The earliest known human settlements in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo have been dated back to the Middle Stone Age, approximately 90,000 years ago. The first real states, such as the Kongo, the Lunda, the Luba and Kuba, appeared south of the equatorial forest on the savannah from the 14th century onwards.

Politics of the Democratic Republic of Congo take place in the framework of a republic in transition from a civil war to a semi-presidential republic.
Telecommunications in the Democratic Republic of the Congo include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications in the Republic of the Congo include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply Congo, is a country in Central Africa. By land area the country is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 109 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean.

Denis Sassou Nguesso is a Congolese politician and former military officer who became president of the Republic of the Congo in 1997. He served a previous term as president from 1979 to 1992. During his first period as president, he headed the Congolese Party of Labour (PCT) for 12 years. He introduced multiparty politics in 1990, but was stripped of executive powers by the 1991 National Conference, remaining in office as a ceremonial head of state. He stood as a candidate in the 1992 presidential election but placed third.

Joseph Kabila Kabange is a Congolese politician who served as President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between January 2001 and January 2019. He took office ten days after the assassination of his father, President Laurent-Désiré Kabila in the context of the Second Congo War. He was allowed to remain in power after the 2003 Pretoria Accord ended the war as the president of the country's new transitional government. He was elected as president in 2006 and re-elected in 2011 for a second term. Since stepping down after the 2018 election, Kabila, as a former president, serves as a senator for life.

The Second Congo War, also known as Africa's World War or the Great War of Africa, was a major conflict that began on 2 August 1998 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), just over a year after the First Congo War. The war initially erupted when Congolese president Laurent-Désiré Kabila turned against his former allies from Rwanda and Uganda, who had helped him seize power. Eventually, the conflict expanded, drawing in nine African nations and approximately 25 armed groups, making it one of the largest wars in African history.

The Ituri conflict is an ongoing low intensity asymmetrical conflict between the agriculturalist Lendu and pastoralist Hema ethnic groups in the Ituri region of the north-eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). While the two groups had fought since as early as 1972, the name "Ituri conflict" refers to the period of intense violence between 1999 and 2003. Armed conflict continues to the present day.

Vital Kamerhe Lwa Kanyiginyi Nkingi is a Congolese politician, currently serving as Deputy Prime Minister of Economy and the leader of the Union for the Congolese Nation (UNC) party. He served as the President of the National Assembly of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 2006 to 2009. After resigning from that office, he went into the opposition and founded the UNC. He ran in the 2011 presidential election. He supported Félix Tshisekedi as a coalition partner in the 2018 presidential election, and became chief of staff when Tshisekedi took office.
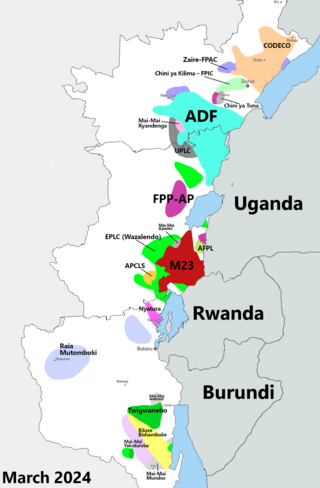
The Kivu conflict is an umbrella term for a series of protracted armed conflicts in the North Kivu and South Kivu provinces in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo which have occurred since the end of the Second Congo War. Including neighboring Ituri province, there are more than 120 different armed groups active in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. Currently, some of the most active rebel groups include the Allied Democratic Forces, the Cooperative for the Development of the Congo, the March 23 Movement, and many local Mai Mai militias. In addition to rebel groups and the governmental FARDC troops, a number of national and international organizations have intervened militarily in the conflict, including the United Nations force known as MONUSCO, and an East African Community regional force.

Floribert Chebeya Bahizire was a leading Congolese human rights activist in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, hailed by the United Nations as "a champion of human rights". His death led to calls for an investigation from more than 50 organisations, including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, many countries and several senior UN officials, including Ban Ki-moon, Navi Pillay, Alan Doss and Philip Alston.

The Allied Democratic Forces insurgency is an ongoing conflict waged by the Allied Democratic Forces in Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, against the governments of those two countries and the MONUSCO. The insurgency began in 1996, intensifying in 2013, resulting in hundreds of deaths. The ADF is known to currently control a number of hidden camps which are home to about 2,000 people; in these camps, the ADF operates as a proto-state with "an internal security service, a prison, health clinics, and an orphanage" as well as schools for boys and girls.

On 19 January 2015, protests led by students at the University of Kinshasa broke out in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The protests began following the announcement of a proposed law that would allow the country's 43-year-old president, Joseph Kabila, to remain in power until a national census could be conducted. Elections had been planned for 2016 and a census would be a massive undertaking that would likely take several years for the developing country.

General elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 30 December 2018, to determine a successor to President Joseph Kabila, as well as for the 500 seats of the National Assembly and the 715 elected seats of the 26 provincial assemblies. Félix Tshisekedi (UDPS) won the presidency with 38.6% of the vote, defeating Martin Fayulu and Emmanuel Ramazani Shadary (PPRD). Fayulu alleged that the vote was rigged against him by Tshisekedi and Kabila, challenging the result in the Constitutional Court. Election observers, including the Catholic Church, also cast doubt on the official result. Nonetheless, on 20 January the Court declared Tshisekedi the winner. Parties supporting Kabila won the majority of seats in the National Assembly. Tshisekedi was sworn in as the 5th President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 24 January 2019, the first peaceful transition of power in the country since its independence from Belgium in 1960.

On 20 December 2016 the Democratic Republic of the Congo's president, Joseph Kabila, announced that he would not leave office despite the end of his constitutional term. Protests subsequently broke out across the country, which had never had a peaceful transfer of power since it gained independence in 1960. The protests were met with the government's blocking of social media, and violence from security forces which left dozens dead. Foreign governments condemned the attacks against protesters.
The Kamwina Nsapu rebellion, also spelled Kamuina Nsapu rebellion, was an uprising that took place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 2016 and 2019. It was instigated by the Kamwina Nsapu militia against state security forces in the provinces of Kasaï-Central, Kasaï, Kasaï-Oriental, Lomami and Sankuru. The fighting began after the militia, led by Kamwina Nsapu, attacked security forces in August 2016.

Ève Bazaiba Masudi is a Congolese lawyer, politician, and human rights activist. As of May 2019, she served as the Secretary General of the Movement for the Liberation of the Congo (MLC) political party. She is Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for the Environment since 2021.

Félix Antoine Tshisekedi Tshilombo is a Congolese politician who has been the president of the Democratic Republic of the Congo since 24 January 2019. He is the leader of the Union for Democracy and Social Progress (UDPS), the DRC's oldest and largest party, succeeding his late father Étienne Tshisekedi in that role, a three-time Prime Minister of Zaire and opposition leader during the reign of Mobutu Sese Seko.

Beginning in 2022, tensions heightened between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Rwanda, marking a significant breakdown in relations between the two countries. Amid this, Rwandan forces have crossed into the DRC multiple times, usually fighting alongside Congolese rebels.
















