In mathematics, the associative property is a property of some binary operations. In propositional logic, associativity is a valid rule of replacement for expressions in logical proofs.
In mathematics, a finite field or Galois field is a field that contains a finite number of elements. As with any field, a finite field is a set on which the operations of multiplication, addition, subtraction and division are defined and satisfy certain basic rules. The most common examples of finite fields are given by the integers mod p when p is a prime number.
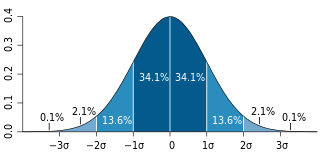
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure that is used to quantify the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of data values. A low standard deviation indicates that the data points tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the data points are spread out over a wider range of values.
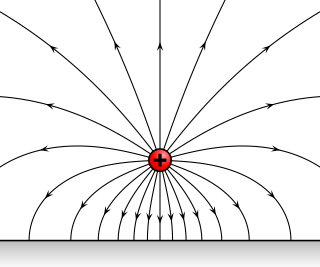
An electric field is a vector field surrounding an electric charge that exerts force on other charges, attracting or repelling them. Mathematically the electric field is a vector field that associates to each point in space the force, called the Coulomb force, that would be experienced per unit of charge by an infinitesimal test charge at that point. The units of the electric field in the SI system are newtons per coulomb (N/C), or volts per meter (V/m). Electric fields are created by electric charges, or by time-varying magnetic fields. Electric fields are important in many areas of physics, and are exploited practically in electrical technology. On an atomic scale, the electric field is responsible for the attractive force between the atomic nucleus and electrons that holds atoms together, and the forces between atoms that cause chemical bonding. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature.

Division is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the others being addition, subtraction, and multiplication.

Q fever is a disease caused by infection with Coxiella burnetii, a bacterium that affects humans and other animals. This organism is uncommon, but may be found in cattle, sheep, goats, and other domestic mammals, including cats and dogs. The infection results from inhalation of a spore-like small-cell variant, and from contact with the milk, urine, feces, vaginal mucus, or semen of infected animals. Rarely, the disease is tick-borne. The incubation period is 9–40 days. Humans are vulnerable to Q fever, and infection can result from even a few organisms. The bacterium is an obligate intracellular pathogenic parasite.
![Dead Sea Scrolls Ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank] near the Dead Sea](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/Flag_of_Israel.svg/320px-Flag_of_Israel.svg.png)
The Dead Sea Scrolls are ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank near the Dead Sea. Scholarly consensus dates these scrolls from the last three centuries BCE and the first century CE. The texts have great historical, religious, and linguistic significance because they include the second-oldest known surviving manuscripts of works later included in the Hebrew Bible canon, along with deuterocanonical and extra-biblical manuscripts which preserve evidence of the diversity of religious thought in late Second Temple Judaism. Almost all of the Dead Sea Scrolls collection is currently under the ownership of the Government of the state of Israel, and housed in the Shrine of the Book on the grounds of the Israel Museum.
In abstract algebra and formal logic, the distributive property of binary operations generalizes the distributive law from Boolean algebra and elementary algebra. In propositional logic, distribution refers to two valid rules of replacement. The rules allow one to reformulate conjunctions and disjunctions within logical proofs.

In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Most familiar as the name of the property that says "3 + 4 = 4 + 3" or "2 × 5 = 5 × 2", the property can also be used in more advanced settings. The name is needed because there are operations, such as division and subtraction, that do not have it ; such operations are not commutative, and so are referred to as noncommutative operations. The idea that simple operations such as the multiplication and addition of numbers are commutative, was for many years implicitly assumed. Thus, this property was not named until the 19th century, when mathematics started to become formalized. A corresponding property exists for binary relations; a binary relation is said to be symmetric if the relation applies regardless of the order of its operands; for example, equality is symmetric as two equal mathematical objects are equal regardless of their order.

Quantitative genetics is a branch of population genetics that deals with phenotypes that vary continuously —as opposed to discretely identifiable phenotypes and gene-products.

Electric potential energy, or electrostatic potential energy, is a potential energy that results from conservative Coulomb forces and is associated with the configuration of a particular set of point charges within a defined system. An object may have electric potential energy by virtue of two key elements: its own electric charge and its relative position to other electrically charged objects.
The physical constant ε0, commonly called the vacuum permittivity, permittivity of free space or electric constant or the distributed capacitance of the vacuum, is an ideal, (baseline) physical constant, which is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It has an exactly defined value that can be approximated as
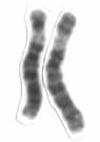
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the Major Histocompatibility Complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
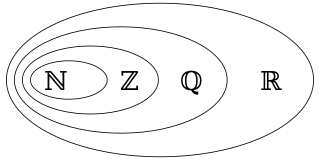
In mathematics, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. Since q may be equal to 1, every integer is a rational number. The set of all rational numbers, often referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by a boldface Q ; it was thus denoted in 1895 by Giuseppe Peano after quoziente, Italian for "quotient".
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arguments, that is, for each combination of values taken by their logical variables. In particular, truth tables can be used to show whether a propositional expression is true for all legitimate input values, that is, logically valid.

Coulomb's law, or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics for quantifying Coulomb's force, or electrostatic force. Electrostatic force is the amount of force with which stationary, electrically charged particles either repel, or attract each other. This force and the law for quantifying it, represent one of the most basic forms of force used in the physical sciences, and were an essential basis to the study and development of the theory and field of classical electromagnetism. The law was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.
These are the results of the Men's 800 metres event at the 1997 World Championships in Athletics in Athens, Greece on 4–8 August.
The 2016 National Premier Soccer League season was the 104th season of FIFA-sanctioned soccer in the United States, and the 14th season of the NPSL.






![Dead Sea Scrolls Ancient Jewish religious, mostly Hebrew, manuscripts found in the Qumran Caves in the West Bank] near the Dead Sea](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/Flag_of_Israel.svg/320px-Flag_of_Israel.svg.png)




