Related Research Articles

James Monroe was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825, a member of the Democratic-Republican Party. He was the last Founding Father to serve as president as well as the last president of the Virginia dynasty. His presidency coincided with the Era of Good Feelings, concluding the First Party System era of American politics. He issued the Monroe Doctrine, a policy of limiting European colonialism in the Americas. Monroe previously served as governor of Virginia, a member of the United States Senate, U.S. ambassador to France and Britain, the seventh secretary of state, and the eighth secretary of war.

Thomas Jefferson was an American statesman, planter, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the Declaration of Independence. Following the American Revolutionary War and before becoming president in 1801, Jefferson was the nation's first U.S. secretary of state under George Washington and then the nation's second vice president under John Adams. Jefferson was a leading proponent of democracy, republicanism, and natural rights, and he produced formative documents and decisions at the state, national, and international levels.

The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations that was enacted by the United States Congress. As a successor or replacement law for the 1806 Non-importation Act and passed as the Napoleonic Wars continued, it represented an escalation of attempts to persuade Britain to stop any impressment of American sailors and to respect American sovereignty and neutrality but also attempted to pressure France and other nations in the pursuit of general diplomatic and economic leverage.

The 10th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1807, to March 4, 1809, during the seventh and eighth years of Thomas Jefferson's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1800 census; both chambers had an overwhelming Democratic-Republican majority.

Thomas Jefferson served as the third president of the United States from March 4, 1801, to March 4, 1809. Jefferson assumed the office after defeating incumbent John Adams in the 1800 presidential election. The election was a political realignment in which the Democratic-Republican Party swept the Federalist Party out of power, ushering in a generation of Jeffersonian Republican dominance in American politics. After serving two terms, Jefferson was succeeded by Secretary of State James Madison, also of the Democratic-Republican Party.
John Adams' First State of the Union Address was delivered on Wednesday, November 22, 1797, in the Congress Hall of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At the time of the address, sickness was spreading through Philadelphia and Adams notes in his introduction that he was tempted to relocate the assembly of the national legislature but avoided this due to inevitable expense and general inconvenience.

The Insurrection Act of 1807 is a United States federal law that empowers the president of the United States to deploy the U.S. military and federalized National Guard troops within the United States in particular circumstances, such as to suppress civil disorder, insurrection, or rebellion.
The origins of the War of 1812 (1812-1815), between the United States and the British Empire and its First Nation allies, have been long debated. The War of 1812 was caused by multiple factors and ultimately led to the US declaration of war on Britain:

The 2002 State of the Union Address was given by the 43rd president of the United States, George W. Bush, on January 29, 2002, at 9:00 p.m. EST, in the chamber of the United States House of Representatives to the 107th United States Congress. It was Bush's first State of the Union Address and his second speech to a joint session of the United States Congress. Presiding over this joint session was the House speaker, Dennis Hastert, accompanied by Dick Cheney, the vice president, in his capacity as the president of the Senate.

Events from the year 1807 in the United States.

An Act Declaring War between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the Dependencies Thereof and the United States of America and Their Territories was passed by the 12th United States Congress on June 18, 1812, thereby beginning the War of 1812. It was signed by James Madison, the 4th President of the United States.
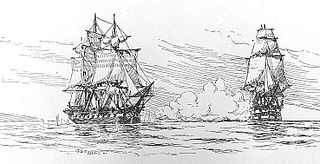
The Chesapeake–Leopard affair was a naval engagement off the coast of Norfolk, Virginia, on June 22, 1807, between the British fourth-rate HMS Leopard and the American frigate USS Chesapeake. The crew of Leopard pursued, attacked, and boarded the American frigate, looking for deserters from the Royal Navy. Chesapeake was caught unprepared and after a short battle involving broadsides received from Leopard, the commander of Chesapeake, James Barron, surrendered his vessel to the British. Chesapeake had fired only one shot.

The history of U.S. foreign policy from 1801 to 1829 concerns the foreign policy of the United States during the presidential administrations of Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, James Monroe, and John Quincy Adams. International affairs in the first half of this period were dominated by the Napoleonic Wars, which the United States became involved with in various ways, including the War of 1812. The period saw the U.S. double in size, gaining control of Florida and lands between the Mississippi River and the Rocky Mountains. The period began with the First inauguration of Thomas Jefferson in 1801. The First inauguration of Andrew Jackson in 1829 marked the start of the next period in U.S. foreign policy.

Thomas Jefferson took office in 1801 after defeating incumbent President John Adams in the 1800 presidential election. By July 1801, Jefferson had assembled his cabinet, which consisted of Secretary of State James Madison, Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin, Secretary of War Henry Dearborn, Attorney General Levi Lincoln Sr., and Secretary of the Navy Robert Smith. Jefferson sought to make collective decisions with his cabinet, and each member's opinion was elicited before Jefferson made major decisions. Gallatin and Madison were particularly influential within Jefferson's cabinet; they held the two most important cabinet positions and served as Jefferson's key lieutenants. During Jefferson's administration, the key foreign policy concerns revolved around relationships with the major European powers, particularly the United Kingdom, France, and Spain—each of which continued to hold substantial territories in North America—and with conflicts with the Barbary pirates.
The 1803 State of the Union address was delivered by the 3rd President of the United States Thomas Jefferson to the Eighth United States Congress on October 17, 1803. This speech centered around the Louisiana Purchase and the expansion of the United States, along with efforts to maintain peace with Native American tribes and establish neutral foreign relations amidst ongoing European conflicts.
The 1804 State of the Union address was delivered by the 3rd President of the United States Thomas Jefferson to the Eighth United States Congress on November 8, 1804. In his address, Jefferson focused on matters of foreign relations, domestic governance, and the ongoing expansion of the United States following the Louisiana Purchase.
The 1806 State of the Union address was delivered by the 3rd President of the United States Thomas Jefferson to the Ninth United States Congress on December 2, 1806. In this address, Jefferson discussed several major themes including foreign relations, national defense, and the growing tensions with Great Britain and France regarding maritime rights.
The 1808 State of the Union Address was delivered by the third President of the United States, Thomas Jefferson, on November 8, 1808. This was Jefferson's final address to the Tenth United States Congress.
The 1809 State of the Union Address was delivered by the fourth President of the United States, James Madison, on November 29, 1809. This was Madison's first State of the Union address, delivered to the Eleventh United States Congress.
The 1811 State of the Union Address was delivered by the fourth President of the United States, James Madison, on November 5, 1811. Addressing the Twelfth United States Congress, Madison emphasized the ongoing diplomatic and economic challenges posed by Great Britain and France, both of which were violating U.S. neutral trading rights amidst the Napoleonic Wars.
References
- 1 2 "Joint Meetings, Joint Sessions, & Inaugurations | US House of Representatives: History, Art & Archives". history.house.gov. Retrieved 25 September 2024.
- ↑ "Thomas Jefferson - State of the Union Address -- 1807". The American Presidency Project. Retrieved 9 October 2024.
- ↑ "Thomas Jefferson 1807 State of the Union Address". Avalon Project. Retrieved 9 October 2024.