Radionuclide therapy uses radioactive substances called radiopharmaceuticals to treat medical conditions, particularly cancer. These are introduced into the body by various means and localise to specific locations, organs or tissues depending on their properties and administration routes. This includes anything from a simple compound such as sodium iodide that locates to the thyroid via trapping the iodide ion, to complex biopharmaceuticals such as recombinant antibodies which are attached to radionuclides and seek out specific antigens on cell surfaces.
In biochemistry, biotinylation is the process of covalently attaching biotin to a protein, nucleic acid or other molecule. Biotinylation is rapid, specific and is unlikely to disturb the natural function of the molecule due to the small size of biotin. Biotin binds to streptavidin and avidin with an extremely high affinity, fast on-rate, and high specificity, and these interactions are exploited in many areas of biotechnology to isolate biotinylated molecules of interest. Biotin-binding to streptavidin and avidin is resistant to extremes of heat, pH and proteolysis, making capture of biotinylated molecules possible in a wide variety of environments. Also, multiple biotin molecules can be conjugated to a protein of interest, which allows binding of multiple streptavidin, avidin or neutravidin protein molecules and increases the sensitivity of detection of the protein of interest. There is a large number of biotinylation reagents available that exploit the wide range of possible labelling methods. Due to the strong affinity between biotin and streptavidin, the purification of biotinylated proteins has been a widely used approach to identify protein-protein interactions and post-translational events such as ubiquitylation in molecular biology.
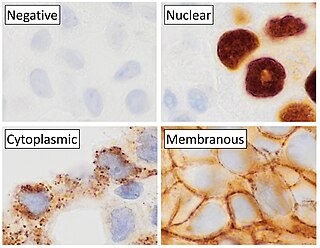
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue. Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941.

Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) describes a set of highly-related glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion. CEA is normally produced in gastrointestinal tissue during fetal development, but the production stops before birth. Consequently, CEA is usually present at very low levels in the blood of healthy adults. However, the serum levels are raised in some types of cancer, which means that it can be used as a tumor marker in clinical tests. Serum levels can also be elevated in heavy smokers.

Streptavidin is a 52 kDa protein (tetramer) purified from the bacterium Streptomyces avidinii. Streptavidin homo-tetramers have an extraordinarily high affinity for biotin. With a dissociation constant (Kd) on the order of ≈10−14 mol/L, the binding of biotin to streptavidin is one of the strongest non-covalent interactions known in nature. Streptavidin is used extensively in molecular biology and bionanotechnology due to the streptavidin-biotin complex's resistance to organic solvents, denaturants, detergents, proteolytic enzymes, and extremes of temperature and pH.

Ibritumomab tiuxetan, sold under the trade name Zevalin, is a monoclonal antibody radioimmunotherapy treatment for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The drug uses the monoclonal mouse IgG1 antibody ibritumomab in conjunction with the chelator tiuxetan, to which a radioactive isotope is added. Tiuxetan is a modified version of DTPA whose carbon backbone contains an isothiocyanatobenzyl and a methyl group.
Avidin is a tetrameric biotin-binding protein produced in the oviducts of birds, reptiles and amphibians and deposited in the whites of their eggs. Dimeric members of the avidin family are also found in some bacteria. In chicken egg white, avidin makes up approximately 0.05% of total protein (approximately 1800 μg per egg). The tetrameric protein contains four identical subunits (homotetramer), each of which can bind to biotin (Vitamin B7, vitamin H) with a high degree of affinity and specificity. The dissociation constant of the avidin-biotin complex is measured to be KD ≈ 10−15 M, making it one of the strongest known non-covalent bonds.

Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) uses an antibody labeled with a radionuclide to deliver cytotoxic radiation to a target cell. It is a form of unsealed source radiotherapy. In cancer therapy, an antibody with specificity for a tumor-associated antigen is used to deliver a lethal dose of radiation to the tumor cells. The ability for the antibody to specifically bind to a tumor-associated antigen increases the dose delivered to the tumor cells while decreasing the dose to normal tissues. By its nature, RIT requires a tumor cell to express an antigen that is unique to the neoplasm or is not accessible in normal cells.
A gallium scan is a type of nuclear medicine test that uses either a gallium-67 (67Ga) or gallium-68 (68Ga) radiopharmaceutical to obtain images of a specific type of tissue, or disease state of tissue. Gallium salts like gallium citrate and gallium nitrate may be used. The form of salt is not important, since it is the freely dissolved gallium ion Ga3+ which is active. Both 67Ga and 68Ga salts have similar uptake mechanisms. Gallium can also be used in other forms, for example 68Ga-PSMA is used for cancer imaging. The gamma emission of gallium-67 is imaged by a gamma camera, while the positron emission of gallium-68 is imaged by positron emission tomography (PET).

Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. The objective is that this treatment will stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapy a radioactive dose localizes a target cell line, delivering lethal chemical doses. Antibodies are used to bind to molecules involved in T-cell regulation to remove inhibitory pathways that block T-cell responses. This is known as immune checkpoint therapy.
Technetium (99mTc) arcitumomab is a drug used for the diagnostic imaging of colorectal cancers, marketed by Immunomedics. It consists of the Fab' fragment of a monoclonal antibody and a radionuclide, technetium-99m.
Pemtumomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody used to treat cancer. The substance has affinity to various types of cancer, like ovarian cancer and peritoneal cancer, via the polymorphic epithelial mucin and delivers the radioisotope Yttrium-90 into the tumour. As of 2009, it is undergoing Phase III clinical trials.
Epratuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody. Potential uses may be found in oncology and in treatment of inflammatory autoimmune disorders, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).

Meir Wilchek is an Israeli biochemist. He is a professor at the Weizmann Institute of Science.

DOTA (also known as tetraxetan) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2NCH2CO2H)4. The molecule consists of a central 12-membered tetraaza (i.e., containing four nitrogen atoms) ring. DOTA is used as a complexing agent, especially for lanthanide ions. Its complexes have medical applications as contrast agents and cancer treatments.
Folate targeting is a method utilized in biotechnology for drug delivery purposes. This Trojan Horse process, which was created by Drs. Christopher P. Leamon and Philip S. Low, involves the attachment of the vitamin, folate, to a molecule/drug to form a "folate conjugate". Based on the natural high affinity of folate for the folate receptor protein (FR), which is commonly expressed on the surface of many human cancers, folate-drug conjugates also bind tightly to the FR and trigger cellular uptake via endocytosis. Molecules as diverse as small radiodiagnostic imaging agents to large DNA plasmid formulations have successfully been delivered inside FR-positive cells and tissues.
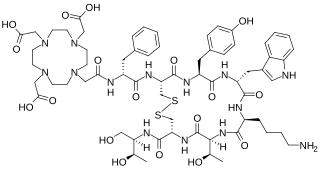
Edotreotide (USAN, also known as (DOTA0-Phe1-Tyr3) octreotide, DOTA-TOC, DOTATOC) is a substance which, when bound to various radionuclides, is used in the treatment and diagnosis of certain types of cancer. When used therapeutically it is an example of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy.
Targeted alpha-particle therapy is an in-development method of targeted radionuclide therapy of various cancers. It employs radioactive substances which undergo alpha decay to treat diseased tissue at close proximity. It has the potential to provide highly targeted treatment, especially to microscopic tumour cells. Targets include leukemias, lymphomas, gliomas, melanoma, and peritoneal carcinomatosis. As in diagnostic nuclear medicine, appropriate radionuclides can be chemically bound to a targeting biomolecule which carries the combined radiopharmaceutical to a specific treatment point.

Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is a type of radionuclide therapy, using a radiopharmaceutical that targets peptide receptors to deliver localised treatment, typically for neuroendocrine tumours (NETs).

Pretargeting (imaging) is a tool for nuclear medicine and radiotherapy. Imaging studies require a high contrast of target to background. This can be provided by using a biomarker which has a high affinity and specificity for its target.












