
The following is a list of Pacific typhoon seasons from 1902 to 1919. Data from these years was extremely unreliable, so there were many more typhoons that did not hit land and were not detected by ships.

The following is a list of Pacific typhoon seasons from 1902 to 1919. Data from these years was extremely unreliable, so there were many more typhoons that did not hit land and were not detected by ships.
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1902 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1902 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 24 [1] |
| Total fatalities | >1300 Total |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1902, there were 24 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
1300 people were killed by a typhoon in Japan on September. [2]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1903 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1903 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 31 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1903, there were 31 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean that were detected by ships or ground stations nearby.
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | March 1904 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1904 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 23 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1904, there were 31 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
From September 7–12, a typhoon left at least 4,000 fatalities in Vietnam. [3]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1905 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1905 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 24 [1] |
| Total fatalities | 496 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1905, there were 24 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
On April 20, a typhoon struck the Marshall Islands, killing 26 people. On June 30, another typhoon moved through the Marshall Islands, killing 230 people. [4]
From September 21–29, a typhoon moved across the Philippines, killing more than 240 people. [5]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1906 |
| Last system dissipated | November 1906 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 24 [1] |
| Total fatalities | 15,000 |
| Total damage | $20 million (1906 USD) |
| Related articles | |
In 1906, there were 24 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
In September 1906, a typhoon struck China near Hong Kong, killing around 15,000 people, and causing US$20 million in damage. [6] [7]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1906 |
| Last system dissipated | November 1906 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 32 [1] |
| Total fatalities | 473 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1907, there were 32 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
From March 26–27, a typhoon moved through the Caroline Islands, killing 473 people in the archipelago. [4]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1908 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1908 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 31 [1] |
| Total fatalities | 428 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1908, there were 31 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
A typhoon struck near Hong Kong, killing 428 people.
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1909 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1909 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 35 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1909, there were 35 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
There is a typhoon with the winds of 135 mph (217 km/h). The typhoon impacted Philippines and caused an instrument to be destroyed. [8]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1910 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1910 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 38 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1910, there were 38 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1911 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1911 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 30 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1911, there were 30 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
A storm was first observed south of Guam on August 21 and moved on a westward trajectory. On August 26, the track shifted more to the west-northwest, bringing it over the Batanes islands offshore northern Luzon. That night, the storm approached southwest coast of Taiwan (then known as Formosa) with great intensity, possibly moving over the island. Kaohsiung reported a minimum pressure of 937 mbar (27.63 inHg), the lowest-ever recorded pressure on the island as of 1955, as well as maximum sustained winds of 177 km/h (110 mph) before the anemometer broke. Peak winds there were estimated around 251 km/h (156 mph), based on the severity of the airborne debris. Elsewhere on the island, the highest recorded wind speed was 196 km/h (122 mph). Across Taiwan, the typhoon destroyed over 30,000 houses, injured 378, and killed 305 people. The storm made landfall in eastern China on August 27 and continued northward for three more days. [9] [10]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1912 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1912 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 27 [1] |
| Total fatalities | 51,002 |
| Total damage | $20 million (1912 USD) |
| Related articles | |
In 1912, there were 27 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
In August, a typhoon struck near Wenzhou, China, killing 50,000 people. [6]
In September, a typhoon killed 1,000 people and left US$20 million in damage when it struck Japan. [11]
In November, typhoon struck Tacloban, Philippines, killing 15,000 people.
Also, on November 26, a typhoon struck Palau, killing two people. [4]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1913 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1913 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 23 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1913, there were 23 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
On November 10, a typhoon hit Guam. The USS Ajax was wrecked during the storm. A hospital steward was reported to have been killed, though they were later found alive. [12]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | March 1914 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1914 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 25 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1914, there were 25 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | March 1915 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1915 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 23 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1915, there were 23 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1916 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1916 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 23 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1916, there were 23 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | March 1917 |
| Last system dissipated | November 1917 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 16 [1] |
| Total fatalities | 4,000 |
| Total damage | $50 million (1916 USD) |
| Related articles | |
In 1917, there were 16 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
In September, a typhoon struck the Japanese island of Honshu, killing 4,000 people and leaving US$50 million in damage. [11]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | March 1916 |
| Last system dissipated | October 1916 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 16 [1] |
| Total fatalities | 129 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1918, there were 16 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.
In November, a typhoon killed 129 people when it struck Majuro in the Marshall Islands. [4]
| 1902–1919 Pacific typhoon seasons | |
|---|---|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 1919 |
| Last system dissipated | December 1919 |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 26 [1] |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
In 1919, there were 26 tropical cyclones in the western Pacific Ocean.

The 2003 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly below average yearlong period of tropical cyclogenesis exhibiting the development of 45 tropical depressions, of which 21 became named storms; of those, 14 became typhoons. Though every month with the exception of February and March featured tropical activity, most storms developed from May through October. During the season, tropical cyclones affected the Philippines, Japan, China, the Korean Peninsula, Indochina, and various islands in the western Pacific.

The 2002 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly above average Pacific typhoon season, producing twenty-six named storms, fifteen becoming typhoons, and eight super typhoons. It had one of the highest ACE of any season worldwide, with over 400 units. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season ran throughout 2002, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Tapah, developed on January 11, while the season's last named storm, Pongsona, dissipated on December 11. The season's first typhoon, Mitag, reached typhoon status on March 1, and became the first super typhoon of the year four days later.

The 1990 Pacific typhoon season was another active season. It has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1990, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1959 Pacific typhoon season was regarded as one of the most devastating years for Pacific typhoons on record, with China, Japan and South Korea sustaining catastrophic losses.

The 1977 Pacific typhoon season was one of the least active Pacific typhoon seasons on record, with only 19 tropical storms forming. It was also the second of three known typhoon seasons during the satellite era to not produce a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon, sandwiched between the 1974 and 2017 seasons. The season's first storm, Severe Tropical Storm Patsy, formed on March 23 and the last, Typhoon Mary, dissipated on January 2, 1978. With Mary spanning two calendar years, it became the fourth typhoon to do so since 1945. Since then, two other typhoons have achieved this feat.

The 1976 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1976, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1973 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1973, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
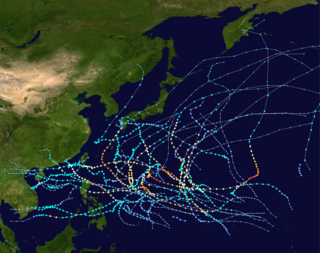
The 1968 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1968, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
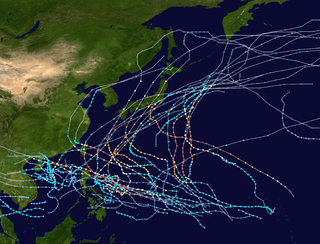
The 1965 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1965, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1960 Pacific typhoon season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1960, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1954 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1954, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1952 Pacific typhoon season had no official bounds, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
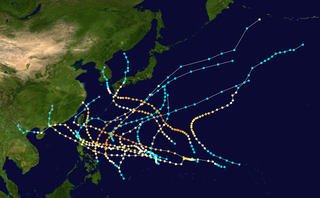
The 1946 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1946, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

In 1900, 23 tropical cyclones were observed in the western Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the International Date Line. In that region of the world, cyclones that attain maximum sustained winds of at least 118 km/h (73 mph) are known as typhoons. Of the 23 storms, 13 were tracked by the Hong Kong Observatory. Activity occurred from January to December, although the majority of the storms formed from June to November.
The following is a list of Pacific typhoon seasons from 1920 to 1937. Data from these years was extremely unreliable, so there were many more typhoons that did not hit land and were not detected by ships. The average from these times was 23 tropical storms, which now would be considered a well-below-average season.
This article encompasses the 1890s Pacific typhoon seasons.