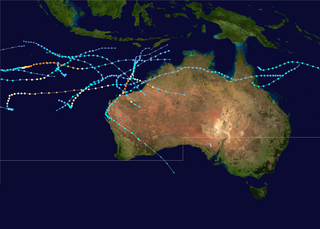
The 1999–2000 Australian region cyclone season was a slightly above average tropical cyclone season. It ran from 1 November 1999 to 30 April 2000. The regional tropical cyclone operational plan also defines a "tropical cyclone year" separately from a "tropical cyclone season", with the "tropical cyclone year" for this season lasting from 1 July 1999 to 30 June 2000.

The Ross River Dam is a rock and earthfill-filled embankment dam across the Ross River, located between Kelso and Mount Stuart in the City of Townsville in northern Queensland, Australia. Built initially for flood control, Lake Ross, the impoundment created by the dam, serves as one of the major potable water supplies for the region.

The 2003–04 Australian region cyclone season was a slightly below average tropical cyclone season. It began on 1 November 2003 and ended on 30 April 2004. The regional tropical cyclone operational plan also defines a tropical cyclone year separately from a tropical cyclone season, which runs from 1 July 2003 to 30 June 2004.

The 2003 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was the last season that tropical cyclones were not publicly labeled by India Meteorological Department (IMD). It was the third consecutive below average season. Also was mostly focused in the Bay of Bengal, where six of the seven depressions developed. The remaining system was a tropical cyclone that developed in the Arabian Sea in November, which was also the only system that did not affect land. There were three cyclonic storms, which was below the average of 4–6. Only one storm formed before the start of the monsoon season in June, although it was also the most notable. On May 10, a depression formed in the central Bay of Bengal, and within a few days became a very severe cyclonic storm. After it stalled, it drew moisture from the southwest to produce severe flooding across Sri Lanka, killing 254 people and becoming the worst floods there since 1947. Damage on the island totaled $135 million (2003 USD). The storm eventually made landfall in Myanmar on May 19. It is possible that the storm contributed to a deadly heat wave in India due to shifting air currents.
In Australia, the Federation Drought is the name given to a prolonged period of drought that occurred around the time of Federation in 1901.
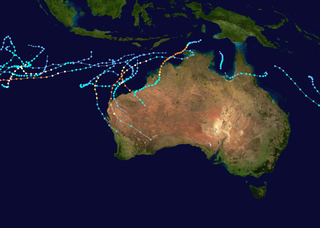
The 1998–99 Australian region cyclone season was an above average tropical cyclone season that featured Gwenda, the most intense tropical cyclone in the Australian Region. It began on 1 November 1998 and ended on 30 April 1999. The regional tropical cyclone operational plan also defines a tropical cyclone year separately from a tropical cyclone season, which runs from 1 July 1998 to 30 June 1999.

Cyclone Graham of the 2002–03 Australian region cyclone season was a weak tropical storm that affected Australia during late February and early March 2003. Graham originated from an area of convection that emerged onto water after sitting over Australia on 23 February. The interaction with a monsoon trough formed an area of low pressure that developed into Tropical Cyclone Graham on 27 February. The storm moved slowly to the east-southeast, and after turning to the south it peaked as a tropical storm and made landfall on Western Australia the next day. The cyclone weakened as it moved inland, and dissipated on 1 March. The storm dropped heavy rainfall and caused high winds, which produced flooding and downed trees. One fatality occurred, though no significant damages were reported.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Rona and Severe Tropical Cyclone Frank were a pair of tropical cyclones that affected Queensland and New Caledonia during the 1998–99 Australian region cyclone season and the 1998–99 South Pacific cyclone season. Rona originated from a low that developed on 9 February about 225 km (140 mi) to the northeast of Cairns. Over the next couple of days, the low slowly developed further before it was upgraded into a Category 1 cyclone on the Australian intensity scale by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology on 10 February as it started to move towards the southwest. Subsequently, Rona rapidly intensified just before making landfall near the Cape York Peninsula. While the low-level circulation became difficult to locate on 12 February, the upper-level circulation eventually emerged into the Coral Sea and later regenerated into Tropical Cyclone Frank. The system rapidly intensified before making landfall on New Caledonia as a Category 2 cyclone on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale in the early morning hours of 20 February. Frank was re-classified as an extratropical cyclone the next day.
Heavy rain in March 2010 saw much of south western and central Queensland undergo major flooding. The floods saw inundation of the towns of Charleville, Roma, St George and Theodore among others. Major rivers affected include the Warrego River, Balonne River, Bulloo River, Paroo River and the Dawson River.

The 2010 Gascoyne River flood was regarded as the most severe flood to take place along the Gascoyne River in Western Australia on record. Triggered by record-breaking rainfall, amounting to over 6,000 percent of the monthly mean, 313.6 mm (12.35 in) and 5 mm (0.20 in) respectively, in just four days, the floods caused widespread damage in the region. By 17 December, the river began to rise in response to the heavy rains, eventually exceeding its banks within two days. Water levels reached record values at three stations along the river, cresting at 15.53 m (51.0 ft) near Fishy Pool. Evacuation orders were issued for several towns affected by rising waters. The most substantial impact was felt in Carnarvon where entire homes were washed away. Following the disaster, emergency supplies and funds were distributed to affected residents to aid them in restoring their livelihoods. Though no people died in the event, an estimated two thousand head of cattle perished and damage was estimated at A$100 million.
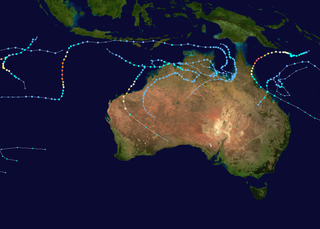
The 2013–14 Australian region cyclone season was a slightly below-average tropical cyclone season, with 10 tropical cyclones occurring within the Australian region. It officially started on 1 November 2013, and ended on 30 April 2014. The regional tropical cyclone operational plan defines a "tropical cyclone year" separately from a "tropical cyclone season"; the "tropical cyclone year" began on 1 July 2013 and ended on 30 June 2014.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Beni was an intense tropical cyclone that affected four countries, on its 18-day journey across the South Pacific Ocean during January and February 2003. The system originally developed during 19 January as a weak tropical disturbance within the monsoon trough, to the northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands. Over the next few days the system gradually developed further before it was classified as a tropical cyclone and named Beni during 24 January.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Joy struck Australia in late 1990, causing the third highest floods on record in Rockhampton, Queensland. This cyclone began as a weak tropical low near the Solomon Islands, and initially moved westward. On 18 December, it was named Joy, becoming the 2nd named storm of the 1990–91 Australian region cyclone season. After turning southwest, Joy developed a well-defined eye and strengthened to maximum sustained winds of 165 km/h (103 mph) while approaching Cairns in Far North Queensland. Brushing the city with strong winds, the cyclone soon weakened and turned southeast. Joy later curved back southwest, making landfall near Townsville, Queensland on 26 December. It dissipated the next day; remnant moisture continued as torrential rainfall over Queensland for two weeks.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Tessi was a small but potent tropical cyclone that caused extensive damage along the coast of North Queensland in early April 2000. The ninth cyclone and fourth severe tropical cyclone of the 1999–2000 Australian region cyclone season, Tessi developed on 1 April from a persistent trough of low pressure in the Coral Sea and slowly tracked west-southwestward. Tessi was an unusually compact storm that strengthened rapidly just before landfall, peaking as a Category 3 severe tropical cyclone on the Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale with 10-minute average maximum winds of 140 km/h. Around 22:00 UTC on 2 April, Tessi moved ashore about 75 km northwest of Townsville and rapidly diminished as it progressed inland. At the height of the storm, Magnetic Island experienced sustained winds of 109 km/h (68 mph), while gusts as high as 130 km/h (81 mph) were recorded in Townsville.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Debbie in 2017 was the strongest tropical cyclone to strike Queensland since Marcia in 2015, and was the costliest tropical cyclone in Australia since Yasi in 2011. Forming as a tropical low on 23 March, the low gradually intensified into a named tropical cyclone on 25 March. After steadily strengthening offshore to a Category 4 system, Debbie eventually made landfall near Airlie Beach, at 12:40 AEST on 28 March. Afterwards, Debbie rapidly weakened into a tropical low by late 28 March, but continued to travel south, causing significant damage and flooding in the populous areas of South East Queensland and Northern Rivers. In total, the storm caused A$3.5 billion (US$2.67 billion) in damage and fourteen deaths across Australia, primarily as a result of extreme flooding. This makes Debbie the deadliest cyclone to hit Australia since Fifi in 1991.

A black nor'easter is a persistent and potentially violent north-easterly storm that occurs on the east coast of Australia, particularly from southeastern Queensland to southern New South Wales, usually between late spring and early autumn, about two days a year.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Savannah was a strong tropical cyclone that brought significant impacts to Java and Bali and minor impacts to Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands during March 2019. It was the sixteenth tropical low, sixth tropical cyclone and third severe tropical cyclone of the 2018–19 Australian region cyclone season. Savannah developed from a tropical low that formed well to the east of Christmas Island on 8 March. The system was slow to develop initially, but reached tropical cyclone intensity on 13 March after adopting a southwesterly track. Savannah underwent rapid intensification and reached peak intensity on 17 March as a Category 4 severe tropical cyclone on the Australian scale. Ten-minute sustained winds were estimated as 175 kilometres per hour (109 mph), with a central barometric pressure of 951 hPa (28.08 inHg). One-minute sustained winds reached 185 kilometres per hour (115 mph) at this time, equivalent to a Category 3 major hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Weakening commenced soon afterwards, and responsibility for the system passed from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology to Météo-France. As it moved into the new region, Savannah became the eighth of a record-breaking ten intense tropical cyclones in the 2018–19 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Savannah was downgraded to a tropical depression on 20 March, and its remnants dissipated in the central Indian Ocean on 24 March.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Nora was a strong tropical cyclone that affected Far North Queensland and the northeastern Northern Territory during March 2018. The ninth named storm and third severe tropical cyclone of the 2017–18 Australian region cyclone season, Nora developed from a tropical low which formed near the Torres Strait on 19 March. The system initially moved quickly to the west-northwest, and then began tracking slowly southwestwards over the Arafura Sea while gradually developing. A turn to the east on 22 March brought the tropical low into a favourable environment for strengthening, and the system reached tropical cyclone intensity later that day. Nora then underwent a period of rapid intensification as it moved southeastwards into the Gulf of Carpentaria. The storm peaked on 23 March as a high-end Category 3 severe tropical cyclone with sustained winds of 155 km/h (96 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 958 hPa (28.29 inHg). Nora made landfall north of Pormpuraaw at about 13:00 UTC on 24 March as a minimal Category 3 system. Nora weakened steadily as it tracked southwards along the coast, and was downgraded to a tropical low the following day. Nora's remnants meandered over land for several days before moving back over the Gulf of Carpentaria and dissipating on 28 March.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Owen was an erratic and long-lived tropical cyclone that affected numerous regions along its track, especially Queensland, in December 2018. Owen was the fourth tropical low, first tropical cyclone, and first severe tropical cyclone of the 2018–19 Australian region cyclone season. Cyclone Owen developed on 29 November 2018 from an area of low pressure that was situated over the Solomon Islands; the system struggled to strengthen in a conflicting environment and degenerated to a tropical low on 3 December. The low drifted westward, and on 9 December, it made its first landfall in Queensland, before moving over the Gulf of Carpentaria, where more favourable conditions allowed it to re-organise. The system regenerated into a tropical cyclone on 12 December and rapidly intensified into a Category 3 severe tropical cyclone that night. At midnight on 13 December, Cyclone Owen made landfall in the Northern Territory, before turning eastward and reaching peak intensity, with sustained winds of 150 km/h (95 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 958 hPa (28.3 inHg). On 13 December, Owen made landfall on Queensland again, just north of the mouth of the Gilbert River near Kowanyama. The cyclone weakened rapidly after its third landfall, and the final advisory on Owen was issued on 15 December, after it had degenerated into a tropical low. However, the system persisted over the Coral Sea for another several days, before dissipating on 20 December.

Tropical Cyclone Seth was a strong tropical cyclone whose main impacts came after it degenerated into a remnant low. The eighth tropical low and the fourth tropical cyclone of the 2021–22 Australian region cyclone season, Seth originated from a tropical disturbance in the Timor Sea and caused severe flooding in southeast Queensland and hazardous surf along the southeastern coast of Australia.



















