a new city was built closer to Akershus Fortress and named Christiania in the king's honour. It was established as a municipality (formannskapsdistrikt) on 1 January 1838. The city's name was spelled Kristiania between 1877 and 1897 by state and municipal authorities. In 1925 the city was renamed Oslo.

Scandinavia is a region in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties. The term Scandinavia in local usage covers the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. The majority national languages of these three, belong to the Scandinavian dialect continuum, and are mutually intelligible North Germanic languages. In English usage, Scandinavia also sometimes refers to the Scandinavian Peninsula, or to the broader region including Finland and Iceland, which is always known locally as the Nordic countries.

Svalbard is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. Situated north of mainland Europe, it is about midway between continental Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. Administratively, the archipelago is not part of any Norwegian county, but forms an unincorporated area administered by a governor appointed by the Norwegian government. Since 2002, Svalbard's main settlement, Longyearbyen, has had an elected local government, somewhat similar to mainland municipalities. Other settlements include the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research station of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Ny-Ålesund is the northernmost settlement in the world with a permanent civilian population. Other settlements are farther north, but are populated only by rotating groups of researchers.

Bergen, historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Hordaland on the west coast of Norway. At the end of the first quarter of 2018, the municipality's population was 280,216, and the Bergen metropolitan region has about 420,000 inhabitants. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers 465 square kilometres (180 sq mi) and is on the peninsula of Bergenshalvøyen. The city centre and northern neighbourhoods are on Byfjorden, 'the city fjord', and the city is surrounded by mountains; Bergen is known as the 'city of seven mountains'. Many of the extra-municipal suburbs are on islands. Bergen is the administrative centre of Hordaland, and consists of eight boroughs: Arna, Bergenhus, Fana, Fyllingsdalen, Laksevåg, Ytrebygda, Årstad, and Åsane.

Harald V is the King of Norway, having ascended to the throne upon the death of his father King Olav V on 17 January 1991.

The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages, a sub-family of the Indo-European languages, along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is sometimes referred to as the "Nordic languages", a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish scholars and laypeople.

Jens Stoltenberg is a Norwegian politician who has been serving as the 13th Secretary General of NATO since 2014. A member of the Labour Party, he was Prime Minister of Norway from 2000 to 2001 and from 2005 to 2013.
Norwegian Air Shuttle ASA, trading as Norwegian, is a Norwegian low-cost airline and Norway's largest airline. It is the third largest low-cost carrier in Europe behind easyJet and Ryanair and the ninth-largest low-cost airline in the world, the largest airline in Scandinavia, and the eighth-largest airline in Europe in terms of passenger numbers. It offers a high-frequency domestic flight schedule within Scandinavia and Finland, and to business destinations such as London, as well as to holiday destinations in the Mediterranean and the Canary Islands, transporting over 30 million people in 2016. The airline is known for its distinctive livery of white with a red nose, with portraits of distinguished Scandinavians on the tail fins of its aircraft.

The Norway men's national football team represents Norway in international association football and is controlled by the Football Association of Norway, the governing body for football in Norway. Norway's home ground is Ullevaal Stadion in Oslo and their head coach is Lars Lagerbäck. It is, as of February 2019, ranked by FIFA as the 48th best national football team in the world.

Norwegians are a North Germanic ethnic group native to Norway. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegian people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in the United States, Canada, Australia, Argentina, Chile, Uruguay, Brazil, Mexico, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and South Africa.

The Norwegian Campaign was the attempted Allied liberation of the Scandinavian nation of Norway from Nazi Germany during the early stages of World War II and directly following the German invasion and occupation of the Norwegian mainland and government. It took place from April 9, 1940, until June 10, 1940. The Allied campaign did not succeed, and it resulted in the fleeing of King Haakon VII along with the remainder of the royal family to Great Britain.

The German occupation of Norway during World War II began on 9 April 1940 after German forces invaded the neutral Scandinavian country of Norway. Conventional armed resistance to the German invasion ended on 10 June 1940 and the Germans controlled Norway until the capitulation of German forces in Europe on 8/9 May 1945. Throughout this period, Norway was continuously occupied by the Wehrmacht. Civil rule was effectively assumed by the Reichskommissariat Norwegen, which acted in collaboration with a pro-German puppet government, the Quisling regime, while the Norwegian King Haakon VII and the prewar government escaped to London, where they acted as a government in exile. This period of military occupation is in Norway referred to as the "war years" or "occupation period".

Denmark–Norway, also known as the Dano–Norwegian Realm, the Oldenburg Monarchy or the Oldenburg realms, was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real union consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway, the Duchy of Schleswig, and the Duchy of Holstein. The state also claimed sovereignty over two historical peoples: Wends and Goths. Denmark–Norway had several colonies, namely the Danish Gold Coast, the Nicobar Islands, Serampore, Tharangambadi, and the Danish West Indies.

The Nordic countries or the Nordics are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic, where they are most commonly known as Norden. The term includes Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, as well as Greenland and the Faroe Islands—which are both part of the Kingdom of Denmark—and the Åland Islands and Svalbard and Jan Mayen archipelagos that belong to Finland and Norway respectively, whereas the Norwegian Antarctic territories are often not considered a part of the Nordic countries, due to their geographical location. Scandinavians, who comprise over three quarters of the region's population, are the largest group, followed by Finns, who comprise the majority in Finland; other groups are indigenous minorities such as the Greenlandic Inuit and the Sami people, and recent immigrants and their descendants. The native languages Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic, and Faroese are all North Germanic languages rooted in Old Norse. Native non-Germanic languages are Finnish, Greenlandic and several Sami languages. The main religion is Lutheran Christianity. The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, history, religion, their use of Scandinavian languages and social structure. The Nordic countries have a long history of political unions and other close relations, but do not form a separate entity today. The Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century, with the indepedence of Finland in the early 20th century, and Iceland in the mid 20th century, this movement expanded into the modern organised Nordic cooperation which includes the Nordic Council and the Nordic Council of Ministers. Especially in English, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for the Nordic countries, but that term more properly refers to the three monarchies of Denmark, Norway and Sweden. Geologically, the Scandinavian Peninsula comprises the mainland of Norway and Sweden as well as the northernmost part of Finland.

The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor, and armaments manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiology or Medicine, and Literature. Since March 1901, it has been awarded annually to those who have "done the most or the best work for fraternity between nations, for the abolition or reduction of standing armies and for the holding and promotion of peace congresses".

The 2011 Norway attacks, referred to in Norway as 22 July or as 22/7, were two sequential lone wolf domestic terrorist attacks by Anders Behring Breivik against the government, the civilian population, and a Workers' Youth League (AUF) summer camp, in which 77 people were killed.

Anders Behring Breivik, since 2017 legally Fjotolf Hansen and also known by his pseudonym Andrew Berwick, is a Norwegian far-right terrorist who committed the 2011 Norway attacks. On 22 July 2011, he killed eight people by detonating a van bomb amid Regjeringskvartalet in Oslo, then shot dead 69 participants of a Workers' Youth League (AUF) summer camp on the island of Utøya. In July 2012, he was convicted of mass murder, causing a fatal explosion, and terrorism.
| This year in Norway article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |