
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the target. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fabrication and in metal finishing, as well as in materials science research. The ions can alter the elemental composition of the target if they stop and remain in the target. Ion implantation also causes chemical and physical changes when the ions impinge on the target at high energy. The crystal structure of the target can be damaged or even destroyed by the energetic collision cascades, and ions of sufficiently high energy can cause nuclear transmutation.
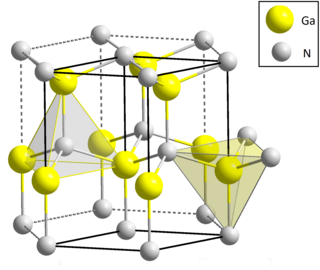
Gallium nitride is a binary III/V direct bandgap semiconductor commonly used in blue light-emitting diodes since the 1990s. The compound is a very hard material that has a Wurtzite crystal structure. Its wide band gap of 3.4 eV affords it special properties for applications in optoelectronics, high-power and high-frequency devices. For example, GaN is the substrate that makes violet (405 nm) laser diodes possible, without requiring nonlinear optical frequency doubling.

A boule is a single-crystal ingot produced by synthetic means.

The Bridgman–Stockbarger method, or Bridgman–Stockbarger technique, is named after physicist Percy Williams Bridgman (1882–1961) and physicist Donald C. Stockbarger (1895–1952). The method includes two similar but distinct techniques primarily used for growing boules, but which can be used for solidifying polycrystalline ingots as well.

Armand Paul Alivisatos is a Greek-American etymologist, chemist and academic administrator who has served as the 14th president of the University of Chicago since September 2021. He is a pioneer in nanomaterials development and an authority on the fabrication of nanocrystals and their use in biomedical and renewable energy applications. He was ranked fifth among the world's top 100 chemists for the period 2000–2010 in the list released by Thomson Reuters.

In materials science, a single crystal is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no grain boundaries. The absence of the defects associated with grain boundaries can give monocrystals unique properties, particularly mechanical, optical and electrical, which can also be anisotropic, depending on the type of crystallographic structure. These properties, in addition to making some gems precious, are industrially used in technological applications, especially in optics and electronics.

The Verneuil method, also called flame fusion, was the first commercially successful method of manufacturing synthetic gemstones, developed in the late 1883 by the French chemist Auguste Verneuil. It is primarily used to produce the ruby, sapphire and padparadscha varieties of corundum, as well as the diamond simulants rutile, strontium titanate and spinel. The principle of the process involves melting a finely powdered substance using an oxyhydrogen flame, and crystallising the melted droplets into a boule. The process is considered to be the founding step of modern industrial crystal growth technology, and remains in wide use to this day.
Soitec is an international company based in France, that manufactures substrates used in the creation of semiconductors.

Isamu Akasaki was a Japanese engineer and physicist, specializing in the field of semiconductor technology and Nobel Prize laureate, best known for inventing the bright gallium nitride (GaN) p-n junction blue LED in 1989 and subsequently the high-brightness GaN blue LED as well.
Sapphire Energy was a San Diego–based American energy company that aimed to produce crude oil with algae.
SunEdison, Inc. is a renewable energy company headquartered in the U.S. In addition to developing, building, owning, and operating solar power plants and wind energy plants, it also manufactures high-purity polysilicon, monocrystalline silicon ingots, silicon wafers, solar modules, solar energy systems, and solar module racking systems. Originally a silicon-wafer manufacturer established in 1959 as the Monsanto Electronic Materials Company, the company was sold by Monsanto in 1989.
Solyndra was a manufacturer of cylindrical panels of copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin film solar cells. It was based in Fremont, California. In 2009, the Obama administration co-signed $535 million in loans to Solyndra.
A home fuel cell or a residential fuel cell is an electrochemical cell used for primary or backup power generation. They are similar to the larger industrial stationary fuel cells, but built on a smaller scale for residential use. These fuel cells are usually based on combined heat and power (CHP) or micro combined heat and power (m-CHP) technology, generating both power and heated water or air.

Between 1992 and 2023, the worldwide usage of photovoltaics (PV) increased exponentially. During this period, it evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricity source. From 2016-2022 it has seen an annual capacity and production growth rate of around 26%- doubling approximately every three years.
Electrotherm (India) Limited (Ltd.) is an Indian technology conglomerate. Its operations span many different segments of the manufacturing and process industries, including steelmaking, foundry, heat treatment, the design and manufacturing of electric vehicles, and the energy industry. Ranging from more energy-efficient alternatives to renewable energy. It's also India's largest manufacturer of induction furnaces.
The Green Launching Pad is a public-private collaborative program developed between the University of New Hampshire and the New Hampshire Office of Energy and Planning and funded by the United States Department of Energy under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009. There are numerous goals of the initiative associated with entrepreneurial venture acceleration for individuals and businesses operating in New Hampshire to reduce environmental degradation and improve economic outlook through the creation of novel, purposeful businesses which will offer employment opportunities as they grow. The program also considers the State Energy Program and the NH Climate Action Plan in choosing which companies to endorse. From February 2010 until August 2012, the program has held three competitive rounds where entrepreneurs from around the state vied for capital rewards up to $90,000 as well as access to professional business consultants and other, community-related forms of support.

Solar Frontier Kabushiki Kaisha is a Japanese photovoltaic company that develops and manufactures thin film solar cells using CIGS technology. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Showa Shell Sekiyu and located in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The company was founded in 2006 as Showa Shell Solar, and renamed Solar Frontier in April 2010.

The Kyropoulos method, also known as the KY method or Kyropoulos technique, is a method of bulk crystal growth used to obtain single crystals.

Shaping processes in crystal growth are a collection of techniques for growing bulk crystals of a defined shape from a melt, usually by constraining the shape of the liquid meniscus by means of a mechanical shaper. Crystals are commonly grown as fibers, solid cylinders, hollow cylinders, and sheets. More complex shapes such as tubes with a complex cross section, and domes have also been produced. Using a shaping process can produce a near net shape crystal and reduce the manufacturing cost for crystals which are composed of very expensive or difficult to machine materials.






