Related Research Articles

Hammurabi, also spelled Hammurapi, was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from c. 1792 to c. 1750 BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered the city-states of Larsa, Eshnunna, and Mari. He ousted Ishme-Dagan I, the king of Assyria, and forced his son Mut-Ashkur to pay tribute, bringing almost all of Mesopotamia under Babylonian rule.
The 18th century BC was the century that lasted from 1800 BC to 1701 BC.
The 1720s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1729 BC to December 31, 1720 BC.

Babylonia was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia. It emerged as an Akkadian populated but Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BC. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad", a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom centered around the city of Babylon.
In the Hebrew Bible, Amraphel was a king of Shinar in Book of Genesis Chapter 14, who invaded Canaan along with other kings under the leadership of Chedorlaomer, king of Elam. Chedorlaomer's coalition defeated Sodom and the other cities in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim.
The 1780s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1789 BC to December 31, 1780 BC.

The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to c. 1894–1595 BC, and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylonia is debated; there is a Babylonian King List A and also a Babylonian King List B, with generally longer regnal lengths. In this chronology, the regnal years of List A are used due to their wide usage.

Sin-Muballit was the father of Hammurabi and the fifth Amorite king of the first dynasty of Babylonia, reigning c. 1813-1792 or 1748-1729 BC. He ruled over a relatively new and minor kingdom; however, he was the first ruler of Babylon to actually declare himself king of the city, and the first to expand the territory ruled by the city, and his son greatly expanded the Babylonian kingdom into the short lived Babylonian Empire.
The 1770s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1779 BC to December 31, 1770 BC.
The 1760s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1769 BC to December 31, 1760 BC.

The 1790s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1799 BC to December 31, 1790 BC. During this decade, the Near East was in the midst of the Middle Bronze Age.

Samsu-iluna was the seventh king of the founding Amorite dynasty of Babylon. His reign is estimated from 1749 BC to 1712 BC, or from 1686 to 1648 BC. He was the son and successor of Hammurabi by an unknown mother. His reign was marked by the violent uprisings of areas conquered by his father and the abandonment of several important cities.

The majority of Egyptologists agree on the outline and many details of the chronology of Ancient Egypt. This scholarly consensus is known as the Conventional Egyptian chronology, which places the beginning of the Old Kingdom in the 27th century BC, the beginning of the Middle Kingdom in the 21st century BC and the beginning of the New Kingdom in the mid-16th century BC.
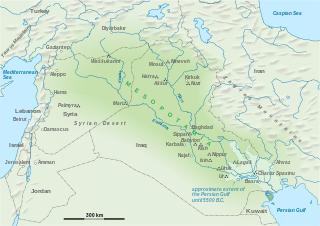
The Civilization of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called a cradle of civilization.
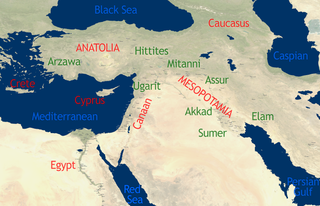
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Comparing many records pieces together a relative chronology relating dates in cities over a wide area.
Hammurabi I is the third attested king of Yamhad (Halab).
Amut-piʾel II was a king of Qatna in the 18th century BC, during the Middle Bronze IIA.

TheWorshipper of Larsa is a Mesopotamian statuette on display in Room 227 at the Louvre Museum, of the paleo-Babylonian era. It depicts a bearded man, kneeling and performing a ritual gesture with his hand to his mouth. The statuette was dedicated to the god Amurru by an inhabitant of Larsa, in order to safeguard the life of King Hammurabi.

Rim-Sîn I ruled the ancient Near East city-state of Larsa from 1758 BC to 1699 BC or 1822 BC to 1763 BC. His sister En-ane-du was high priestess of the moon god in Ur. Rim-Sin I was a contemporary of Hammurabi of Babylon and Irdanene of Uruk. He was of Elamite descent, notwithstanding his Akkadian name.
References
- ↑ "3,762 Years of Global Volcanic Eruptions. | the Rapture is Imminent!". Archived from the original on 2013-11-06. Retrieved 2013-11-05.
- ↑ NatureWorldNews (15 August 2013). "Alaskan Volcano Eruption Causes Rumbles but No Worries".
- ↑ "Hammurabi (1792-1750 B.C)". www.thelatinlibrary.com.