
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA. The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences, and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome.
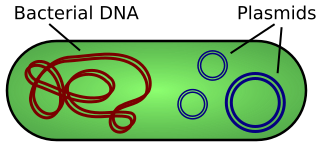
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the internet.

A transposable element is a nucleic acid sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genetic identity and genome size. Transposition often results in duplication of the same genetic material. In the human genome, L1 and Alu elements are two examples. Barbara McClintock's discovery of them earned her a Nobel Prize in 1983. Its importance in personalized medicine is becoming increasingly relevant, as well as gaining more attention in data analytics given the difficulty of analysis in very high dimensional spaces.

Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution.
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. As of 28 June 2019, approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented phenotypes; the rest represented genes, many of which were related to known phenotypes.

Acholeplasmataceae is a family of bacteria. It is the only family in the order Acholeplasmatales, placed in the class Mollicutes. The family comprises the genera Acholeplasma and Phytoplasma. Phytoplasma has the candidatus status, because members still could not be cultured.

The Genetic Information Research Institute (GIRI) is a non-profit institution that was founded in 1994 by Jerzy Jurka. The mission of the institute "is to understand biological processes which alter the genetic makeup of different organisms, as a basis for potential gene therapy and genome engineering techniques." The institute specializes in applying computer tools to analysis of DNA and protein sequence information. GIRI develops and maintains Repbase Update, a database of prototypic sequences representing repetitive DNA from different eukaryotic species, and Repbase Reports, an electronic journal established in 2001. Repetitive DNA is primarily derived from transposable elements (TEs), which include DNA transposons belonging to around 20 superfamilies and retrotransposons that can also be sub-classified into subfamilies. The majority of known superfamilies of DNA transposons were discovered or co-discovered at GIRI, including Helitron, Academ, Dada, Ginger, Kolobok, Novosib, Sola, Transib, Zator, PIF/Harbinger and Polinton/Maverick. An ancient element from the Transib superfamily was identified as the evolutionary precursor of the Recombination activating gene. GIRI has hosted three international conferences devoted to the genomic impact of eukaryotic transposable elements.
In biology, a gene cassette is a type of mobile genetic element that contains a gene and a recombination site. Each cassette usually contains a single gene and tends to be very small; on the order of 500–1000 base pairs. They may exist incorporated into an integron or freely as circular DNA. Gene cassettes can move around within an organism's genome or be transferred to another organism in the environment via horizontal gene transfer. These cassettes often carry antibiotic resistance genes. An example would be the kanMX cassette which confers kanamycin resistance upon bacteria.
Virulence factors are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens to achieve the following:

Mobile genetic elements (MGEs) sometimes called selfish genetic elements are a type of genetic material that can move around within a genome, or that can be transferred from one species or replicon to another. MGEs are found in all organisms. In humans, approximately 50% of the genome is thought to be MGEs. MGEs play a distinct role in evolution. Gene duplication events can also happen through the mechanism of MGEs. MGEs can also cause mutations in protein coding regions, which alters the protein functions. These mechanisms can also rearrange genes in the host genome generating variation. These mechanism can increase fitness by gaining new or additional functions. An example of MGEs in evolutionary context are that virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes of MGEs can be transported to share genetic code with neighboring bacteria. However, MGEs can also decrease fitness by introducing disease-causing alleles or mutations. The set of MGEs in an organism is called a mobilome, which is composed of a large number of plasmids, transposons and viruses.

The mobilome is the entire set of mobile genetic elements in a genome. Mobilomes are found in eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and viruses. The compositions of mobilomes differ among lineages of life, with transposable elements being the major mobile elements in eukaryotes, and plasmids and prophages being the major types in prokaryotes. Virophages contribute to the viral mobilome.
In Jewish tradition, the term androgynos refers to someone who possesses both male and female sexual characteristics. Due to the ambiguous nature of the individual's sex, Rabbinic literature discusses the gender of the individual and the legal ramifications that result based on potential gender classifications. In traditionally observant Judaism, gender plays a central role in legal obligations.
Gypsy (GyDB) is a wiki-style database of mobile genetic elements.
Islander is a database of integrative islands in prokaryotic genomes.
Mawes is a Papuan language of Indonesia.
The PiggyBac (PB) transposon is a mobile genetic element that efficiently transposes between vectors and chromosomes via a "cut and paste" mechanism. During transposition, the PB transposase recognizes transposon-specific inverted terminal repeat sequences (ITRs) located on both ends of the transposon vector and efficiently moves the contents from the original sites and integrates them into TTAA chromosomal sites. The powerful activity of the PiggyBac transposon system enables genes of interest between the two ITRs in the PB vector to be easily mobilized into target genomes. The TTAA-specific transposon piggyBac is rapidly becoming a highly useful transposon for genetic engineering of a wide variety of species, particularly insects. They were discovered in 1989 by Malcolm Fraser at the University of Notre Dame.
DNA transposons are DNA sequences, sometimes referred to "jumping genes", that can move and integrate to different locations within the genome. They are class II transposable elements (TEs) that move through a DNA intermediate, as opposed to class I TEs, retrotransposons, that move through an RNA intermediate. DNA transposons can move in the DNA of an organism via a single-or double-stranded DNA intermediate. DNA transposons have been found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. They can make up a significant portion of an organism's genome, particularly in eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, TE's can facilitate the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance or other genes associated with virulence. After replicating and propagating in a host, all transposon copies become inactivated and are lost unless the transposon passes to a genome by starting a new life cycle with horizontal transfer. It is important to note that DNA transposons do not randomly insert themselves into the genome, but rather show preference for specific sites.
ARGminer is database that focuses on the novel method of crowd-sourced curation over manual curation of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARG) pulled from a multiple sources such as CARD, ARDB, NDARO, DeepARG, Uniprot, ResFinder, and SARG. Additionally, due to the existence of Mobile Genetic Elements (MGE), ARGminer also interfaces with PATRIC and ACLAME. ARGminer annotated genes using their gene name, antibiotic category, resistance mechanism, evidence for mobility and occurrence in clinically important bacterial strains. There are two groups of crowd-sourced curators. One was hired on Amazon Mechanical Turk which offers a broad audience of crowd-sourced experts and non-experts that can annotate for monetary reward. Due to the presence of mixed expertise, each user is only allowed maximum 20 annotations. The other group is a graduate-level microbiology class.
Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) are mobile genetic elements present in both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In a donor cell, ICEs are located primarily on the chromosome, but have the ability to excise themselves from the genome and transfer to recipient cells via bacterial conjugation.







