
The Battle of Mill Springs, also known as the Battle of Fishing Creek in Confederate terminology, and the Battle of Logan's Cross Roads in Union terminology, was fought in Wayne and Pulaski counties, near current Nancy, Kentucky, on January 19, 1862, as part of the American Civil War. The Union victory concluded an early Confederate offensive campaign in eastern Kentucky.

The Big Sandy Expedition was an early campaign of the American Civil War in Kentucky that began in mid-September 1861 when Union Brig. Gen. William "Bull" Nelson received orders to organize a new brigade at Maysville, Kentucky and conduct an expedition into the Big Sandy Valley region of Eastern Kentucky and stop the build-up of Confederate forces under Col. John S. Williams. This was done in three phases. From September 21 to October 20, 1861, Nelson assembled a brigade of 5,500 Union volunteers from Ohio and Kentucky. On October 23, the southern prong secured Hazel Green and the northern prong West Liberty. The two prongs were consolidated at Salyersville and they began the final phase on October 31. This led to the Battle of Ivy Mountain on November 8 and the withdrawal of Confederate forces from Pikeville (Piketon) on November 9, 1861.

John Thomas Wilder was a colonel in the Union Army during the American Civil War, noted principally for capturing a key mountain pass in the Tullahoma Campaign in Central Tennessee in June 1863. Wilder had personally ensured that his 'Lightning Brigade' of mounted infantry would be equipped with the new Spencer repeating rifle, though he initially had to appeal to the rank-and-file to pay for these weapons themselves, before the government agreed to carry the cost. Victory at Hoover's Gap was attributed largely to Wilder's persistence in procuring the new rifles, which totally disoriented the enemy.
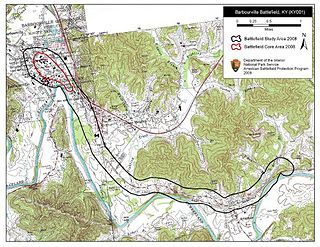
The Battle of Barbourville was one of the early engagements of the American Civil War. It took place on September 19, 1861, in Knox County, Kentucky during the campaign known as the Kentucky Confederate Offensive. The battle is considered the first Confederate victory in the commonwealth, and threw a scare into Federal commanders, who rushed troops to central Kentucky to try to repel the invasion, which was finally stopped at the Battle of Camp Wildcat in October.

To a large extent, the American Civil War was fought in cities and farms of Tennessee, as only Virginia saw more battles. However, Tennessee is the only state to have major battles or skirmishes fought in every single county. Tennessee was the last of the Southern states to declare secession from the Union as a substantial portion of the population were against secession, but saw more than its share of the devastation resulting from years of warring armies criss-crossing the state. Its rivers were key arteries to the Deep South, and, from the early days of the war, Union efforts focused on securing control of those transportation routes, as well as major roads and mountain passes such as the Cumberland Gap. Tennessee was also considered "the Bread Basket" of the Confederacy, for its rich farmland that fed both armies during the war.
The 19th Tennessee Infantry Regiment, or Nineteenth Tennessee Volunteer Infantry Regiment, was an infantry regiment in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The 19th Tennessee fought in every major battle and campaign of the Army of Tennessee except the Battle of Perryville. First Lieutenant Robert D. Powell of Company K, killed at the Battle of Barbourville, Kentucky, is believed to be the first soldier killed during the Civil War in that state.

In mid-May 1861, U. S. Navy lieutenant William "Bull" Nelson armed Kentuckians loyal to the Union and that soon became the foundation for his receiving authority to enlist 10,000 troops for a campaign into East Tennessee. On August 6, 1861, those recruits marched into Camp Dick Robinson, making it the first Federal base south of the Ohio River. For Col. George C. Kniffen, "the wisdom of President Lincoln commissioning. .. Nelson to organize a military force on the [neutral] soil of Kentucky" prevented making the state a "battle ground for many months" and it thereby changed the whole direction of the war. In 1864, Salmon P. Chase declared in a speech at Louisville "when Kentucky faltered, hesitated" in the early stages of the Civil War, that undecided "status was settled by WILLIAM NELSON, at Camp Dick Robinson." Six years later, Indiana Senator Daniel D. Pratt reported to the U. S. Senate that Camp Dick Robinson "was one of the most noted military encampments of the war.. .. From its admirable locality and advantages, it was almost indispensable for the successful operations of the" Civil War.

John Wesley Frazer was an American soldier, planter, and businessman. He was a career officer in the United States Army, and then served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War.

Robert Charles Tyler was a Confederate Brigadier General during the American Civil War. He was the last general killed in the conflict.

The 7th Arkansas Volunteer Infantry (1861−1865) was a Confederate Army infantry regiment during the American Civil War composed of troops from northeast Arkansas. Organized mainly from companies, including several prewar volunteer militia companies, raised in northeastern Arkansas, the regiment was among the first transferred to Confederate Service, and spent virtually the entire war serving in Confederate forces east of the Mississippi River. After the unit sustained heavy casualties during the Battle of Shiloh and Bragg's Kentucky Campaign, the unit spent most of the rest of the war field consolidated with the 6th Arkansas Infantry Regiment, to form the 6th/7th Arkansas Infantry Regiment.
James Patton Brownlow was a Union Army officer during the American Civil War. Brownlow was the son of East Tennessee Unionist preacher, newspaper publisher and editor, Governor of Tennessee and U.S. Senator "Parson" William G. Brownlow. James P. Brownlow served in several positions in the Union Army, finishing the war as colonel of the 1st Tennessee Volunteer Cavalry Regiment (Union). He was noted for his courage and perceptiveness in battle and keen sense of military tactics. He led several daring raids and attacks. The United States Senate confirmed the award of the grade of brevet brigadier general of volunteers, to rank from March 13, 1865, to Brownlow on March 12, 1866. After the war, he was adjutant general of the State of Tennessee and then a railroad superintendent. He died in 1879 at the age of 36.
The 27th Tennessee Infantry Regiment was an infantry formation in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War, and was successively commanded by Colonels C. H. Williams and A. W. Caldwell. The regiment was assigned to Maney's Brigade, Cheatham's Division, 1st Corps, Army of Tennessee, and on January 1, 1863, consolidated with the 1st (Field's) Tennessee Infantry Regiment.

Tyree Harris Bell was a Confederate States Army brigadier general, during the American Civil War.

The 9th Arkansas Infantry was a Confederate Army infantry regiment during the American Civil War. It served throughout the war in the western theater, seeing action in the Vicksburg, Tennessee and Georgia campaigns. Following its depletion in numbers the regiment was consolidated several times with other Arkansas regiments, finally merging in 1865 into the 1st Arkansas Consolidated Mounted Rifles.

Alfred Eugene Jackson was a Confederate States Army brigadier general during the American Civil War. Before the war, he was a farmer, produce wholesaler, miller, manufacturer and transporter of goods by wagon and boat. After the war, he was a tenant farmer in Virginia until he regained some of his property in Tennessee.

Joel Allen Battle was an American politician and soldier. He was appointed a Tennessee militia general in 1835 during the Second Seminole War. He was a colonel in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.

The 1st Florida Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment raised by the Confederate state of Florida during the American Civil War. Raised for 12 months of service its remaining veterans served in the 1st (McDonell's) Battalion, Florida Infantry from April 1862 on. In August the depleted battalion was consolidated with the 3rd (Miller's) Battalion into the reorganized 1st Florida Infantry Regiment again. In December 1862 it merged with the 3rd Florida Infantry Regiment and received the form it kept till the war's end as the 1st and 3rd Consolidated Florida Infantry Regiment. Fighting as part of the Army of Tennessee in the Western Theater of the American Civil War it was surrendered on April 26, 1865.

The Battle of Camp Wildcat was one of the early engagements of the American Civil War. It occurred October 21, 1861, in northern Laurel County, Kentucky during the campaign known as the Kentucky Confederate Offensive or Operations in Eastern Kentucky (1861). The battle is considered one of the first Union victories of the Civil War, and marked the second engagement of troops in the Commonwealth of Kentucky.





















