Related Research Articles

John H. Morgan was a Confederate general in the American Civil War. Morgan never used his middle name of Hunt during the war - it is a post war appellation.

The Battle of Perryville was fought on October 8, 1862, in the Chaplin Hills west of Perryville, Kentucky, as the culmination of the Confederate Heartland Offensive during the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Braxton Bragg's Army of Mississippi initially won a tactical victory against primarily a single corps of Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell's Union Army of the Ohio. The battle is considered a strategic Union victory, sometimes called the Battle for Kentucky, since Bragg withdrew to Tennessee soon thereafter. The Union retained control of the critical border state of Kentucky for the remainder of the war.

The Battle of Nashville was a two-day battle in the Franklin-Nashville Campaign that represented the end of large-scale fighting west of the coastal states in the American Civil War. It was fought at Nashville, Tennessee, on December 10–19, 1864, between the Confederate Army of Tennessee under Lieutenant General John Bell Hood and Union Major General George H. Thomas. In one of the largest victories achieved by the Union Army during the war, Thomas attacked and routed Hood's army, largely destroying it as an effective fighting force.

The Battle of Resaca was part of the Atlanta Campaign of the American Civil War. The battle was waged in both Gordon and Whitfield counties, Georgia, May 13–15, 1864. It ended inconclusively with the Confederate Army retreating. The engagement was fought between the Military Division of the Mississippi on the side of the Union and the Army of Tennessee for the Confederates.

Benjamin Henry Grierson was a music teacher, then a career officer in the United States Army. He was a cavalry general in the volunteer Union Army during the Civil War and later led troops in the American Old West. He is most noted for Grierson's Raid, an 1863 expedition through Confederate-held territory that severed enemy communication lines between Vicksburg, Mississippi and Confederate commanders in the Eastern Theater. After the war he organized and led the Buffalo Soldiers of the 10th Cavalry Regiment from 1866 to 1890.

The Tullahoma campaign was a military operation conducted from June 24 to July 3, 1863, by the Union Army of the Cumberland under Maj. Gen. William Rosecrans, and regarded as one of the most brilliant maneuvers of the American Civil War. Its effect was to drive the Confederates out of Middle Tennessee and to threaten the strategic city of Chattanooga.
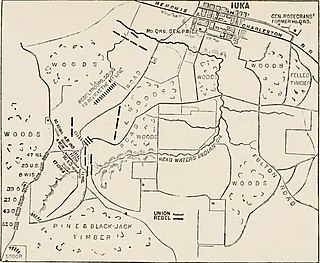
The Battle of Iuka was fought on September 19, 1862, in Iuka, Mississippi, during the American Civil War. In the opening battle of the Iuka-Corinth Campaign, Union Maj. Gen. William Rosecrans stopped the advance of the Confederate Army of the West commanded by Maj. Gen. Sterling Price.
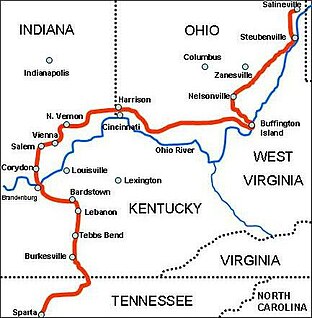
Morgan's Raid was a diversionary incursion by Confederate cavalry into the northern (Union) states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio and, briefly, West Virginia, during the American Civil War. The raid took place from June 11–July 26, 1863, and is named for the commander of the Confederates, Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan. Although it caused temporary alarm in the North, the raid was ultimately classed as a failure.
The Battle of Salineville occurred July 26, 1863, near Salineville, Ohio during Morgan's Raid in the American Civil War. Except for the St. Albans (Vermont) Raid, it was the northernmost military action involving the Confederate States Army. The Union victory shattered John Hunt Morgan's remaining Confederate cavalry and led to his capture later that day.
The 8th Ohio Volunteer Infantry was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It served in the Eastern Theater in a number of campaigns and battles, but perhaps is most noted for its actions in helping repulse Pickett's Charge during the Battle of Gettysburg.
The Battle of Griswoldville was the first battle of Sherman's March to the Sea, fought November 22, 1864, during the American Civil War. A Union Army brigade under Brig. Gen. Charles C. Walcutt fought three brigades of Georgia militia under Brig. Gen. Pleasant J. Philips, at Griswoldville, near Macon, Georgia, and continued its march toward Savannah.
The Battle of Buffington Island, also known as the St. Georges Creek Skirmish, was an American Civil War engagement in Meigs County, Ohio, and Jackson County, West Virginia, on July 19, 1863, during Morgan's Raid. The largest battle in Ohio during the war, Buffington Island contributed to the capture of the famed Confederate cavalry raider, Brig. Gen. John H. Morgan, who was seeking to escape Union army pursuers across the Ohio River at a ford opposite Buffington Island.

Henry Moses Judah was a career officer in the United States Army, serving during the Mexican–American War and American Civil War. He is most remembered for his role in helping thwart Morgan's Raid in 1863 and for leading a disastrous attack during the Battle of Resaca.
The Battle of Lebanon occurred July 5, 1863, in Lebanon, Kentucky, during Morgan's Raid in the American Civil War. Confederate troops under Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan fought for six hours to overcome the small Union garrison before moving northward, eventually riding through Kentucky, Indiana, and much of Ohio before surrendering.
The Department of the Ohio was an administrative military district created by the United States War Department early in the American Civil War to administer the troops in the Northern states near the Ohio River.

The Knoxville campaign was a series of American Civil War battles and maneuvers in East Tennessee during the fall of 1863 designed to secure control of the city of Knoxville and with it the railroad that linked the Confederacy east and west, and position the First Corps under Longstreet for return to the Army of Northern Virginia. Union Army forces under Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside occupied Knoxville, Tennessee, and Confederate States Army forces under Lt. Gen. James Longstreet were detached from Gen. Braxton Bragg's Army of Tennessee at Chattanooga to prevent Burnside's reinforcement of the besieged Federal forces there. Ultimately, Longstreet's own siege of Knoxville ended when Union Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman led elements of the Army of the Tennessee and other troops to Burnside's relief after Union troops had broken the Confederate siege of Chattanooga. Although Longstreet was one of Gen. Robert E. Lee's best corps commanders in the East in the Army of Northern Virginia, he was unsuccessful in his attempt to penetrate the Knoxville defenses and take the city.

The 80th Illinois Volunteer Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment was composed of ten companies that drew primarily from eight southern Illinois counties. Over the course of the war the regiment traveled approximately 6,000 miles, and was in over 20 battles.

Kenner Garrard was a brigadier general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. A member of one of Ohio's most prominent military families, he performed well at the Battle of Gettysburg, and then led a cavalry division in the army of Major General William T. Sherman during the Atlanta Campaign. He developed a reputation for personal bravery and was cited for gallantry at the Battle of Nashville as an infantry division commander.
The Battle of Marion was a military engagement fought between units of the Union Army and the Confederate Army during the American Civil War near the town of Marion, Virginia. The battle was part of Union Maj. Gen. George Stoneman's attack upon southwest Virginia, aimed at destroying Confederate industrial infrastructure near Saltville and Marion. Union Cavalry and Infantry regiments—some 4,500 soldiers in total—left Tennessee on December 17 for southwestern Virginia.
The 5th Regiment, Ohio Cavalry was a regiment of Union cavalry raised in seven counties in southwestern Ohio for service during the American Civil War. It primarily served in the Western Theater in several major campaigns of the Army of the Tennessee.
References
- Eicher, David J., The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War, Simon & Schuster, 2001, ISBN 0-684-84944-5.
- Stevens, Larry, 7th Ohio Cavalry, 1995.
- Civil War Soldiers and Sailors System
