Related Research Articles

The Piaggio PD.808 was an Italian business jet built by Piaggio. It was designed as a joint venture between Piaggio and Douglas Aircraft Company of Long Beach, California, United States.

The Harbin Y-11 is a high wing twin-engine piston utility and geological survey aircraft built by Harbin Aircraft Manufacturing Corporation (HAMC).
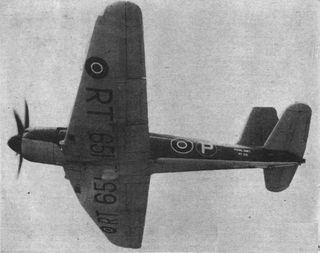
The Blackburn B.48 Firecrest, given the SBAC designation YA.1, was a single-engine naval strike fighter built by Blackburn Aircraft for service with the British Fleet Air Arm during the Second World War. It was a development of the troubled Firebrand, designed to Air Ministry Specification S.28/43, for an improved aircraft more suited to carrier operations. Three prototypes were ordered with the company designation of B-48 and the informal name of "Firecrest", but only two of them actually flew. The development of the aircraft was prolonged by significant design changes and slow deliveries of components, but the determination by the Ministry of Supply in 1946 that the airframe did not meet the requirements for a strike fighter doomed the aircraft. Construction of two of the prototypes was continued to gain flight-test data and the third was allocated to strength testing. The two flying aircraft were sold back to Blackburn in 1950 for disposal and the other aircraft survived until 1952.
The Civil Aviation Department Revathi was a light utility aircraft designed in India principally for use by that country's flying clubs.

The VSO 10 Vosa is a Standard and Club-Class glider designed and manufactured in the Czechoslovak Republic from December 1978 as a replacement for the VT-116 Orlik II.

The Malmö MFI-10 Vipan was a four-seat light utility monoplane designed and built in Sweden by Malmö Flygindustri. Only three aircraft were built and the type did not enter quantity production.

The Spencer Amphibian Air Car is an American light amphibious aircraft. The name was first used in 1940 for a prototype air vehicle that developed into the Republic Seabee. The name was later used by its designer Percival Spencer for a series of homebuilt amphibious aircraft roughly based on the Seabee design.
The Beagle B.218X was a 1960s British four-seat twin-engined light transport monoplane built by Beagle Aircraft Limited at Shoreham Airport. The prototype was modified into the Beagle B.242X but neither variant entered production.

The Ameur Altania was a single-engine light aircraft of pusher configuration with side-by-side seats for two and a V-tail, designed in France in the 1990s. Several prototypes were built and flown, including a 15 m span motorglider version; the final prototype was constructed from carbon composites rather than glass fibre. Another version, the UCA Carbon Bird has been built by Universal Composite Aviation after the bankruptcy of Ameur Aviation.

The MacFam Cavalier is a homebuilt aircraft designed by Stan McLeod, developed through a progressing series of models, all using all-wooden construction. The model range includes the SA102, SA102.5, SA103, SA104 and the SA105.
The Tisserand Hydroplum is a small amphibious aircraft with a single, pusher engine, built in France in the 1980s. Originally a single-seat, high-wing monoplane, it was developed into a two-seat biplane for production in kit form as the SMAN Pétrel.
The Procaer Cobra was a two-seat turbojet powered light aircraft designed and built in Italy and flown in the early 1960s. Only one was completed.

The Aviamilano F.14 Nibbio is a four-seat, single engine cabin monoplane built in Italy in the late 1950s. Only ten production aircraft were completed.

The Pasotti F.9 Sparviero was a four-seat, low-wing touring aircraft, built in Italy in the 1950s. Designed by Stelio Frati, it was a single-engine version of his earlier twin-engined Airone. Only one was built.

The Kawasaki KAL-2 is a Japanese four/five seat, single engine aircraft, designed for both military and civil markets in the mid-1950s. Only two were completed.

The SGP M-222 Flamingo was an Austrian twin engine, four seat light aircraft, developed with a series of prototypes into the early 1960s. There was no series production.

The Jameson RJJ-1 Gipsy Hawk was a single-engine light aircraft intended to be homebuilt from plans. The prototype was designed and constructed in the U.S. by Richard Jameson in the late 1960s-early 1970s.

The Der Kricket DK-1 is a single seat, single engine biplane designed and built in the United States in the 1970s with an emphasis on simplicity. Several were built, as intended, by amateurs from plans in addition to some constructed by the four man design consortium.
The Lambert Twin Monocoach was a light, twin-engined U.S. aircraft, designed to carry three or four passengers. Initially it was fitted with economical, low-powered engines but even given a large increase of power it failed to attract customers.

The CAMS 52 was a twin-engined floatplane torpedo-bomber. It was not ordered by the French Navy and only one CAMS 52 was completed. It first flew in the summer of 1930.
References
- ↑ Johnson, E.R. (2009). American Flying Boats and Amphibious Aircraft: An Illustrated History. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Co. pp. 353–355. ISBN 978-0786439744.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Stone, Irving (9 September 1957). "Turbofan seaplane will fly next year". Aviation Week: 131–135.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Bridgman, Leonard, ed. (1958). Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1958-59. London: Jane's All the World's Aircraft Publishing Co. Ltd. p. 250.