
Hurricane Opal was a large and powerful Category 4 hurricane that caused severe and extensive damage along the northern Gulf Coast of the United States in October 1995. The fifteenth named storm, ninth hurricane and strongest tropical cyclone of the unusually active 1995 Atlantic hurricane season, Opal developed from the interaction of a tropical wave and a low-pressure area near the Yucatán Peninsula on September 27 as Tropical Depression Seventeen. The depression crossed the Yucatán Peninsula and intensified into a tropical storm on September 30. Opal intensified into a hurricane on October 2 after entering the Gulf of Mexico. The cyclone turned northeastward and strengthened significantly. By October 4, Opal was an intense 150 mph (240 km/h), Category 4 hurricane. With a minimum pressure of 916 mbar (hPa), Hurricane Opal was the most intense category 4 Atlantic hurricane on record. However, the cyclone abruptly weakened to a low-end Category 3 hurricane prior to making landfall on the Florida Panhandle near Pensacola later that day. The storm quickly unraveled as it moved inland and became extratropical on October 5. The remnants of Opal moved northward and dissipated over Ontario the following day.

The 1999 Salt Lake City tornado was a rare tornado that struck downtown Salt Lake City, Utah, United States, on August 11, 1999. It was among the most notable tornadoes to hit west of the Great Plains in the 20th century and the second tornado to hit in Utah that resulted in a fatality. This was the sixth significant tornado in Utah since June 1963, and one of only two F2 tornadoes to have hit Salt Lake County since 1950.

KSL-TV is a television station in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States, affiliated with NBC. It is the flagship television property of locally based Bonneville International, the for-profit broadcasting arm of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, and is sister to KSL radio. The three stations share studios at the Broadcast House building in Salt Lake City's Triad Center; KSL-TV's transmitter is located on Farnsworth Peak in the Oquirrh Mountains, southwest of Salt Lake City. The station has a large network of broadcast translators that extend its over-the-air coverage throughout Utah, as well as portions of Arizona, Idaho, Nevada and Wyoming.

A derecho is a widespread, long-lived, straight-line wind storm that is associated with a fast-moving group of severe thunderstorms known as a mesoscale convective system.

Hurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, especially Florida, in August–September. The fifth tropical cyclone, third hurricane, and first major hurricane of the season, Donna developed south of Cape Verde on August 29, spawned by a tropical wave to which 63 deaths from a plane crash in Senegal were attributed. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Donna by the following day. Donna moved west-northwestward at roughly 20 mph (32 km/h) and by September 1, it reached hurricane status. Over the next three days, Donna deepened significantly and reached maximum sustained winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) on September 4. Thereafter, it maintained intensity as it struck the Lesser Antilles later that day. On Sint Maarten, the storm left a quarter of the island's population homeless and killed seven people. An additional five deaths were reported in Anguilla, and there were seven other fatalities throughout the Virgin Islands. In Puerto Rico, severe flash flooding led to 107 fatalities, 85 of them in Humacao alone.

The Columbus Day storm of 1962 was a Pacific Northwest windstorm that struck the West Coast of Canada and the Pacific Northwest coast of the United States on October 12, 1962. Typhoon Freda was the twenty-eighth tropical depression, the twenty-third tropical storm, and the eighteenth typhoon of the 1962 Pacific typhoon season. Freda originated from a tropical disturbance over the Northwest Pacific on September 28. On October 3, the system strengthened into a tropical storm and was given the name Freda, before becoming a typhoon later that day, while moving northeastward. The storm quickly intensified, reaching its peak as a Category 3-equivalent typhoon on October 5, with maximum 1-minute sustained winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) and a minimum central pressure of 948 millibars (28.0 inHg). Freda maintained its intensity for another day, before beginning to gradually weaken, later on October 6. On October 9, Freda weakened into a tropical storm, before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on the next day. On October 11, Freda turned eastward and accelerated across the North Pacific, before striking the Pacific Northwest on the next day. On October 13, the cyclone made landfall on Washington and Vancouver Island, and then curved northwestward. Afterward, the system moved into Canada and weakened, before being absorbed by another developing storm to the south on October 17.
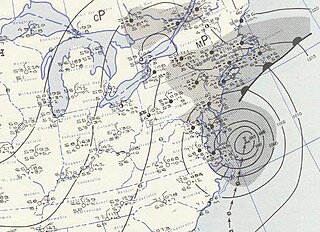
Hurricane Carol was among the worst tropical cyclones on record to affect the states of Connecticut and Rhode Island in the United States. It developed from a tropical wave near the Bahamas on August 25, 1954, and slowly strengthened as it moved northwestward. On August 27, Carol intensified to reach winds of 105 mph (169 km/h), but weakened as its motion turned to a northwest drift. A strong trough of low pressure turned the hurricane northeastward, and Carol later intensified into a major hurricane. While paralleling the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States, the storm produced strong winds and rough seas that caused minor coastal flooding and slight damage to houses in North Carolina, Virginia, Washington, D.C., Delaware, and New Jersey. The well-organized hurricane accelerated north-northeastward and made landfall on eastern Long Island, New York, and then over eastern Connecticut on August 31 with sustained winds estimated at 110-mph and a barometric pressure near 956 mb. Carol later transitioned into an extratropical cyclone over New Hampshire, on August 31, 1954.
KJZZ-TV is an independent television station in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It is owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group alongside CBS affiliate KUTV and MyNetworkTV affiliate KMYU in St. George. The stations share studios on South Main Street in downtown Salt Lake City; KJZZ-TV's transmitter is located on Farnsworth Peak in the Oquirrh Mountains, southwest of Salt Lake City. KJZZ-TV is the ATSC 3.0 host station for the Salt Lake City market; in turn, other stations broadcast its subchannels on its behalf.

KMYU is a television station licensed to St. George, Utah, United States, serving as the MyNetworkTV affiliate for the state of Utah. It is owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group alongside Salt Lake City–based CBS affiliate KUTV and independent station KJZZ-TV. The stations share studios on South Main Street in downtown Salt Lake City; KMYU's transmitter is located atop Webb Hill, 2+1⁄4 miles (3.6 km) south of downtown St. George. Previously, KMYU-TV maintained separate studios in the J. C. Snow Building on East St. George Boulevard in downtown St. George, while KUTV's facilities only housed KMYU's master control and some internal operations.

KUTV is a television station in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States, affiliated with CBS. It is owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group alongside independent station KJZZ-TV and St. George–licensed MyNetworkTV affiliate KMYU. The stations share studios on South Main Street in downtown Salt Lake City; KUTV's transmitter is located on Farnsworth Peak in the Oquirrh Mountains, southwest of Salt Lake City.
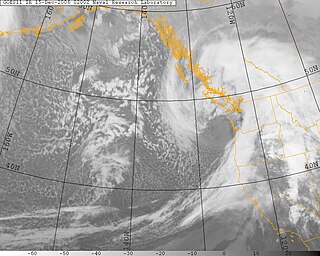
The Hanukkah Eve windstorm of 2006 was a powerful Pacific Northwest windstorm in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States and southern British Columbia, Canada between December 14, 2006 and December 15, 2006. The storm produced hurricane-force wind gusts and heavy rainfall, causing hundreds of millions of dollars in damage and leaving over 1.8 million residences and businesses without power. Eighteen people were killed, most of whom died of carbon monoxide poisoning in the days following the storm because of improper use of barbecue cookers and generators indoors. The name of the storm was chosen in a contest run by the National Weather Service office in Seattle from about 8,000 entries.

European windstorms are powerful extratropical cyclones which form as cyclonic windstorms associated with areas of low atmospheric pressure. They can occur throughout the year, but are most frequent between October and March, with peak intensity in the winter months. Deep areas of low pressure are common over the North Atlantic, and occasionally start as nor'easters off the New England coast. They frequently track across the North Atlantic Ocean towards the north of Scotland and into the Norwegian Sea, which generally minimizes the impact to inland areas; however, if the track is further south, it may cause adverse weather conditions across Central Europe, Northern Europe and especially Western Europe. The countries most commonly affected include the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Netherlands, Norway, Germany, the Faroe Islands and Iceland.

The 1949 Florida hurricane, also known as the Delray Beach hurricane, caused significant damage in the southern portions of the state late in the month of August. The second recorded tropical cyclone of the annual hurricane season, the system originated from a tropical wave near the northern Leeward Islands on August 23. Already a tropical storm upon initial observations, the cyclone curved west-northwestward and intensified, becoming a hurricane on August 25. Rapid intensification ensued as the storm approached the central Bahamas early on August 26, with the storm reaching Category 4 hurricane strength later that day and peaking with maximum sustained winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) shortly after striking Andros. Late on August 26, the storm made landfall near Lake Worth, Florida, at the same intensity. The cyclone initially weakened quickly after moving inland, falling to Category 1 status early the next day. Shortly thereafter, the system curved northward over the Nature Coast and entered Georgia on August 28, where it weakened to a tropical storm. The storm then accelerated northeastward and became extratropical over New England by August 29. The remnants traversed Atlantic Canada and much of the Atlantic Ocean before dissipating near Ireland on September 1.
A high wind storm which began early in the morning of December 1, 2011, reached wind speeds as high as 102 miles per hour (164 km/h) in Centerville, Utah, United States and surrounding cities. Fruit Heights, a neighborhood just 15 miles from the Utah State Capitol, saw gusts of up to 146 mph (235 km/h) during the event. Damage was reported throughout Davis County, and extending into Weber and Salt Lake counties, ranging from Ogden down to Salt Lake City. That morning Mayor Ron Russell of Centerville declared a local state of emergency. Due to the extensive damage, Davis County declared a state of emergency later that evening. The windstorm extended throughout the Western United States, with power outages and structural damage also reported in California and Nevada.

Storm Darwin a European windstorm that Western Europe, particularly Ireland and the United Kingdom on 12 February 2014. The storm brought hurricane-force winds to Ireland the with the Met Office and Met Éireann describing the storm as one of the most significant to affect Ireland, Wales and West England in recent decades. Tini was one of the strongest storms of the 2013–2014 Atlantic winter storms in Europe, and also brought heavy across the UK and Ireland exacerbating the 2013–2014 United Kingdom winter floods, and may have been the most damaging storm of the period.

Hurricane Zeta was a late-season major hurricane in 2020 that made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula and then in southeastern Louisiana, the latest on record to do so at such strength in the United States. Zeta was the record-tying sixth hurricane of the year to make landfall in the United States. The twenty-seventh named storm, twelfth hurricane and fifth major hurricane of the extremely active 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Zeta formed from a broad area of low pressure that formed in the western Caribbean Sea on October 19. After battling wind shear, the quasi-stationary low organized into Tropical Depression Twenty-Eight on October 24. The system strengthened into Tropical Storm Zeta early on October 25 before becoming a hurricane the next day as it began to move northwestward. Hurricane Zeta made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula late on October 26 and weakened while inland to a tropical storm, before moving off the northern coast of the peninsula on October 27. After weakening due to dry air entrainment, Zeta reorganized and became a hurricane again, and eventually a Category 2 hurricane, as it turned northeastward approaching the United States Gulf Coast on October 28. It continued to strengthen until it reached its peak intensity as a major Category 3 hurricane with 115-mile-per-hour (185 km/h) sustained winds and a minimum pressure of 970 mbar (28.64 inHg) as it made landfall at Cocodrie, Louisiana, that evening. Zeta continued on through Mississippi and parts of Alabama with hurricane-force winds. Zeta gradually weakened as it accelerated northeastward, and became post-tropical on October 29, as it moved through central Virginia, dissipating shortly afterwards off the coast of New Jersey. After bringing accumulating snow to parts of New England, the extratropical low-pressure system carrying Zeta's remnant energy impacted the United Kingdom on November 1 and 2.

The October 2017 nor'easter was a major explosive cyclogenesis storm, also called a bomb cyclone, in the Northeastern United States and Atlantic Canada from October 29–31, 2017. Forming from an extratropical cyclone on October 29 the system moved rapidly up the East Coast of the United States, bombing out with a minimum pressure of 975 millibars (28.8 inHg) on October 30. It brought heavy rain and extremely strong winds, and power outages, over 1.3 million customers being without power in the Northeast. Hurricane-force wind gusts resulted in downed trees, power lines, and widespread damage to buildings. The number of power outages in the state of Maine surpassed the Ice Storm of 1998.

In August 2020, eight artists painted a Black Lives Matter street mural in Salt Lake City's Washington Square Park, outside the Salt Lake City and County Building, in the U.S. state of Utah. The city had commissioned the painting with a contest "to support and memorialize the national movement to eliminate systemic racism".
















