Related Research Articles

Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by gene duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for transcription or translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to frameshifts or premature stop codons. Pseudogenes are a type of junk DNA.

Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm.
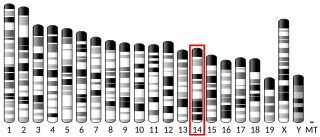
L-Gulonolactone oxidase is an enzyme that produces vitamin C, but is non-functional in Haplorrhini, in some bats, and in guinea pigs. It catalyzes the reaction of L-gulono-1,4-lactone with oxygen to form L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone (2-keto-gulono-γ-lactone) and hydrogen peroxide. It uses FAD as a cofactor. The L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone then converts to ascorbic acid spontaneously, without enzymatic action.

Actin, alpha skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTA1 gene.

Actin beta is one of six different actin isoforms which have been identified in humans. This is one of the two nonmuscle cytoskeletal actins. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha actins are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus.

Actin, cytoplasmic 2, or gamma-actin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTG1 gene. Gamma-actin is widely expressed in cellular cytoskeletons of many tissues; in adult striated muscle cells, gamma-actin is localized to Z-discs and costamere structures, which are responsible for force transduction and transmission in muscle cells. Mutations in ACTG1 have been associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss and Baraitser-Winter syndrome, as well as susceptibility of adolescent patients to vincristine toxicity.

Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 (eEF1a1) is a translation elongation protein, expressed across eukaryotes. In humans, it is encoded by the EEF1A1 gene.

Acyl-CoA-binding protein in humans belongs to the family of Acyl-CoA-binding proteins.

Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TPM3 gene.

Filamin-C (FLN-C) also known as actin-binding-like protein (ABPL) or filamin-2 (FLN2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FLNC gene. Filamin-C is mainly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscles, and functions at Z-discs and in subsarcolemmal regions.

Beta-adducin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADD2 gene.

Interleukin 9 receptor (IL9R) also known as CD129 is a type I cytokine receptor. IL9R also denotes its human gene.

Actin, gamma-enteric smooth muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTG2 gene.

Ig gamma-2 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHG2 gene.

Ig alpha-2 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHA2 gene.

60S ribosomal protein L13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL13 gene.

Gamma-crystallin A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRYGA gene.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 1 (GGT1), also known as CD224, is a human gene.

Ig gamma-4 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHG4 gene.
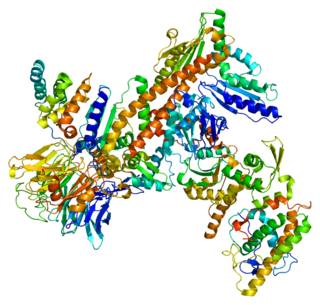
Actin-related protein 3B also known as ARP3-beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTR3B gene. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on chromosomes 2, 4, 10, 16, 22 and Y. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants and protein isoforms.
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: Actin, gamma 1 pseudogene 6" . Retrieved 2013-09-23.