
John Flamsteed was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, Catalogus Britannicus, and a star atlas called Atlas Coelestis, both published posthumously. He also made the first recorded observations of Uranus, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a star, and he laid the foundation stone for the Royal Greenwich Observatory.

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars.

Eta Cassiopeiae is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. Its binary nature was first discovered by William Herschel in August 1779. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance to this system is 19.42 light-years from the Sun. The two components are designated Eta Cassiopeiae A and B.

Alpha Cassiopeiae or α Cassiopeiae, also named Schedar, is a second magnitude star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. Though listed as the "alpha star" by Johann Bayer, α Cas's visual brightness closely matches the 'beta' (β) star in the constellation and it may appear marginally brighter or dimmer, depending on which passband is used. However, recent calculations from NASA's WISE telescope confirm that α Cas is the brightest in Cassiopeia, with an apparent magnitude of 2.240. Its absolute magnitude is 18 times greater than β Cas, and it is located over four times farther away from the Sun.

Beta Cassiopeiae, officially named Caph, is a Delta Scuti variable star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It is a giant star belonging to the spectral class F2. The white star of second magnitude has an absolute magnitude of +1.3 mag.

Rho Cassiopeiae is a yellow hypergiant star in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is about 3,400 light-years (1,000 pc) from Earth, yet can still be seen by the naked eye as it is over 300,000 times brighter than the Sun. On average it has an absolute magnitude of −9.5, making it visually one of the most luminous stars known. Its diameter measures between 400 and 500 times that of the Sun, approximately 627,000,000 kilometers, or about twice the size of the Earth's orbit.

Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is a supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately 11,000 light-years (3.4 kpc) away within the Milky Way; given the width of the Orion Arm, it lies in the next-nearest arm outwards, the Perseus Arm, about 30 degrees from the Galactic anticenter. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova now appears approximately 10 light-years (3 pc) across from Earth's perspective. It has been seen in wavelengths of visible light with amateur telescopes down to 234 mm (9.25 in) with filters.

SN 1572, or B Cassiopeiae, was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records. It appeared in early November 1572 and was independently discovered by many individuals.

Epsilon Cassiopeiae or ε Cassiopeiae, officially named Segin, is a single star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.4, this is one of the brightest stars in the constellation. The distance to this star has been determined directly using parallax measurements, yielding a value of around 460–430 light-years from the Sun. It is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −8 km/s.

Gamma Cassiopeiae, Latinized from γ Cassiopeiae, is a bright star at the center of the distinctive "W" asterism in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cassiopeia. Although it is a fairly bright star with an apparent visual magnitude that varies from 1.6 to 3.0, it has no traditional Arabic or Latin name. It sometimes goes by the informal name Navi.

Zeta Cassiopeiae, Latinized from ζ Cassiopeiae, and officially named Fulu, is a variable star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It has a blue-white hue and is classified as a B-type subgiant with an apparent magnitude of +3.66. Based upon parallax measurements, it is approximately 590 light-years from the Sun.

Kappa Cassiopeiae is a star in the constellation Cassiopeia.
48 Cassiopeiae is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.49. With an annual parallax shift of 28.36±0.44 mas as seen from Earth's orbit, it is located approximately 115 light years away. The system is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −12.4 km/s.

Phi Cassiopeiae is a star in the constellation Cassiopeia. φ Cassiopeiae is a multiple star with a combined apparent magnitude of +4.95. The two brightest components are A and C, sometimes called φ1 and φ2 Cas. φ Cas A is an F0 bright supergiant of magnitude 4.95 and φ Cas C is a 7.08 magnitude B6 supergiant at 134".

4 Cassiopeiae is a red giant in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia, located approximately 790 light-years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. At the distance of this system, its visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction of 0.56 due to interstellar dust. This system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −39 km/s.
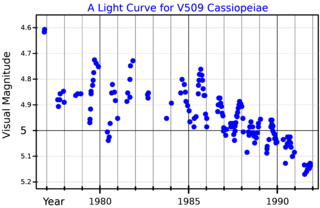
V509 Cassiopeiae is one of two yellow hypergiant stars found in the constellation Cassiopeia, which also contains Rho Cassiopeiae.

6 Cassiopeiae is a white hypergiant in the constellation Cassiopeia, and a small-amplitude variable star.
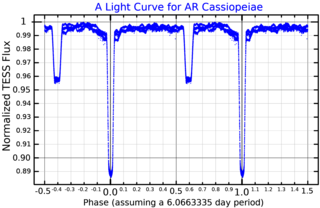
AR Cassiopeiae is a variable star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It is thought to be a member of a septuple star system, one of only two known star systems with a multiplicity of 7, the other being Nu Scorpii.
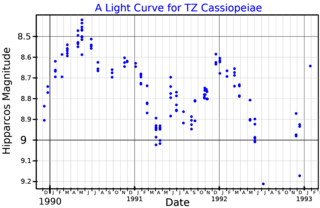
TZ Cassiopeaie(TZ Cas, HIP 117763, SAO 20912) is a variable star in the constellation Cassiopeia with an apparent magnitude of around +9 to +10. It is approximately 8,400 light-years away from Earth. The star is a red supergiant star with a spectral type of M3 and a temperature below 4,000 K.

HD 224355, also known as V1022 Cassiopeiae, HR 9059 and Boss 6148, is an eclipsing binary star in the constellation Cassiopeia. It ranges in apparent magnitude from 5.57 to 5.68, which means it is faintly visible to the naked eye for an observer located well away from city lights. It is one of the few binaries known to be an astrometric, spectroscopic and eclipsing binary, a combination that allows the parameters of the stellar system to be calculated with high accuracy. HD 224355 lies 16′ west of the 5th-magnitude σ Cassiopeiae.











