Rfam is a database containing information about non-coding RNA (ncRNA) families and other structured RNA elements. It is an annotated, open access database originally developed at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in collaboration with Janelia Farm, and currently hosted at the European Bioinformatics Institute. Rfam is designed to be similar to the Pfam database for annotating protein families.

In molecular biology, Small Cajal body specific RNA 14 is a small nucleolar RNA found in Cajal bodies.
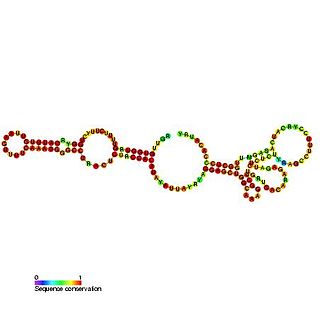
In molecular biology, U108 belongs to the H/ACA family of snoRNAs. The sequence is predicted to guide the pseudouridylation of the U372 residue in the 28S rRNA subunit. However it has not been reported as a pseudouridylation site.
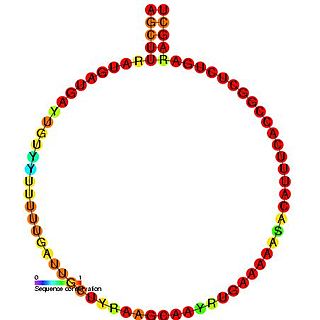
In molecular biology, snoRNA U102 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, snoRNA U103 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, U105 belongs to the C/D family of snoRNAs. It is encoded in an intron of the Peter pan homolog gene and is predicted to guide 2'O-ribose methylation of residue U799 of the small 18S rRNA subunit.
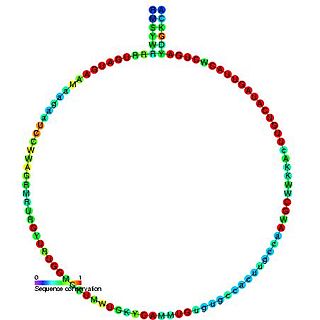
In molecular biology, snoRNA U46 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.
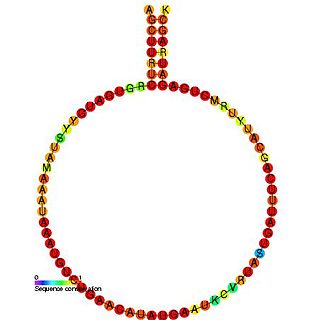
In molecular biology, SNORD72 belongs to the C/D family of snoRNAs. It is the human orthologue of the mouse MBII-240 and is predicted to guide 2'O-ribose methylation of the large 28S rRNA at residue U4590.
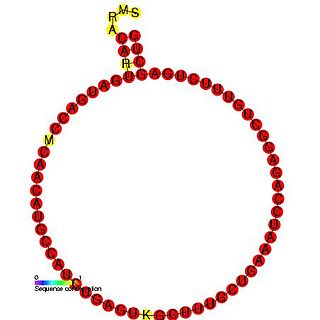
In molecular biology, snoRNA U95 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the modification of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is usually located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

In molecular biology, the small nucleolar RNAs SNORD106 and SNORD12 are two related snoRNAs which belongs to the C/D class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs). Both contain the conserved C (UGAUGA) and D (CUGA) box sequence motifs
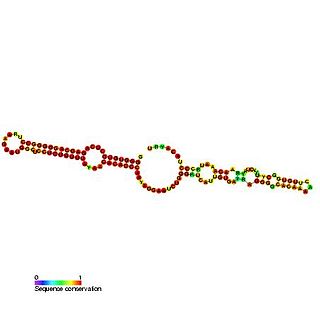
In molecular biology, small nucleolar RNA SNORA11 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA).
Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements are found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of many messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that code for proto-oncogenes, nuclear transcription factors, and cytokines. AREs are one of the most common determinants of RNA stability in mammalian cells.
This microRNA database and microRNA targets databases is a compilation of databases and web portals and servers used for microRNAs and their targets. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent an important class of small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that regulate gene expression by targeting messenger RNAs.
Competing endogenous RNAs hypothesis: ceRNAs regulate other RNA transcripts by competing for shared microRNAs. They are playing important roles in developmental, physiological and pathological processes, such as cancer. Multiple classes of ncRNAs and protein-coding mRNAs function as key ceRNAs (sponges) and to regulate the expression of mRNAs in plants and mammalian cells.
The ViennaRNA Package is a set of standalone programs and libraries used for prediction and analysis of RNA secondary structures. The source code for the package is distributed freely and compiled binaries are available for Linux, macOS and Windows platforms. The original paper has been cited over 2000 times.
Non-coding RNAs have been discovered using both experimental and bioinformatic approaches. Bioinformatic approaches can be divided into three main categories. The first involves homology search, although these techniques are by definition unable to find new classes of ncRNAs. The second category includes algorithms designed to discover specific types of ncRNAs that have similar properties. Finally, some discovery methods are based on very general properties of RNA, and are thus able to discover entirely new kinds of ncRNAs.
DIMPL is a bioinformatic pipeline that enables the extraction and selection of bacterial GC-rich intergenic regions (IGRs) that are enriched for structured non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). The method of enriching bacterial IGRs for ncRNA motif discovery was first reported for a study in "Genome-wide discovery of structured noncoding RNAs in bacteria".









