
Kūt, officially Al-Kut, also spelled Kutulamare or Kut al-Imara, is a city in eastern Iraq, on the left bank of the Tigris River, about 160 kilometres south east of Baghdad. As of 2018 the estimated population is about 389,400 people. It is the capital of the province long known as Al Kut, but since the 1960s renamed Wasit.

The Mesopotamian Half-Flight (MHF), or Australian Half-Flight, was the first Australian Flying Corps (AFC) unit to see active service during World War I. Formed in April 1915 at the request of the Indian Government, the half-flight's personnel were sent to Mesopotamia where they were equipped with a small number of outdated and barely serviceable aircraft. They later operated in the Tigris Valley in support of British and Indian forces under the command of Major General Charles Townshend. The unit's operations came to an end in December 1915 and the following month the flight was subsumed into other units of the AFC which were being formed in Egypt. It was officially disbanded in October 1916.

The 13th (Western) Division was one of the Kitchener's Army divisions in the First World War, raised from volunteers by Lord Kitchener. It fought at Gallipoli, in Mesopotamia and Persia.

The First Australian Imperial Force was the main expeditionary force of the Australian Army during the First World War. It was formed as the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) following Britain's declaration of war on Germany on 15 August 1914, with an initial strength of one infantry division and one light horse brigade. The infantry division subsequently fought at Gallipoli between April and December 1915, with a newly raised second division, as well as three light horse brigades, reinforcing the committed units.

The landing at Anzac Cove on Sunday, 25 April 1915, also known as the landing at Gaba Tepe and, to the Turks, as the Arıburnu Battle, was part of the amphibious invasion of the Gallipoli Peninsula by the forces of the British Empire, which began the land phase of the Gallipoli Campaign of the First World War.

The New Zealand Expeditionary Force (NZEF) was the title of the military forces sent from New Zealand to fight alongside other British Empire and Dominion troops during World War I (1914–1918) and World War II (1939–1945). Ultimately, the NZEF of World War I became known as the First New Zealand Expeditionary Force. The NZEF of World War II was known as the Second New Zealand Expeditionary Force (2NZEF).

The Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) was originally a First World War army corps of the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force. It was formed in Egypt in December 1914, and operated during the Gallipoli campaign. General William Birdwood commanded the corps, which primarily consisted of troops from the First Australian Imperial Force and 1st New Zealand Expeditionary Force, although there were also British and Indian units attached at times throughout the campaign. The corps disbanded in 1916, following the Allied evacuation of the Gallipoli peninsula and the formation of I ANZAC Corps and II ANZAC Corps. The corps was reestablished, briefly, in the Second World War during the Battle of Greece in 1941. The term 'ANZAC' has been used since for joint Australian–New Zealand units of different sizes.

The Corps of Royal New Zealand Engineers is the administrative corps of the New Zealand Army responsible for military engineering. The role of the Engineers is to assist in maintaining friendly forces' mobility, deny freedom of movement to the enemy, and provide general engineering support. The corps has been involved in numerous conflicts over the course of its history including World War I, World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War and the war in Afghanistan. The corps consists of a single regiment, 2nd Engineer Regiment, primarily based at Linton Military Camp near Palmerston North.

The Mesopotamian campaign was a campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I fought between the Allies represented by the British Empire, troops from Britain, Australia and the vast majority from British India, against the Central Powers, mostly the Ottoman Empire.

The Fall of Baghdad occurred during the Mesopotamia Campaign, fought between the forces of the British Empire and the Ottoman Empire in the First World War.
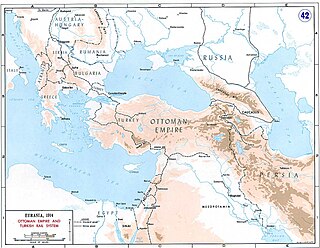
Dunsterforce was an Allied military force, established in December 1917 and named after its commander, Major-General Lionel Dunsterville. The force comprised fewer than 350 Australian, New Zealand, British and Canadian officers and NCOs, who were drawn from the Western and Mesopotamian fronts. The force was intended to organise local units in northern Iran (Persia) and South Caucasus, to replace the Tsarist army that had fought the Ottoman armies in Armenia. The Russians had also occupied northern Iran in co-operation with the British occupation of southern Iran, to create a cordon to prevent German and Ottoman agents from reaching Central Asia, Afghanistan and India.

In Australia, the outbreak of World War I was greeted with considerable enthusiasm. Even before Britain declared war on Germany on 4 August 1914, the nation pledged its support alongside other states of the British Empire and almost immediately began preparations to send forces overseas to engage in the conflict. The first campaign that Australians were involved in was in German New Guinea after a hastily raised force known as the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force was dispatched in September 1914 from Australia and seized and held German possessions in the Pacific. At the same time another expeditionary force, initially consisting of 20,000 men and known as the First Australian Imperial Force (AIF), was raised for service overseas.

The military history of New Zealand during World War I began in August 1914. When Britain declared war on Germany at the start of the First World War, the New Zealand government followed without hesitation, despite its geographic isolation and small population. It was believed at the time that any declaration of war by the United Kingdom automatically included New Zealand; and the Governor announced that New Zealand was at war with Germany from the steps of Parliament on 5 August.
The Cavalry Division was formed in 1916 during First World War by units of the British Army and the British Indian Army stationed in India for service in Mesopotamia in the Mesopotamia Campaign. The Division was broken up in 1918, but its brigades then served independently.

The Battle of Sheikh Sa'ad occurred between 6–8 January 1916 during the Mesopotamian Campaign of the First World War. The battle took place along the banks of the Tigris River between the Anglo-Indian Tigris Corps and elements of the Ottoman Sixth Army. The engagement was the first in a series of assaults by the Tigris Corps to try to break through the Ottoman lines to relieve the besieged garrison at Kut.
William Wallace Allison Burn was a New Zealand aviator, who served with the New Zealand Military Forces during the First World War.

The Desert Column was a First World War British Empire army corps which operated in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign from 22 December 1916. The Column was commanded by Lieutenant General Philip W. Chetwode and formed part of Eastern Force. When Chetwode took command of Eastern Force after the Second Battle of Gaza, Harry Chauvel took command and oversaw the expansion of the column to three divisions.

The Force in Egypt was a British Army formation established in August 1914 to administer garrisoning armed forces in Egypt at the beginning of the First World War. The force had the objective of protecting the Suez Canal and was originally commanded by Major General Julian Byng, but he was replaced by General J. Maxwell, who took command on 8 September 1914. Initially, the main threat to the Suez came from Germany and throughout the early months several of the force's elements were sent to Europe to take part in the fighting on the Western Front. On 5 November 1914, Britain and France declared war on the Ottoman Empire, after which the Force in Egypt faced a direct threat from Ottoman forces, which was realised in February 1915 with a raid on the Suez Canal. This threat remained until 1916 when the British forces went on the offensive.

The third attack on Anzac Cove was an engagement during the Gallipoli Campaign of the First World War. The attack was conducted by the forces of the Ottoman Turkish Empire, against the forces of the British Empire defending the cove.

The 1/1st Hertfordshire Yeomanry was the active service unit formed by the Hertfordshire Yeomanry during World War I. It was sent to garrison Egypt and then served dismounted in the Gallipoli Campaign. On return to Egypt it was engaged in the Senussi Campaign in the Western Desert. The regiment was then split into independent squadrons acting as divisional cavalry to different infantry divisions. These served in Palestine, on the Western Front and in Mesopotamia, where one of its squadrons were the first troops to enter Baghdad. Later in the war two of the squadrons fought alongside each other in XXI Corps Cavalry Regiment during the final victory in Palestine and the advance into Syria, while the other operated with the North Persia Force and on peacekeeping duties in India.



















