Related Research Articles
The Guard Ersatz Division (Garde-Ersatz-Division) was a division of the Imperial German Army during World War I. Ersatz is German for "replacement"; the division was formed from companies of the replacement battalions (Ersatz-Bataillone) of the regiments of Prussian Guards and several other Prussian regiments. The division was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914.

The 2nd Landwehr Division was an infantry division of the Imperial German Army during World War I. It was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914 under the "Higher Landwehr Commander 2". The Landwehr was the third category of the German Army, after the regular Army and the reserves. Thus Landwehr divisions were made up of older soldiers, who had passed from the reserves and were intended primarily for occupation and security duties rather than heavy combat. However, the circumstances of war often changed this.
The 8th Landwehr Division was a unit of the Prussian/German Army. The division was formed on January 31, 1915, out of the formerly independent 56th Landwehr Infantry Brigade, which had been dissolved on January 25, 1915. The division spent the period from its formation to early 1917 mainly involved in positional warfare in Upper Alsace, after which it occupied the trenchlines near Verdun. It remained in positional warfare in this general region until the end of the war. It participated in no major battles, but was primarily suited to quieter sectors of the line. Allied intelligence rated the division as a fourth class division, though it noted that "in the attack it did fairly well, without heavy loss." The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
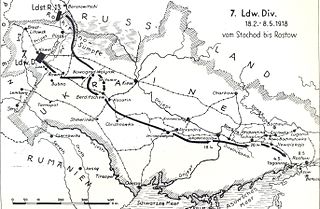
The 7th Landwehr Division was a unit of the Prussian/German Army. The division was formed on January 27, 1915, out of two formerly Mixed Landwehr Brigades. The division spent the period from its formation to early 1917 on the Western Front, mainly involved in positional warfare in Upper Alsace, after which it went to the Lorraine front. It was transferred to the Eastern Front in the Spring of 1917, where it remained after the 1917 armistice on that front. In 1918, it served on internal security missions in Ukraine, where it was located when World War I ended. Allied intelligence rated the division as a fourth class division. The division was disbanded in 1919, during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 5th Ersatz Division was a unit of the German Army, in World War I. The division was formed in June 1915 as a temporary division known as the Division Basedow, named after its commander, Heino von Basedow. It was formed from two previously independent Brigades: 37th Mixed Landwehr and 2nd Reserve Ersatz. The division was converted into the 5th Ersatz Division in June 1916. The 5th Ersatz Division was disbanded in 1919, during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 35th Reserve Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914. The division was disbanded during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division began the war as part of the central reserve of Fortress Thorn. Although designated a reserve division, initially, it was primarily composed of Landwehr units. In 1916, it was completely reorganized, receiving new brigade headquarters and newly formed regiments.
The 33rd Reserve Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914. The division was disbanded in August 1918. The division began the war as part of the central reserve of Fortress Metz.
The 77th Reserve Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed at the end of December 1914 and organized over the next month, arriving in the line in early February 1915. It was part of the second large wave of new divisions formed at the outset of World War I, which were numbered the 75th through 82nd Reserve Divisions. The division was initially part of XXXIX Reserve Corps. The division was disbanded in September 1918 and its assets distributed to other units. When originally formed, the division had two reserve infantry regiments from the Province of Westphalia and one from the Rhine Province (257th). The two Westphalian regiments were replaced late in the war by the 332nd Infantry Regiment, a garrison regiment from Posen with two Rhineland battalions and one Posen battalion, and the 419th Infantry Regiment, a thoroughly mixed unit made of companies taken from different regiments.
The 58th Infantry Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed on March 6, 1915, and organized over the next two months. It was part of a wave of new infantry divisions formed in the spring of 1915 and was originally formed from troops from the Kingdom of Saxony and the Kingdom of Württemberg, but became a fully Saxon division by 1916. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 4th Ersatz Division was a unit of the German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on mobilization of the German Army in August 1914. The division was disbanded in 1919, during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.

The 10th Ersatz Division was a unit of the German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 109th Infantry Division was a formation of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in November 1915. It was the last of a wave of new infantry divisions formed in 1915. The division was disbanded in August 1918 and its assets distributed to other units.
The 84th Infantry Division was a formation of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in November 1914 as the "Division Posen 2", part of the Posen Corps, and became the 84th Infantry Division in June 1915. It was initially formed from the garrison infantry regiments of Fortress Posen. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 85th Landwehr Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in November 1914 as the Breugel Division, named after its commander, Generalleutnant Willem Hendrick Clifford Kocq von Breugel, and became the 85th Landwehr Division on September 13, 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The Landwehr was the third category of the German Army, after the regular Army and the reserves. Thus Landwehr divisions were generally made up of older soldiers who had passed from the reserves, and were intended primarily for occupation and security duties rather than heavy combat.
The 86th Infantry Division was a formation of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in November 1914 as the Wernitz Division, named after its commander General Theodor von Wernitz, and became the 86th Infantry Division in August 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 89th Infantry Division was a formation of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in November 1914 as the provisional Westernhagen Division, named after its commander. The nucleus of the unit was troops collected at Posen. It became the 89th Infantry Division in August 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 5th Landwehr Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in October 1914 as the Waldow Division, named after its commander. It was made up primarily of Landwehr soldiers from the garrison of Metz. It became the 5th Landwehr Division in January 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 9th Landwehr Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in January 1915 as the Mühlenfels Division, named after its commander, and became the 9th Landwehr Division on February 14, 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 1st Bavarian Landwehr Division was a unit of the Bavarian Army, part of the Imperial German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on August 21, 1914, as the "Reinforced Bavarian Landwehr Division" and was also known initially as the Wening Division, named after its commander, Otto Wening. It became the 1st Bavarian Landwehr Division in September 1914. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 6th Bavarian Landwehr Division was a unit of the Bavarian Army, part of the Imperial German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on February 20, 1915. It was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. It was composed primarily of troops of the Landwehr and the Landsturm from the 1st Bavarian Corps district.
References
- Division-Posen-1 (Chronik 1914/1915) - Der erste Weltkrieg
- 83. Infanterie-Division (Chronik 1915/1918) - Der erste Weltkrieg
- Hermann Cron et al., Ruhmeshalle unserer alten Armee (Berlin, 1935)
- Hermann Cron, Geschichte des deutschen Heeres im Weltkriege 1914-1918 (Berlin, 1937)
- Günter Wegner, Stellenbesetzung der deutschen Heere 1825-1939. (Biblio Verlag, Osnabrück, 1993), Bd. 1
- Histories of Two Hundred and Fifty-One Divisions of the German Army which Participated in the War (1914-1918), compiled from records of Intelligence section of the General Staff, American Expeditionary Forces, at General Headquarters, Chaumont, France 1919 (1920)