Related Research Articles

The Boeing CIM-10 BOMARC was a supersonic ramjet powered long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) used during the Cold War for the air defense of North America. In addition to being the first operational long-range SAM and the first operational pulse doppler aviation radar, it was the only SAM deployed by the United States Air Force.

Eglin Air Force Base is a United States Air Force (USAF) base in the western Florida Panhandle, located about three miles (5 km) southwest of Valparaiso in Okaloosa County.

Hurlburt Field is a United States Air Force installation located in Okaloosa County, Florida, immediately west of the town of Mary Esther. It is part of the greater Eglin Air Force Base reservation and is home to Headquarters Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), the 1st Special Operations Wing (1 SOW), the USAF Special Operations School (USAFSOS) and the Air Combat Command's (ACC) 505th Command and Control Wing. It was named for First Lieutenant Donald Wilson Hurlburt, who died in a crash at Eglin. The installation is nearly 6,700 acres (27 km2) and employs nearly 8,000 military personnel.

Holloman Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base established in 1942 located six miles (10 km) southwest of the central business district of Alamogordo, and a census-designated place in Otero County, New Mexico, United States. The base was named in honor of Col. George V. Holloman, a pioneer in guided missile research. It is the home of the 49th Wing of the Air Education and Training Command (AETC).

Piccadilly Lilly II is a B-17 Flying Fortress currently on display at the Planes of Fame air museum in Chino, California. Built in 1945 as a B-17G and assigned serial number 44-83684, this plane was possibly the last aircraft assigned to the Eighth Air Force / 447th Bomb Group, but perhaps not delivered. It was the last active B-17 in the United States Air Force, and retired in 1959 after nine years as a DB-17P drone director. Following its military career, the plane appeared in various television shows and movies.

Sentimental Journey (44-83514) is the nickname of a B-17G Flying Fortress bomber. It is based at the Commemorative Air Force Museum in Mesa, Arizona, US. The aircraft is regularly flown to airshows throughout North America.

The 514th Flight Test Squadron is a squadron of the United States Air Force, which has been stationed at Hill Air Force Base, Utah since 1973, performing functional flight checks on aircraft undergoing major maintenance.

The 513th Electronic Warfare Squadron is a United States Air Force unit assigned to the 350th Spectrum Warfare Group at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida.

This is a list of United States Army Air Forces B-17 Flying Fortress units of the United States Army Air Forces, including variants and other historical information. Heavy bomber training organizations primarily under II Bomber Command in the United States and non-combat units are not included.

The 1st Tactical Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 585th Tactical Missile Group at Bitburg Air Base, West Germany, where it was inactivated on 18 June 1958.
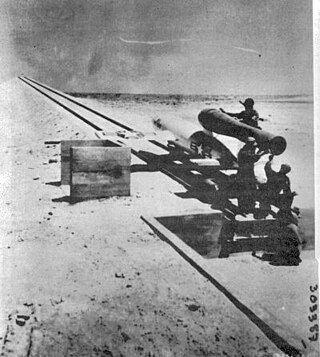
The 1st Experimental Guided Missiles Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the Air Proving Ground Command and stationed at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 22 July 1949.

The 550th Guided Missiles Wing is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the Long Range Proving Ground Division at Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 30 December 1950. From 1949 through 1950 it was the Air Force's only experimental missile unit.
Eglin Air Force Base, a United States Air Force base located southwest of Valparaiso, Florida, was established in 1935 as the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base. It is named in honor of Lieutenant Colonel Frederick I. Eglin, who was killed in a crash of his Northrop A-17 pursuit aircraft on a flight from Langley to Maxwell Field, Alabama.

The 3205th Drone Group is a discontinued United States Air Force unit that operated obsolete aircraft during the 1950s as radio-controlled aerial targets for various tests. It was the primary post-World War II operator of surplus Boeing B-17G Flying Fortress aircraft, and also operated Lockheed F-80 Shooting Star and a few Boeing RB-47 Stratojet bombers that were converted into drone aircraft during the early years of the Cold War. It was last active with the Air Proving Ground Center, based at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, where it was discontinued on 1 February 1961.

The 3205th Drone Squadron is a discontinued United States Air Force unit. It was last active with the Air Proving Ground Center based at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, where it was discontinued on 25 October 1963. The squadron operated various drones between 1950 and 1963 to provide targets to support development of weapons and for interceptor training.

The 3225th Drone Squadron is a discontinued United States Air Force unit. It was last active with the Air Force Missile Development Center, based at Holloman Air Force Base, New Mexico. It was discontinued on 25 October 1963.
The 3235th Drone Squadron is a discontinued United States Air Force unit. It was last active with the 3205th Drone Group, based at NAS Point Mugu, California. It was discontinued on 1 January 1957.

The 3200th Proof Test Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last active with the Air Armament Center, based at Eglin AFB, Florida. It was inactivated on 1 July 1953.

Boeing B-17G Flying Fortress No.44-83690 is a B-17 Flying Fortress heavy bomber currently undergoing restoration at the Museum of Aviation near Robins Air Force Base in Georgia. It was built as a B-17G-95-DL by the Douglas Aircraft Company and delivered for use on May 9, 1945. It was flown to Grissom Air Force Base for display as a museum piece in 1961. The plane was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1993. It was moved to the Museum of Aviation in August 2015.

The 96th Test Wing is a United States Air Force unit assigned to the Air Force Test Center of Air Force Materiel Command at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. The wing was activated at Eglin in 1994 as the 96th Air Base Wing, the headquarters for all support units on Eglin, the largest installation in the Air Force. In 2012, it absorbed the mission and resources of the 46th Test Wing and added the mission of testing and evaluating weapons, navigation and guidance systems and command and control systems.
References
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 See Mueller, p. 139
- ↑ Thompson [ page needed ]
- ↑ Jablonski [ page needed ]
- ↑ Parsch, Andreas. "Bomarc". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 17 August 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
Bibliography
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
- Jablonski, Edward (1965), Flying Fortress: The Illustrated Biography of the B-17s and the Men Who Flew Them, Doubleday & Company ISBN 1199376744
- Mueller, Robert (1989). Air Force Bases, Vol. I, Active Air Force Bases Within the United States of America on 17 September 1982 (PDF). Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-912799-53-6.
- Thompson, Scott (2011), Final Cut: The Post-War B-17 Flying Fortress and Survivors (4th Edition), Pictorial Histories & Aero Vintage Books ISBN 1575101564