Related Research Articles

Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.

Management of tuberculosis refers to techniques and procedures utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB), or simply a treatment plan for TB.
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are classifications of antimicrobial agents based on their mode of action and specific to target organisms. The MDR types most threatening to public health are MDR bacteria that resist multiple antibiotics; other types include MDR viruses, parasites.
Latent tuberculosis (LTB), also called latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is when a person is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but does not have active tuberculosis (TB). Active tuberculosis can be contagious while latent tuberculosis is not, and it is therefore not possible to get TB from someone with latent tuberculosis. The main risk is that approximately 10% of these people will go on to develop active tuberculosis. This is particularly true, and there is added risk, in particular situations such as medication that suppresses the immune system or advancing age.
TB Alliance is a not-for-profit product development partnership (PDP) dedicated to the discovery and development of new, faster-acting and affordable tuberculosis (TB) medicines. Since its inception in 2000, TB Alliance has worked to grow the field of available treatments for TB and now manages the largest pipeline of new TB drugs in history. It was founded in Cape Town, South Africa, and has since expanded. It is headquartered in New York City and has a regional office in Pretoria.
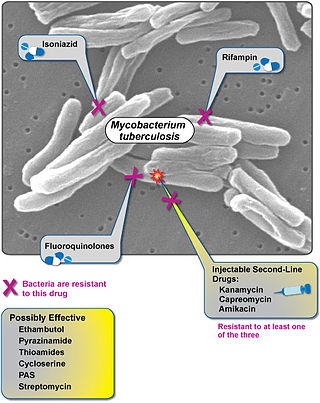
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is a form of tuberculosis caused by bacteria that are resistant to some of the most effective anti-TB drugs. XDR-TB strains have arisen after the mismanagement of individuals with multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of tuberculosis (TB) infection caused by bacteria that are resistant to treatment with at least two of the most powerful first-line anti-TB medications (drugs): isoniazid and rifampicin. Some forms of TB are also resistant to second-line medications, and are called extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB).

Bedaquiline, sold under the brand name Sirturo, is a medication used for the treatment of active tuberculosis. Specifically, it is used to treat multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis along with other medications for tuberculosis. It is taken by mouth.

Tuberculosis is a serious public health problem in China. China has the world's third largest cases of tuberculosis, but progress in tuberculosis control was slow during the 1990s. Detection of tuberculosis had stagnated at around 30% of the estimated total of new cases, and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis was a major problem. These signs of inadequate tuberculosis control can be linked to a malfunctioning health system. The spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003, brought to light substantial weaknesses in the country's public health system. After the government realized the impact that the SARS outbreak had on the country, they increased leadership in their health department. After the SARS epidemic was brought under control, the government increased its commitment and leadership to tackle public health problems and, among other efforts, increased public health funding, revised laws that concerned the control of infectious diseases, implemented the world's largest internet-based disease reporting system to improve transparency, reach and speed, and started a program to rebuild local public health facilities and national infrastructure.

In health care facilities, isolation represents one of several measures that can be taken to implement in infection control: the prevention of communicable diseases from being transmitted from a patient to other patients, health care workers, and visitors, or from outsiders to a particular patient. Various forms of isolation exist, in some of which contact procedures are modified, and others in which the patient is kept away from all other people. In a system devised, and periodically revised, by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), various levels of patient isolation comprise application of one or more formally described "precaution".
Totally drug-resistant tuberculosis (TDR-TB) is a generic term for tuberculosis strains that are resistant to a wider range of drugs than strains classified as extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Extensively drug resistant tuberculosis is tuberculosis that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin, any fluoroquinolone, and any of the three second line injectable TB drugs. TDR-TB has been identified in three countries; India, Iran, and Italy. The term was first presented in 2006, in which it showed that TB was resistant to many second line drugs and possibly all the medicines used to treat the disease. Lack of testing made it unclear which drugs the TDR-TB were resistant to.

Tuberculosis in India is a major health problem, causing about 220,000 deaths every year. In 2020, the Indian government made statements to eliminate tuberculosis from the country by 2025 through its National TB Elimination Program. Interventions in this program include major investment in health care, providing supplemental nutrition credit through the Nikshay Poshan Yojana, organizing a national epidemiological survey for tuberculosis, and organizing a national campaign to tie together the Indian government and private health infrastructure for the goal of eliminating the disease.

Prisons in Russia consist of four types of facilities: pre-trial institutions; educative or juvenile colonies; corrective colonies; and prisons.

Four laboratory-confirmed cases of Ebola virus disease occurred in the United States in 2014. Eleven cases were reported, including these four cases and seven cases medically evacuated from other countries. The first was reported in September 2014. Nine of the people contracted the disease outside the US and traveled into the country, either as regular airline passengers or as medical evacuees; of those nine, two died. Two people contracted Ebola in the United States. Both were nurses who treated an Ebola patient; both recovered.

The Aeromedical Biological Containment System (ABCS) is an aeromedical evacuation capability devised by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and government contractor Phoenix Air between 2007 and 2010. Its purpose is to safely air-transport a highly contagious patient; it comprises a transit isolator and an appropriately configured supporting aircraft. Originally developed to support CDC staff who might become infected while investigating avian flu and SARS in East Asia, it was never used until the 2014 Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa, transporting 36 Ebola patients out of West Africa.
Zarir Udwadia is an Indian pulmonologist and researcher. His work on drug resistant tuberculosis has led to improvements in India's National Tuberculosis Control Programme. Udwadia was the only Indian invited by the WHO to be part of the TB ‘Guidelines Group’, which formulated the 4th edition of the TB Guidelines, published in 2010. He was also the only doctor to be named among India's best strategists.

An N95 respirator is a disposable filtering facepiece respirator or reusable elastomeric respirator filter that meets the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) N95 standard of air filtration, filtering at least 95% of airborne particles that have a mass median aerodynamic diameter of 0.3 micrometers under 42 CFR 84, effective July 10, 1995. A surgical N95 is also rated against fluids, and is regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration under 21 CFR 878.4040, in addition to NIOSH 42 CFR 84. 42 CFR 84, the federal standard which the N95 is part of, was created to address shortcomings in the prior United States Bureau of Mines respirator testing standards, as well as tuberculosis outbreaks, caused by the HIV/AIDS epidemic in the United States. Since then, N95 respirator has continued to be solidified as a source control measure in various pandemics that have been experienced in the United States and Canada, including the 2009 swine flu and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Jaime Bayona García is a Peruvian physician who focuses on public health and he has become a specialist in studying the epidemiology of tuberculosis. He is also known for his case studies on HIV/AIDS in Peru and other developing countries. Dr. Bayona has also done work on how public health systems should improve, in terms of providing the best approach to help the sick that cannot afford health care.
Phumeza Tisile is a healthcare activist from South Africa who advocates for making tuberculosis medication inexpensive and widely available. Tisile survived extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB), enduring three years and 8 months of treatment. Tisile's initial misdiagnoses led to months of incorrect treatment, which caused her to become deaf. As an activist, Tisile advocates for improved access to tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis and treatment, improved counseling for patients, research into better treatments, and elimination of TB stigma.
References
- ↑ Border security scrutinized after TB patient slips in Archived 2008-03-08 at the Wayback Machine , CNN.com
- 1 2 3 Emily Brown and Jeff Bliss, "Border Agents Failed to Stop Man With Tuberculosis" (Update4).
- ↑ "Fact Sheet on Isolation and Quarantine". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved June 3, 2007.
- ↑ "Odd twist in TB alert: Patient is TB researcher's son-in-law". CIDRAP. May 31, 2007. Archived from the original on June 3, 2007. Retrieved June 2, 2007.
- 1 2 3 "A Timeline of Andrew Speaker's Infection, June, 2007". NPR. Retrieved April 16, 2016.
- ↑ Andrew Speaker Says He's Being Unfairly Attacked by Eve Conant, Newsweek, 2 Jun 2007. Accessed 2009-04-30. Archived 2009-05-21.
- ↑ "TB patient insists he was never banned from travel". CNN. June 7, 2007
- ↑ "CDC Stands by Decision to Sound Public Alarm". ABC News. July 4, 2007
- ↑ Park, Alice. "The TB Scare: A Broken System?" Time. May 31, 2007.
- 1 2 Mike McPhee, TB patient apologizes Denver Post. June 1, 2007. Accessed 2009-04-30. Archived 2009-05-21.
- ↑ "Border agent fired after allowing TB patient into country". Fox News. Archived from the original on July 19, 2012. Retrieved June 11, 2007.
- ↑ "Flight Itinerary of U.S. Traveler with Extensively Drug–Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB) (May 30, 2007)". Cdc.gov. Archived from the original on October 12, 2008. Retrieved November 8, 2008.
- ↑ "Foxnews.com: TB Patient moved to Denver hospital, May 31, 2007". Foxnews.com. May 31, 2007. Archived from the original on October 2, 2008. Retrieved November 8, 2008.
- ↑ "CNN web site: TB patient's name released; father-in-law works at CDC". Cnn.com. Archived from the original on March 8, 2008. Retrieved November 8, 2008.
- ↑ "ABCNews.com: TB Patient: "I Really Believed I Wasn't Putting People at Risk" June 1, 2007". Abcnews.go.com. Archived from the original on September 29, 2008. Retrieved November 8, 2008.
- ↑ "Doctors: TB traveler's diagnosis more treatable than thought". CNN. July 4, 2007. Archived from the original on July 12, 2007. Retrieved July 4, 2007.
- ↑ "TB-infected lawyer released from hospital". CNN.com. July 26, 2007. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ↑ "Plane passengers sue TB patient - CNN.com". www.cnn.com. July 12, 2007. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ↑ Mashnitski, Aleksandr (April 30, 2009). "Andrew Speaker Sues CDC Over Handling of '07 TB Scare". FindLaw. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ↑ "Lawyer in 2007 TB scare sues CDC". CNN.com. April 30, 2009. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ↑ Poole, Shelia M. (November 23, 2009). "Judge dismisses Andrew Speaker suit against CDC". ajc. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ↑ Rankin, Bill (March 15, 2012). "Suit over TB case dismissed against CDC". ajc. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ↑ "The Legal Questions Behind the TB Case". Law.com. Retrieved June 8, 2007.
- ↑ CDC (April 17, 2024). "Legal Authorities for Isolation and Quarantine". Port Health. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- ↑ "TB patient travel may have been illegal". Physorg.com. Archived from the original on August 26, 2007. Retrieved July 18, 2007.