Related Research Articles

The United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) was established by United Nations Security Council Resolution 858 on 24 August 1993 to verify compliance with a 27 July 1993 ceasefire agreement between the Republic of Georgia and forces in Abkhazia with special attention given to the situation in the city of Sukhumi, Georgia. It was also to investigate reports of ceasefire violations, attempt to resolve such incidents with the parties involved, and to report to the Secretary-General of the United Nations on the implementation of its mandate. 88 military advisors were authorized to be deployed to the region. It ended on 15 June 2009, when Russia vetoed an extension of the mission. The last observers left the region on 15 July 2009.
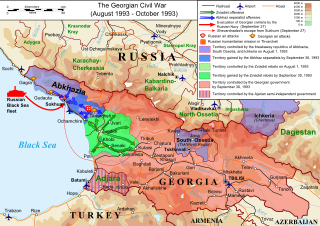
The Georgian Civil War lasted from 1991 to 1993 in the South Caucasian country of Georgia. It consisted of inter-ethnic and international conflicts in the regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, as well as the violent military coup d'état against the first democratically-elected President of Georgia, Zviad Gamsakhurdia, and his subsequent uprising in an attempt to regain power.
The Kodori Valley, also known as the Kodori Gorge, is a river valley in Abkhazia, Georgia's breakaway autonomous republic. The valley's upper part, populated by Svans, was the only corner of the post-1993 Abkhazia directly controlled by the central Georgian government, which since 2006 officially styles the area as Upper Abkhazia. On August 12, 2008, Russo–Abkhazian forces gained control of the Upper Kodori Valley, previously controlled by Georgia.

The Georgian–Ossetian conflict is an ethno-political conflict over Georgia's former autonomous region of South Ossetia, which evolved in 1989 and developed into a war. Despite a declared ceasefire and numerous peace efforts, the conflict remained unresolved. In August 2008, military tensions and clashes between Georgia and South Ossetian separatists erupted into the Russo-Georgian War. Since then, South Ossetia has been under a de-facto Russian control.

The ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia, also known in Georgia as the genocide of Georgians in Abkhazia, refers to the ethnic cleansing, massacres, and forced mass expulsion of thousands of ethnic Georgians living in Abkhazia during both the 1992–1993 and 1998 Wars of Abkhazia by Abkhaz separatists and their allies. Armenians, Greeks, Russians, and opposing Abkhazians were also killed.
Contacts between Russia and Georgia date back to the 15th and 16th centuries, and the most important stage started in the 1580s, when the Georgian kingdom of Kakheti and the Russian Empire signed a treaty of alliance in 1587. Relations between the two countries developed vibrantly and culminated in the Treaty of Georgievsk, which established eastern Georgia as a protectorate of Russia. At that time, Georgia saw Russia as a powerful Christian and modernizing neighbor, capable of protecting Georgia from invading Muslim empires and North Caucasian raiders.

The history of Abkhazia, a region in the South Caucasus, spans more than 5,000 years from its settlement by the lower-paleolithic hunter-gatherers to its present status as a partially recognized state.
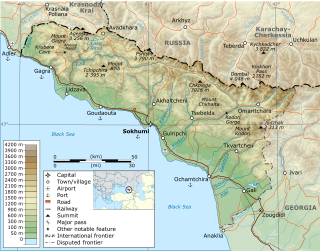
The War in Abkhazia was fought between Georgian government forces for the most part and Abkhaz separatist forces, Russian government armed forces and North Caucasian militants between 1992 and 1993. Ethnic Georgians who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population largely supported the Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists received support from thousands of North Caucasus and Cossack militants and from the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.
The 2007 Bokhundjara incident, in Georgia more commonly known as the special operation Kodori 2007, was a confrontation between Georgian Interior Ministry commandos and forces of Georgia's breakaway republic of Abkhazia and Russia near the de facto border in Tkvarcheli District on September 20, 2007. The United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) launched an independent investigation of the incident. On October 11, 2007, it released a progress report, confirming the incident took place on Abkhaz-controlled territory at the foot of Mount Bokhundjara, thus confirming the Abkhaz version of the event. On October 27, 2007, Georgia released the arrested Abkhazians and handed them over to the U.N. observers as a "sign of good will."
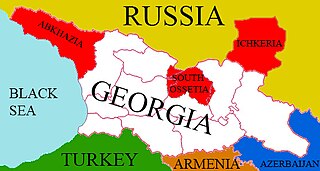
The War in Abkhazia in 1998 took place in the Gali district of Abkhazia, after ethnic Georgians launched an insurgency against the Abkhazian separatist government. The conflict is sometimes referred to as the Six-Day War of Abkhazia; however, this name only takes into account the Abkhazian offensive that lasted from 20 to 26 May 1998, while hostilities and insurgent attacks had already occurred before that date.

The Abkhazian town of Tkvarcheli was put under siege by the Georgian National Guard during the 1992–93 War in Abkhazia. The siege lasted from October 1992 to September 1993, almost the entire duration of the war, but was eventually unsuccessful. It was accompanied by inconclusive fighting in surrounding villages. Russian aid, both humanitarian and military, was critical for the defence of the town which suffered a severe humanitarian crisis during the siege.
The Forest Brothers were a guerrilla group consisting mostly of ethnic Georgians who remained in the breakaway republic of Abkhazia after the Georgian regular army's defeat in the War in Abkhazia (1992–1993) and resisted the ethnic cleansing of Georgians in the disputed territory.

Though tensions had existed between Georgia and Russia for years and more intensively since the Rose Revolution, the diplomatic crisis increased significantly in the spring of 2008, namely after Western powers recognized the independence of Kosovo in February and following Georgian attempts to gain a NATO Membership Action Plan at the 2008 Bucharest Summit; and while the eventual war saw a full-scale invasion of Georgia by Russia, the clashes that led up to it were concentrated in the breakaway republics of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, two separatist Georgian regions that received considerable Russian support over the years.
In June and July 2008 a series of bombings took place in Georgia's breakaway republic of Abkhazia, killing 4 and injuring 18 people.

The 2008 Georgian drone shootdowns refer to a series of military incidents involving Georgian unmanned aerial vehicles brought down over the breakaway republic of Abkhazia between March and May 2008. The skirmishes were part of a larger context of tensions between Georgia and Russia, eventually leading up to the Russo-Georgian War.

Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It covers 8,665 square kilometres (3,346 sq mi) and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi.
The 2008 Achamkhara incident refers to the armed confrontation, that took place on July 9, 2008, on the flanks of Mount Achamkhara in the internationally unrecognised Republic of Abkhazia, between Abkhazian and Georgian troops.

Ganarjiis Mukhuri is a village in the Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti region of western Georgia, in the Zugdidi municipality. It is situated at the border with Abkhazia and the city of Zugdidi. The village area is located by the Black Sea and on the right bank of the Enguri River, with the village center six kilometers from the sea. Within the administrative division of the municipality, Ganmukhuri is not part of a community, but is an so called independent village.

Gali District is one of the districts of Abkhazia. Its capital is Gali, the town by the same name. The district is smaller than the eponymous one in the de jure subdivision of Georgia, as some of its former territory is now part of Tkvarcheli District, formed by de facto Abkhaz authorities in 1995.
The War in Abkhazia from 1992 to 1993 was waged chiefly between Georgian government forces on one side, Russian military forces on other side supporting separatist forces demanding independence of Abkhazia from Georgia. http://www.historyorb.com/russia/georgia.php Ethnic Georgians, who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population, largely supported Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists were supported by thousands of the North Caucasus and Cossack militants and by the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.
References
- 1 2 "Questions Raised by the Khurcha Incident". Human Rights Information and Documentation Center. 2008-05-24. Retrieved 2008-08-21.
- 1 2 "UN Blames Georgians For Khurcha Incident". The Georgian Times. 2008-08-04. Archived from the original on 2008-08-20. Retrieved 2008-08-21.
- ↑ "Report of the Secretary-General on the situation in Abkhazia, Georgia" (PDF). United Nations Security Council. 2008-07-23. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-07-25. Retrieved 2008-08-21.
- ↑ "Verdict Delivered in Trial over 2008 Polling Day Blast in Khurcha". Civil Georgia. 30 July 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2014.