Related Research Articles
Karachi has a tropical arid climate, albeit a moderate version of this climate, influenced by monsoons. Karachi has a tropical climate, despite being located slightly above the Tropic of Cancer. It is situated in the monsoon region of Pakistan. It is located on the coast bordering the Arabian Sea, and as a result, has a relatively mild climate. However, in more recent years, rainfall has become more abundant, with annual rainfall projected to reach over 500 mm by 2100. For this reason, the city may be classed as almost semi-arid (BSh), since it has a mild climate with a short but defined wet season, along with a lengthy dry season.

Pakistan's climate varies from a continental type of climate in the north (Gilgit-Baltistan,Kashmir,KPK), a mountainous dry climate in the west (Baluchistan), a wet climate in the East (Punjab) an arid climate in the Thar Desert, to a tropical climate in the southeast (Sindh), characterized by extreme variations in temperature, both seasonally and daily, because it is located on a great landmass barely north of the Tropic of Cancer.
Quetta, Pakistan features a continental semi-arid climate with a large variation between summer and winter temperatures. The highest temperature recorded in Quetta was 42 °C (108 °F) on 10 July 1998. The lowest temperature in Quetta is −18.3 °C (−0.9 °F) which was recorded on 8 January 1970.
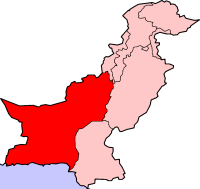
The 2011 Balochistan floods started from the last week of February and continued until the first week of March. Balochistan province was already badly affected from last year's devastating floods as UNHCR claims that 166,000 flood victims are still homeless in the province with 240 people still living in camps.
The 2012 Pakistan floods began in early September 2012, resulting from heavy monsoon rains in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Upper Sindh, Southern Punjab and Balochistan regions of Pakistan.

The Counter Terrorism Department (Urdu: سررشتہِ تحقیقاتِ جرائم ، پاکستان; CTD) formerly known as the Crime Investigation Department (CID), are crime scene investigation, interrogation, anti-terrorism, and intelligence bureaus of the provincial police services of Pakistan.

On the night of 26 April 2015, a severe storm hit areas of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, causing considerable damage in the cities of Peshawar, Nowshera, and Charsadda. The storm featured heavy rains accompanied by hail and high-speed winds of over 120 kilometers per hour. As a result of the storm's damaging effects, 45 people were killed and over 200 were wounded.
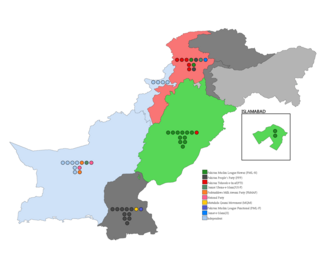
The triennial Senate Electionsof Pakistan were held on 3 March 2018 to replace 52 retiring senators - half of the Senate's strength - with the winning candidates serving six-year terms. Overall, Pakistan Muslim League (N) came out as the largest party, followed by the Pakistan Peoples Party and the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf. The results of these elections were steeped in controversy due to rampant allegations of horse trading and vote-buying, which lead to the Prime Minister and opposition leader Imran Khan calling for reforms. Prior to this election, PML (N) candidates were declared as independents by the Election Commission of Pakistan owing to a Supreme Court judgment.
Operation Radd-ul-Fasaad was a combined military operation by the Pakistani military in support of local law enforcement agencies to disarm and eliminate the terrorist sleeper cells across all states of Pakistan, started on 22 February 2017. The operation aimed to eliminate the threat of terrorism, and consolidating the gains of Operation Zarb-e-Azb which was launched in 2014 as a joint military offensive. It was further aimed at ensuring the security of Pakistan's borders. The operation underwent active participation from the Pakistan Army, Pakistan Air Force, Pakistan Navy, Pakistan Police and other Warfare and Civil Armed Forces managed under the Government of Pakistan. More than 375,000 intelligence-based operations had been carried out as of 2021. This operation has been mostly acknowledged after Operation Zarb e Azb.
In mid-March 2019, monsoonal downpours caused widespread flooding and landslides across South Asia.
In 2016 Pakistan experienced higher rainfall than normal (10-20%), especially in the pre-monsoon season. Heavy monsoon rains are common in the region. This led to multiple periods of flooding, landslides, and damage particularly in Northern Pakistan. The Swat River overflowed and multiple landslides occurred around Pakistan including in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Gilgit-Baltistan, Azad Jammu, and Kashmir.
From January to October 2022, excessive rainfall and widespread monsoon flooding occurred in the South Asian countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It has become the region's deadliest floods since 2020, with over 4,700 people dead.
The events listed below are both anticipated and scheduled for the year 2023 in Pakistan.
The 2023 Pakistan floods occurred from March to July of 2023, caused by monsoon rains which returned to Pakistan after nine months after the 2022 Pakistan floods. Floods worsened at the end of June due to upcoming monsoon rains. At least 159 people were killed, including many children.

Flooding affected parts of South Asia since March of 2023, killing many and destroying buildings.
The events listed below are both anticipated and scheduled for the year 2024 in Pakistan.
Since 29 February 2024, flooding affected various regions across the country, including Sindh, Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Gilgit-Baltistan. At least 40 people were killed and 62 injured in the floods. Floods caused by heavy rains caused widespread destruction, disrupting normal life and damaging infrastructure. The government declared a state of emergency in several areas, and relief operations were launched by various agencies, including the Pakistan Navy, Pakistan Army, and the Frontier Corps.
Since 6 March 2024, unseasonably heavy rains and resultant flash flooding in Afghanistan and Pakistan killed over 1,000 people, and injured many more. This extensively damaged infrastructure and agriculture.
References
- ↑ Sasoli, Dawn com | Ismail (3 March 2019). "1,500 families rescued from Balochistan's flood-hit areas with army's help: ISPR". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- 1 2 "Death toll from Pakistan flash floods, rains rises to 26". aljazeera.com. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- 1 2 "Flash floods in Afghanistan, Pakistan kill at least 45 people". aljazeera.com. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- 1 2 "Pakistan – Deadly Landslide in Balochistan Province". floodlist.com. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- 1 2 "Rainstorms kill 6, injure 50 in Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa". thenews.com.pk. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- ↑ "Flash flood in South Waziristan kills 8". dawn.com. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- 1 2 "Flash flood in South Waziristan kills 12". dawn.com. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- ↑ "Pakistan: Floods in Balochistan – 6 March 2019 – Pakistan". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- ↑ Report, Dawn (1 February 2019). "Four killed, 14 injured in rain-related incidents". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ↑ "28 killed in torrential rains, heavy snowfall in Pakistan – Xinhua | English.news.cn". www.xinhuanet.com. Archived from the original on 22 February 2019. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ Report, Dawn (22 February 2019). "Flash floods, heavy rains claim 19 lives across country". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ Ali, Dawn com | Ismail Sasoli | Imtiaz (15 April 2019). "5 killed, 36 injured as Karachi gripped by gusty winds, dust storm". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ Report, Dawn (16 April 2019). "25 killed as rain, dust storms lash Pakistan". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ "28 killed as flash floods, thunderstorms lash Pakistan". Business Standard India. Press Trust of India. 16 April 2019. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ "28 Killed as Flash Floods, Thunderstorms, Dust Storms Lash Pakistan". News18. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ "Thunderstorms lash parts of Pakistan, triggering floods". www.aljazeera.com. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ IANS. "Video: 26 dead in Pakistan torrential rains, duststorm". Khaleej Times. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ↑ "Dozens Killed as Hail, Rain and Lightning Pummel India and Pakistan". The Weather Channel. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ↑ IANS. "Rains, dust storm kill nearly 100 in India, Pakistan". Khaleej Times. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ↑ IANS (17 April 2019). "39 killed as rain wreaks havoc across Pakistan". Business Standard India. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ↑ "Rains claim 39 lives across Pakistan | Pakistan Today". www.pakistantoday.com.pk. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ↑ Report, Dawn (17 May 2019). "Dust storm, rain in several districts cause widespread damage to crops in Sindh". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ↑ "Two killed in Lakki incidents". DAWN.COM . 19 May 2019. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ↑ "Two children killed in Kurram roof collapse". DAWN.COM . 19 May 2019. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ↑ Reporter, A. (20 May 2019). "Woman killed as rain lashes parts of KP". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ↑ Report, Dawn (21 May 2019). "Woman dies as windstorm damages houses, crops in Bajaur". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ↑ Report, Dawn (25 May 2019). "Boy killed as downpour plays havoc in several KP towns". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ↑ "Six dead, 300 feeders tripped as heavy rain lashes parts of country". Dunya News. Retrieved 25 May 2019.