
The 71st Infantry Division was a reserve division of the Philippine Army that fought under the United States Army Forces in the Far East (USAFFE). It was known for its fight with Japanese invading forces in Layac Junction, that was ordered to hold until all retreating Fil-American forces of crossed into Bataan Peninsula.

The 73rd Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Commonwealth Army was activated on August 25, 1941, was inducted to United States Army Forces in the Far East on September 1, 1941, by Captain Eugene B. Hicker of US Army. It was the last regiment among the three authorized to organized so it was not included when the entire 71st Infantry Division was ordered transferred to the main island of Luzon in September 1941.

81st Infantry Regiment is a military unit and formation of the Philippine Commonwealth Army

Visayan Force is a US Forces in the Philippines subcommand which was created and took effect on March 17, 1942, after General Douglas MacArthur departed for Australia. It was disintegrated in the month after its creation due to the loss of contact of Visayan Force headquarters during the Japanese invasion of Cebu in April 16 to 19, 1942, it resorted to guerilla warfare. Eventually all forces in the Visayas was ordered to surrender on May 11, 1942.

102nd Infantry Regiment is a military unit of the Philippine Commonwealth Army during World War II. I was activated in September 1941 and inducted to USAFFE on the same month. It fought under 101st Infantry Division

82nd Infantry Regiment is a unit activated by the Philippine Commonwealth Army for the defense of the Philippine during World War II. It defended the Cebu Island particularly in the southern part of Cebu during the Japanese landings in Cebu island on April 16, 1942. It surrendered on May 12, 1942, after it was ordered by Visayas-Mindanao Force commander General Sharp to surrender.
Negros Force was a WWII-era Philippine Army unit activated by the United States Army Forces in the Far East (USAFFE) from September 1, 1941, to May 12, 1942. The force did not fight during the war but played a role in organizing units deployed to different sectors. The force also continued to fight as a guerilla force after the war. The two provinces on the island were never united during the conflict, due to the different affiliations of their commanders.
101st Field Artillery Regiment is a reserve field artillery regiment activated in August 1941 as part of 101st Infantry Division based in Camp Casisang in Bukidnon Province. Visayas-Mindanao Force only received 8 QF 2.95inch Mountain Guns and divided it between two divisions in the island 101st and 81st in Lanao sector. The regiment retrained into fighting as infantry due to lack of guns to operate.
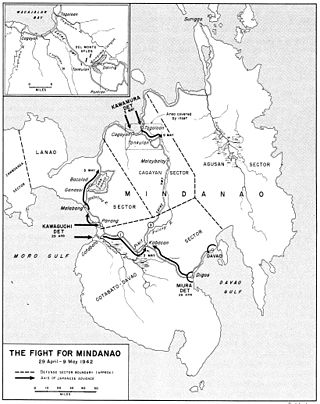
Japanese invasion of Cotabato is one of the three landings made by Japanese Army during their
Japanese invasion of Zamboanga took place in March 1942 as part of Mindanao siege during Japanese campaign to invade the Philippines in December 1941 to May 1942.

75th (Provisional) Infantry Regiment was a reserve unit of Philippine Commonwealth Army activated under Negros Force in January 1942. It saw no action as it was disbanded in May 1942 after it surrendered to Japanese during World War II. Most of its soldiers escaped and joined guerilla movement organized by Major Salvador Abcede.

71st Field Artillery Regiment was a military unit of Philippine Army activated in 1941 as part of 71st Infantry Division. It fought in Luzon during Japanese landing and also in Bataan. All officers and men was captured during surrender of Fil-American forces in Bataan on April 9, 1942.

61st Field Artillery Regiment was a reserve unit of Philippine Army activated in August 1941 as part of 61st Infantry Division based in Panay Island. It fought as infantry as the SS Corregidor, the ship transporting their guns, was sunk when it hit a landmine in Manila Bay.
81st Field Artillery Regiment is a reserve unit of Philippine Commonwealth Army activated in August 1941 as part of 81st Infantry Division. It was organized and inducted in Cebu out of reserve soldiers and officers.
51st Field Artillery Regiment is a reserve unit of Philippine Commonwealth Army activated and organized in 1941 and fought during World War II. The regiment is a component of 51st Infantry Division under Brigadier General Albert M. Jones, responsible for the defense of Bicol Peninsula.
91st Field Artillery Regiment is a reserve unit of Philippine Commonwealth Army activated and organized in August 1941. It is part of 91st Infantry Division under Brigadier General Luther R. Stevens, PA who fought in Battle of Bataan. Whole regiment became POW after surrendering on April 9, 1942, to Japanese 14th Army.

104th Infantry Regiment, was a unit of Philippine Commonwealth Army activated and organized while the war progressed. It was organized with moros and local recruits within Cotabato-Davao Sector under 101st Infantry Division under Brigadier General Joseph Vachon in Mindanao Island during World War II.
105th Infantry Regiment was a special troops of activated and organized by 101st Infantry Division during Japanese invasion of Mindanao island. Irregular soldiers from Moros and local volunteers where trained and put into one unit. During Japanese invasion of Mindanao in Cotabato-Davao Sector.
71st Infantry Regiment is a reserve unit of Philippine Commonwealth Army under 71st Infantry Division activated and organized in Negros Island. It was transferred to Luzon island to bolster its defending forces during World War II. It fought in Northern Luzon and in Bataan where it defeated Japanese at the battle of points.
72nd Infantry Regiment, is a reserve military unit and formation of Philippine Commonwealth Army who fought during World War II in Northern Luzon and in Bataan Peninsula. 72nd Infantry was under 71st Division and was first designated as reserve unit of North Luzon Force under Major General Jonathan M. Wainwright IV, USA that can only be committed if permitted from USAFFE Headquarters.





