
Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a viral disease of humans and livestock that can cause mild to severe symptoms. The mild symptoms may include: fever, muscle pains, and headaches which often last for up to a week. The severe symptoms may include: loss of sight beginning three weeks after the infection, infections of the brain causing severe headaches and confusion, and bleeding together with liver problems which may occur within the first few days. Those who have bleeding have a chance of death as high as 50%.

Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In about 15% of people, within a day of improving the fever comes back, abdominal pain occurs, and liver damage begins causing yellow skin. If this occurs, the risk of bleeding and kidney problems is increased.

This timeline of computer viruses and worms presents a chronological timeline of noteworthy computer viruses, computer worms, Trojan horses, similar malware, related research and events.

Antivirus software, or antivirus software, also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware.

CIH, also known as Chernobyl or Spacefiller, is a Microsoft Windows 9x computer virus which was coded with the creators first intitial and first emerged in 1998. Its payload is highly destructive to vulnerable systems, overwriting critical information on infected system drives, and in some cases destroying the system BIOS. The virus was created by Chen Ing-hau who was a student at Tatung University in Taiwan. Sixty million computers were believed to be infected by the virus internationally, resulting in an estimated US$1 billion in commercial damages.
mydoom also known as, my.doom, W32.MyDoom@mm, Novarg, Mimail.R and Shimgapi, is a computer worm affecting Microsoft Windows. It was first sighted on January 26, 2004. It became the fastest-spreading e-mail worm ever, exceeding previous records set by the Sobig worm and ILOVEYOU, a record which as of 2021 has yet to be surpassed.
Ross River virus (RRV) is a small encapsulated single-strand RNA Alphavirus endemic to Australia, Papua New Guinea and other islands in the South Pacific. It is responsible for a type of mosquito-borne non-lethal but debilitating tropical disease known as Ross River fever, previously termed "epidemic polyarthritis". The virus is suspected to be enzootic in populations of various native Australian mammals, and has been found on occasion in horses.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) is a rodent-borne viral infectious disease that presents as aseptic meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Its causative agent is lymphocytic choriomeningitis mammarenavirus (LCMV), a member of the family Arenaviridae. The name was coined by Charles Armstrong in 1934.
Mokola lyssavirus, commonly called Mokola virus (MOKV), is a RNA virus related to rabies virus that has been sporadically isolated from mammals across sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of isolates have come from domestic cats exhibiting symptoms characteristically associated to rabies virus infection.

Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a viral disease. Symptoms of CCHF may include fever, muscle pains, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding into the skin. Onset of symptoms is less than two weeks following exposure. Complications may include liver failure. In those who survive, recovery generally occurs around two weeks after onset.
Jerusalem is a logic bomb DOS virus first detected at Hebrew University of Jerusalem, in October 1987. On infection, the Jerusalem virus becomes memory resident, and then infects every executable file run, except for COMMAND.COM. COM files grow by 1,813 bytes when infected by Jerusalem and are not re-infected. Executable files grow by 1,808 to 1,823 bytes each time they are infected, and are then re-infected each time the files are loaded until they are too large to load into memory. Some .EXE files are infected but do not grow because several overlays follow the genuine .EXE file in the same file. Sometimes .EXE files are incorrectly infected, causing the program to fail to run as soon as it is executed.

Vero cells are a lineage of cells used in cell cultures. The 'Vero' lineage was isolated from kidney epithelial cells extracted from an African green monkey. The lineage was developed on 27 March 1962, by Yasumura and Kawakita at the Chiba University in Chiba, Japan. The original cell line was named "Vero" after an abbreviation of verdareno, which means "green kidney" in Esperanto, while vero itself means "truth" in Esperanto.

African swine fever virus (ASFV) is a large, double-stranded DNA virus in the Asfarviridae family. It is the causative agent of African swine fever (ASF). The virus causes a hemorrhagic fever with high mortality rates in domestic pigs; some isolates can cause death of animals as quickly as a week after infection. It persistently infects its natural hosts, warthogs, bushpigs, and soft ticks of the genus Ornithodoros, which likely act as a vector, with no disease signs. It does not cause disease in humans. ASFV is endemic to sub-Saharan Africa and exists in the wild through a cycle of infection between ticks and wild pigs, bushpigs, and warthogs. The disease was first described after European settlers brought pigs into areas endemic with ASFV, and as such, is an example of an emerging infectious disease.
Lumpy skin disease (LSD) is an infectious disease in cattle caused by a virus of the family Poxviridae, also known as Neethling virus. The disease is characterized by fever, enlarged superficial lymph nodes and multiple nodules on the skin and mucous membranes. Infected cattle also may develop edematous swelling in their limbs and exhibit lameness. The virus has important economic implications since affected animals tend to have permanent damage to their skin, lowering the commercial value of their hide. Additionally, the disease often results in chronic debility, reduced milk production, poor growth, infertility, abortion, and sometimes death.

A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses.

Zika virus is a member of the virus family Flaviviridae. It is spread by daytime-active Aedes mosquitoes, such as A. aegypti and A. albopictus. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where the virus was first isolated in 1947. Zika virus shares a genus with the dengue, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, and West Nile viruses. Since the 1950s, it has been known to occur within a narrow equatorial belt from Africa to Asia. From 2007 to 2016, the virus spread eastward, across the Pacific Ocean to the Americas, leading to the 2015–2016 Zika virus epidemic.
Usutu virus (USUV) is a flavivirus belonging to the Japanese encephalitis complex, which is an emerging zoonotic arbovirus of concern because of its pathogenicity to humans and its similarity in ecology with other emerging arboviruses such as West Nile virus. It mainly infects Culex mosquitoes and birds; humans form a dead-end host. First identified in South Africa in 1959, the virus has caused outbreaks in birds across Europe since 1996. Nearly 50 cases in humans have been reported as of 2019, mainly in Europe. These are predominantly asymptomatic, but some people experience neurological symptoms.

Shamoon, also known as W32.DistTrack, is a modular computer virus that was discovered in 2012, targeting then-recent 32-bit NT kernel versions of Microsoft Windows. The virus was notable due to the destructive nature of the attack and the cost of recovery. Shamoon can spread from an infected machine to other computers on the network. Once a system is infected, the virus continues to compile a list of files from specific locations on the system, upload them to the attacker, and erase them. Finally the virus overwrites the master boot record of the infected computer, making it unusable.

Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected—about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear.
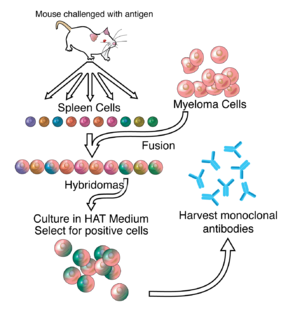
ZMapp is an experimental biopharmaceutical drug comprising three chimeric monoclonal antibodies under development as a treatment for Ebola virus disease. Two of the three components were originally developed at the Public Health Agency of Canada's National Microbiology Laboratory (NML), and the third at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases; the cocktail was optimized by Gary Kobinger, a research scientist at the NML and underwent further development under license by Mapp Biopharmaceutical. ZMapp was first used on humans during the 2014 West Africa Ebola virus outbreak, having only been previously tested on animals and not yet subjected to a randomized controlled trial. The NIH ran a clinical trial starting in January 2015 with subjects from Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Liberia aiming to enroll 200 people, but the epidemic waned and the trial closed early, leaving it too statistically underpowered to give a meaningful result about whether ZMapp worked.











