In mathematics, the classic Möbius inversion formula is a relation between pairs of arithmetic functions, each defined from the other by sums over divisors. It was introduced into number theory in 1832 by August Ferdinand Möbius.

In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution or negative exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the distance between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate; the distance parameter could be any meaningful mono-dimensional measure of the process, such as time between production errors, or length along a roll of fabric in the weaving manufacturing process. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts.
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a mechanical or electronic system during normal system operation. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (average) time between failures of a system. The term is used for repairable systems while mean time to failure (MTTF) denotes the expected time to failure for a non-repairable system.

In linear algebra, a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose. Formally,
In mathematics, particularly in linear algebra, a skew-symmetricmatrix is a square matrix whose transpose equals its negative. That is, it satisfies the condition
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Laplacian matrix, also called the graph Laplacian, admittance matrix, Kirchhoff matrix or discrete Laplacian, is a matrix representation of a graph. Named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, the graph Laplacian matrix can be viewed as a matrix form of the negative discrete Laplace operator on a graph approximating the negative continuous Laplacian obtained by the finite difference method.
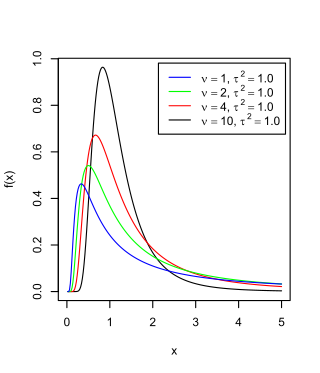
The scaled inverse chi-squared distribution, where is the scale parameter, equals the univariate inverse Wishart distribution with degrees of freedom .
In coding theory, the weight enumerator polynomial of a binary linear code specifies the number of words of each possible Hamming weight.
The System Average Interruption Duration Index (SAIDI) is commonly used as a reliability index by electric power utilities. SAIDI is the average cumulative outage duration for each customer served, and is calculated as:
The System Average Interruption Frequency Index (SAIFI) is commonly used as a reliability index by electric power utilities. SAIFI is the average number of interruptions that a customer would experience, and is calculated as
The Customer Average Interruption Duration Index (CAIDI) is a reliability index commonly used by electric power utilities. It is related to SAIDI and SAIFI, and is calculated as
In the field of mathematical modeling, a radial basis function network is an artificial neural network that uses radial basis functions as activation functions. The output of the network is a linear combination of radial basis functions of the inputs and neuron parameters. Radial basis function networks have many uses, including function approximation, time series prediction, classification, and system control. They were first formulated in a 1988 paper by Broomhead and Lowe, both researchers at the Royal Signals and Radar Establishment.
In mathematics, the Jacobsthal numbers are an integer sequence named after the German mathematician Ernst Jacobsthal. Like the related Fibonacci numbers, they are a specific type of Lucas sequence for which P = 1, and Q = −2—and are defined by a similar recurrence relation: in simple terms, the sequence starts with 0 and 1, then each following number is found by adding the number before it to twice the number before that. The first Jacobsthal numbers are:
The Momentary Average Interruption Frequency Index (MAIFI) is a reliability index used by electric power utilities. MAIFI is the average number of momentary interruptions that a customer would experience during a given period. Electric power utilities may define momentary interruptions differently, with some considering a momentary interruption to be an outage of less than 1 minute in duration while others may consider a momentary interruption to be an outage of less than 5 minutes in duration.
Krippendorff's alpha coefficient, named after academic Klaus Krippendorff, is a statistical measure of the agreement achieved when coding a set of units of analysis. Since the 1970s, alpha has been used in content analysis where textual units are categorized by trained readers, in counseling and survey research where experts code open-ended interview data into analyzable terms, in psychological testing where alternative tests of the same phenomena need to be compared, or in observational studies where unstructured happenings are recorded for subsequent analysis.
Explicit formulas for eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the second derivative with different boundary conditions are provided both for the continuous and discrete cases. In the discrete case, the standard central difference approximation of the second derivative is used on a uniform grid.
The Average Service Availability Index (ASAI) is a reliability index commonly used by electric power utilities. ASAI is calculated as
The PM (particulate matter) NowCast is a weighted average of hourly air monitoring data used by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) for real-time reporting of the Air Quality Index (AQI) for PM (PM10 - particles less than 10 micrometers, or PM2.5 - particles less than 2.5 micrometers).
The Customer Total Average Interruption Duration Index (CTAIDI) is a reliability index associated with electric power distribution. CTAIDI is the average total duration of interruption for customers who had at least one interruption during the period of analysis, and is calculated as:
Evaluation measures for an information retrieval (IR) system assess how well an index, search engine, or database returns results from a collection of resources that satisfy a user's query. They are therefore fundamental to the success of information systems and digital platforms.








