
Mesa Del Rey Airport is a public airport a mile northeast of King City, in Monterey County, California, United States. The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015 categorized it as a general aviation facility.

Twentynine Palms Airport is a public use airport located six nautical miles (11 km) east of the central business district of Twentynine Palms, a city in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It is owned by the County of San Bernardino.

Sequoia Field Airport is a county-owned, public-use airport located eight nautical miles (15 km) north of the central business district of Visalia, a city in Tulare County, California, United States.

Airglades Airport is a county-owned public-use airport in Hendry County, Florida, United States. It is located 5 miles (8.0 km) west of the central business district of Clewiston, Florida.

The United States Army Air Forces during World War II had major subordinate Commands below the Air Staff level. These Commands were organized along functional missions. One such Command was the Flying Training Command (FTC). It began as Air Corps Flying Training Command on 23 January 1942, was redesignated Army Air Forces Flying Training Command (AAFTC) on 15 March 1942, and merged with Army Air Forces Technical Training Command to become Army Air Forces Training Command on 31 July 1943. Continuing service after the war, it was redesignated Air Training Command on 1 July 1946. During the consolidation of Air Force Major Commands in the retrenchment of the 1990s, Air Training Command assumed control of Air University and became Air Education and Training Command on 1 July 1993—today's Air Education and Training Command (AETC), which celebrated its 75th anniversary 23 January 2017. see the Lineage and honors statement for AETC.

Malden Regional Airport is a city-owned, public-use airport located three nautical miles (6 km) north of the central business district of Malden, a city in Dunklin County, Missouri, United States. This airport is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems, which categorized it as a general aviation facility.

Echeverria Field is an abandoned airfield, located approximately 15 miles (24 km) west of Wickenburg, Arizona.

Thompson–Robbins Airport is 6 miles (9.7 km) northwest of the center of Helena–West Helena, in unincorporated Phillips County, Arkansas, United States. It is owned by the city of Helena–West Helena.

Coleman Municipal Airport is an airport two miles northeast of Coleman, Texas.

Arledge Field is a public general aviation airport located approximately 4 miles (6.4 km) east of Stamford, Texas. Owned by the city of Stamford, it provides general aviation service. Approximately 80 aircraft use the airport on a weekly basis.

During World War II civilian flying schools, under government contract, provided a considerable part of the flying training effort undertaken by the United States Army Air Forces.
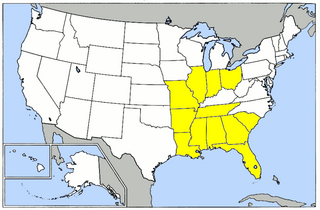
The Army Air Forces Eastern Flying Training Command (EFTC) was a unit of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to the Army Air Forces Training Command, stationed at Maxwell Field, Alabama. It was inactivated on 15 December 1945.
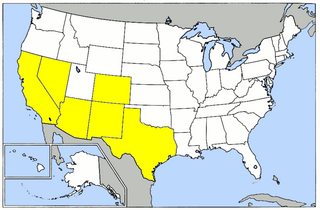
The Army Air Forces Western Flying Training Command (WFTC) was a command of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to the Army Air Forces Training Command, stationed at Santa Ana Army Air Base, California. It was inactivated on 1 November 1945.

The Flying Division, Air Training Command, was a training formation of the United States Air Force. The unit was established in 1926 as the Air Corps Training Center to be the primary pilot training center for the Air Corps. It was reorganized into one of three training commands created by the Office of the Chief of the Air Corps in 1940 to accommodate the large number of air cadets being recruited as a result of the expansion of the corps after the fall of France. During World War II, thousands of cadets attended various flight schools throughout the Central United States being trained as pilots for fighters, bombers and transports. It also trained the navigators, bombardiers and gunners necessary for the bombers to attack enemy targets in the combat areas overseas. After World War II, it became the primary pilot and aircrew training unit of the United States Air Force Air Training Command.

The 29th Flying Training Wing was a wing of the United States Army Air Forces. It was last assigned to the Western Flying Training Command, and was disbanded on 16 June 1946 at Napier Field, Alabama. The wing controlled World War II Phase One primary flying training units of the Army Air Forces Training Command. Headquartered at Moody Field, Georgia for most of its operational service, it controlled contract civilian-operated pilot schools primarily in the Southeastern United States.

The 31st Flying Training Wing was a training formation of the U.S. Army Air Forces (AAF) during World War II.

The 35th Flying Training Wing is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the Western Flying Training Command, and was disbanded on 16 June 1946 at the Minter Field, California.
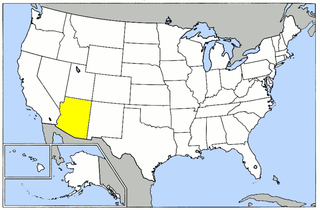
The 37th Flying Training Wing is an inactive United States Army Air Forces unit. It was last assigned to the Western Flying Training Command, and was disbanded on 16 June 1946 at Luke Field, Arizona.

The 28th Flying Training Wing was a unit of the United States Army Air Forces. It was last assigned to the Eastern Flying Training Command, and was disbanded on 30 December 1945 at Craig Field, Alabama.

Victorville Army Airfield auxiliary fields were four airfields used during World War II to support the Victorville Army Airfield pilot training near Victorville, California, and Adelanto, California. After the war the Victorville Army Airfield was renamed George Air Force Base on January 13, 1948. The airfields were built in 1941 by the United States Army Air Corps just before the war. Victorville Army Airfield covered 2,200-acre in the Mojave Desert. The US Army held a groundbreaking ceremony on 12 July 1941. The base, called Victorville Army Flying School, was ready to use before the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. The Army built four runways in a triangle configuration, with one runway down the middle of the triangle. Seven hangars were built to support operation. On April 23, 1943, the base was renamed Victorville Army Airfield.





















