The 1920-24 Pacific hurricane seasons all began on May 15 of their respective years in the eastern north Pacific Ocean and on June 1 in the central north Pacific. They ended on November 30, of each year. These dates conventionally delimit the time of year when most tropical cyclones form in northeast Pacific Ocean tropical cyclone basin, between the International Date Line and the west coast of North America. However, tropical cyclone formation is possible at any time of the year. Before the dawn of the satellite era in the 1960s, data on Pacific hurricanes is extremely unreliable. For a few years, there are no reported cyclones, although many systems likely formed and went undocumented.
| Pacific hurricane seasons |
Three known tropical cyclones formed this year in the eastern Pacific proper. One of them existed from September 10 to 13. It passed close to the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula but never made landfall.
Nine tropical cyclones are known this year in the eastern Pacific proper.
I. After crossing central Baja California, a tropical cyclone moved northward into southwestern Arizona on August 20, causing up to 2 inches (51 mm) of rain.
II. A system stayed at sea from September 25 to 30. It paralleled the coast of Mexico without making landfall. The remnants of this tropical cyclone moved northeastward through Baja California and Arizona, producing up to 4 inches (100 mm) of rain in the desert region.
III. and IV. Two possible tropical cyclones exited in the central Pacific during the month of October. The first developed on October 5 near Hawaii, and moved northward until being absorbed by an extratropical storm over the Aleutian Islands. The second was observed on October 17 well to the northeast of Hawaii. For both of these systems, it is unknown what, if any, tropical characteristics they had. It is possible they were Kona-type storms due to their locations.
Seven tropical cyclones formed this year.
I. One of them was an extremely unusual hurricane that formed between February 6 and 18 and hassled a ship moving between San Pedro and Panama City. This is the only Eastern Pacific hurricane to form in the month of February. [1]
II. Another cyclone paralleled the coast of Mexico from August 27 to 30. It passed south of the Revilla Gigedo Islands but otherwise stayed at sea.
III. A "tropical hurricane" formed offshore western Mexico on September 9, and moved northwest, parallel but well offshore the coast, dissipating on September 13. [2]
IV. A tropical cyclone was tracked from October 14 to 16. It moved northeast and made landfall near Mazatlán.
Five known tropical cyclones existed in the eastern Pacific proper this year.
I. The initial low pressure area formed on August 20 well southwest of Hawaii. [2] Moving generally westward, it was a small hurricane on August 23 when it was last noted. This storm is known as the Vega Cyclone, named after the USS Vega (AK-17) which reported the storm.
II. A tropical storm formed on October 12. After moving north, it made landfall near Salina Cruz. It crossed the Isthmus of Tehuantepec and emerged into the Bay of Campeche. It strengthened into Atlantic hurricane 6 and eventually made landfall in Louisiana as a weak Category 2.
Three known tropical cyclones formed this year in the eastern Pacific proper.
I. One was detected on September 2. It stayed at sea and was lost track of on September 8.
II. Another system was discovered on September 6. It moved in a generally northerly direction. It dissipated on September 9 after making landfall about midway between Acapulco and a place called "C. Corrigules". However, weather associated with it crossed into the Gulf of Mexico. [3]

The 2003 Pacific hurricane season was the first season to feature no major hurricanes – storms of Category 3 intensity or higher on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) – since 1977. The dates conventionally delimiting the period when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific Ocean are May 15 in the Eastern Pacific Ocean and June 1 in the Central Pacific, with both seasons ending on November 30. The 2003 season featured 16 tropical storms between May 19 and October 26; 7 of these became hurricanes, which was then considered an average season. Damage across the basin reached US$129 million, and 23 people were killed by the storms.

The 1990 Pacific hurricane season was a very active season which observed 21 named storms within the basin. The season also produced the fourth highest ACE index value on record. The season was officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated in 1990 by the formation of the season's first named storm, Hurricane Alma, on May 12. At the time, this was the earliest formation of a tropical storm on record in the eastern Pacific

The 1988 Pacific hurricane season was the least active Pacific hurricane season since 1981. It officially began May 15, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, in the central Pacific and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. The first named storm, Tropical Storm Aletta, formed on June 16, and the last-named storm, Tropical Storm Miriam, was previously named Hurricane Joan in the Atlantic Ocean before crossing Central America and re-emerging in the eastern Pacific; Miriam continued westward and dissipated on November 2.

The 1973 Pacific hurricane season was an event in tropical cyclone meteorology. The most important system this year was Hurricane Ava, which was the most intense Pacific hurricane known at the time. Several other much weaker tropical cyclones came close to, or made landfall on, the Pacific coast of Mexico. The most serious of these was Hurricane Irah, which downed power and communication lines in parts of the Baja California Peninsula; the other landfalling storms caused rain and some flooding. No tropical cyclone this season caused any deaths.

The 1939 Pacific hurricane season ran through the summer and fall of 1939. Before the satellite age started in the 1960s, data on east Pacific hurricanes was extremely unreliable. Most east Pacific storms were of no threat to land. However, 1939 saw a large number of storms threaten California.

A Pacific hurricane is a tropical cyclone that develops within the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean to the east of 180°W, north of the equator. For tropical cyclone warning purposes, the northern Pacific is divided into three regions: the eastern, central, and western, while the southern Pacific is divided into 2 sections, the Australian region and the southern Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. Identical phenomena in the western north Pacific are called typhoons. This separation between the two basins has a practical convenience, however, as tropical cyclones rarely form in the central north Pacific due to high vertical wind shear, and few cross the dateline.

The 1971 Pacific hurricane season began on May 15, 1971 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, 1971 in the Central Pacific ; both ended on November 30, 1971. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these regions of the Pacific. It was the first year that continuous Weather satellite coverage existed over the entire Central Pacific. As such, this season is often viewed as the start year for modern reliable tropical cyclone data in the Pacific Ocean.
The 1900s Pacific hurricane seasons all began on May 15 of their respective years in the eastern north Pacific Ocean and on June 1 in the central north Pacific. They ended on November 30, of each year. These dates conventionally delimit the time of year when most tropical cyclones form in northeast Pacific Ocean tropical cyclone basin, between the International Date Line and the west coast of North America. However, tropical cyclone formation is possible at any time of the year. Before the dawn of the satellite era in the 1960s, data on Pacific hurricanes is extremely unreliable. For a few years, there are no reported cyclones, although many systems likely formed and went undocumented.

The 1959 Pacific hurricane season saw 15 storms develop, 5 of which became hurricanes, and 3 of those became major hurricanes. The season officially started on May 15, 1959 in the Eastern Pacific, and ended on November 30, 1959.
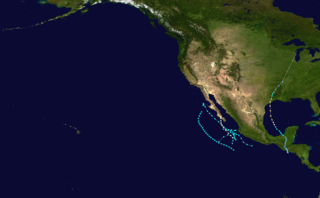
The 1949 Pacific hurricane season was the first hurricane season in the Eastern Pacific hurricane database. Six tropical cyclones were known to have existed during the season, of which the first formed on June 11 and the final dissipated on September 30. Another tropical cyclone had formed within the basin in 1949, but was included in the Atlantic hurricane database, had it been classified operationally in the Eastern Pacific basin, would have tallied the overall season to seven tropical cyclones. In addition, there were two tropical cyclones that attained hurricane status, but none of them reached major hurricane intensity. Tropical Storm Three threatened the Baja California Peninsula, while an unnumbered hurricane crossed into the Atlantic, later becoming the 1949 Texas hurricane.

The 1967 Pacific hurricane season started on June 1 and ended on November 30, 1967. The season was of little note except for Hurricanes Katrina and Olivia. Katrina made landfall on the Baja Peninsula, killing at least one and made 2,500 homeless. Olivia made landfall on the eastern side of the Baja Peninsula as a major hurricane—only one of two storms ever to do so. Hurricane/Typhoon Sarah formed in the Central Pacific and reached category 1 strength before crossing over to the Western Pacific.

The 1963 Pacific hurricane season was a below-average season, with 8 storms and 4 hurricanes forming. The season ran through the summer and fall of 1963.

The 1957 Pacific hurricane season was a moderately active year in which 13 tropical cyclones formed. The hurricane season ran through the summer and fall months which conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. The first tropical cyclone developed on July 15. The final storm dissipated on December 6, becoming one of the few Pacific storms to exist outside of the seasonal dates. Of the season's 13 storms, five of these formed or crossed into the central Pacific.
The 1910s Pacific hurricane seasons all began on May 15 of their respective years in the eastern north Pacific Ocean and on June 1 in the central north Pacific. They ended on November 30 of each year. These dates conventionally delimit the time of year when most tropical cyclones form in northeast Pacific Ocean tropical cyclone basin, between the International Date Line and the west coast of North America. However, tropical cyclone formation is possible at any time of the year. Before the dawn of the satellite era in the 1960s, data on Pacific hurricanes is extremely unreliable. For a few years, there are no reported cyclones, although many systems likely formed and went undocumented.

The 2018 Pacific hurricane season was one of the most active Pacific hurricane seasons on record, producing the highest accumulated cyclone energy value on record in the basin. The season had the fourth-highest number of named storms – 23, tied with 1982. The season also featured eight landfalls, six of which occurred in Mexico. The season officially began on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, tropical cyclone formation is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated when the first tropical depression formed on May 10, five days prior to the official start of the season.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link){{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)