Contents
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2024 in Nauru .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2024 in Nauru .
Source: [8]
Nauru, officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Micronesia, part of the Oceania region in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba of Kiribati about 300 km (190 mi) to the east.

History of Nauru, is about Nauru, an island country in the Pacific Ocean. Human activity is thought to have begun roughly 3,000 years ago when clans settled the island. A people and culture developed on the island, the Nauru which had 12 tribes. At the end of the 1700s, a British ship came, and this was the first known contact with the outside world. The British ship called it "pleasant island" and it was a friendly greeting; the British sailed on. Thirty years later, in 1830, an escaped Irish convict took over the island and was finally evicted in 1841. There were scattered interactions with passing vessels and trade. In the mid-to-late 19th century, a devastating civil war started, which took the lives of many Nauru. This war was ended when Germany annexed the island in 1888, and negotiations ended the fighting. In the 1900s, phosphate mining started, and the Germans built some modern facilities on the island. German control ended at the end of World War I, and it was passed to Australia as protectorate. This continued until WW2, when the Empire of Japan invaded the island. Although it was occupied for a few years, many Nauru died at this time, and much of the population was deported from the island and/or used for slave labor. With the surrender of Japan, the Nauru were returned to the island, and it was put under Australian administration again, under the condition it would become independent. This happened in 1968, and Nauru has been a stable democracy since that time. In the last three decades of the 20th century, Nauru had enormous per capita wealth from the phosphate mining, to the point they were some of the richest people on the planet. However, when this ended and the investments were depleted, it has had a harder time, and international aid is important in the 21st century.

The politics of Nauru take place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Nauru is the head of government of the executive branch. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the parliament. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

The economy of Nauru is tiny, based on a population in 2019 of only 11,550 people. The economy has historically been based on phosphate mining. With primary phosphate reserves exhausted by the end of the 2010s, Nauru has sought to diversify its sources of income. In 2020, Nauru's main sources of income were the sale of fishing rights in Nauru's territorial waters, and revenue from the Regional Processing Centre.
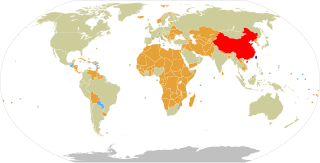
Foreign relations of the Republic of China (ROC), more commonly known as Taiwan, are accomplished by efforts of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China, a cabinet-level ministry of the Government of the Republic of China. As of January 2024, the ROC has formal diplomatic relations with 11 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs the Vatican City State. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories (Guam, Hong Kong, and Macau), and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates. In 2021, the Government of the Republic of China had the 33rd largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.

Nauru became a sovereign, independent republic on 31 January 1968, following the passage of the Nauru Independence Act 1967 by the Parliament of Australia and the end of its status as a United Nations Trust Territory. Nauru has established diplomatic relations with a number of nations, including most of its Pacific neighbors with which it maintains economic, cultural and administrative ties.

Kieren Aedogan Ankwong Keke is a Nauruan politician and medical doctor. He is a member of the Parliament of Nauru and former Minister of Finance and Minister of Foreign Affairs.
Ruben James Kun was a political figure from the Pacific nation of Nauru and was president of the Republic of Nauru.

David Ranibok Waiau Adeang is a Nauruan politician, currently serving as President of Nauru. Adeang is the former Speaker of the Parliament of Nauru, and Nauru's Minister of Finance and Justice, as well as the Minister Assisting the President of Nauru.

Marcus Ajemada Stephen is a Nauruan politician and former sportsperson who previously was a member of the Cabinet of Nauru, and who served as President of Nauru from December 2007 to November 2011. The son of Nauruan parliamentarian Lawrence Stephen, Stephen was educated at St Bedes College and RMIT University in Victoria, Australia. Initially playing Australian rules football, he opted to pursue the sport of weightlifting, in which he represented Nauru at the Summer Olympics and Commonwealth Games between 1990 and 2002, winning seven Commonwealth gold medals.

Frederick William Pitcher is a Nauruan political figure. In December 2007, Pitcher was appointed Minister of Finance of Nauru, to serve in the Administration of President Marcus Stephen.

Oceania is, to the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China, a stage for continuous diplomatic competition. The PRC dictates that no state can have diplomatic relations with both the PRC and the ROC. As of 2024, eleven states in Oceania have diplomatic relations with the PRC, and three have diplomatic relations with the ROC. These numbers fluctuate as Pacific Island nations re-evaluate their foreign policies, and occasionally shift diplomatic recognition between Beijing and Taipei. The issue of which "Chinese" government to recognize has become a central theme in the elections of numerous Pacific island nations, and has led to several votes of no-confidence.

Foreign relations exist between Australia and Nauru. Australia administered Nauru as a dependent territory from 1914 to 1968 and has remained one of Nauru's foremost economic and aid partners thereafter. Nauru has a High Commission in Canberra and a consulate-general in Brisbane. Australia is one of only two countries to have a High Commission in Nauru. Both countries are members of the Commonwealth of Nations.

Parliamentary elections were held in Nauru on April 26, 2008, following the dissolving of Parliament by President Marcus Stephen on April 18. The decision came after what Stephen referred to as "months of political deadlock". Of the parliament's eighteen members, nine supported the Stephen government and nine were in opposition.

Baron Divavesi Waqa is a Nauruan politician who currently serves as the secretary-general of the Pacific Islands Forum. He was the President of Nauru from 11 June 2013 until 27 August 2019. He previously served as Minister of Education from 2004 to 2007.

China–Nauru relations are relations between the People's Republic of China and the Republic of Nauru. The Republic of Nauru and the People's Republic of China established diplomatic relations on 21 July 2002, and resumed on 24 January 2024. Between 2005 and 2024, The government of Nauru recognized the Republic of China, and, in accordance with the "One China" policy, the People's Republic of China did not have diplomatic relations to the country.

Nauru–Taiwan relations are relations between the Republic of Nauru and the Republic of China (Taiwan). Official diplomatic relations were first established in 1980. Relations were first severed in 2003, when Nauru opted to recognize the People's Republic of China. Formal bilateral relations with Nauru were reestablished in 2005, and maintained until 2024.
The New Nauru Stadium is a multi-use stadium currently under construction on the Pacific island nation of Nauru.
Events in the year 2023 in Nauru.
Events in the year 2025 in Nauru.