
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution or negative exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the distance between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate; the distance parameter could be any meaningful mono-dimensional measure of the process, such as time between production errors, or length along a roll of fabric in the weaving manufacturing process. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts.
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a mechanical or electronic system during normal system operation. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (average) time between failures of a system. The term is used for repairable systems while mean time to failure (MTTF) denotes the expected time to failure for a non-repairable system.
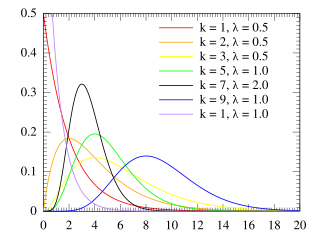
The Erlang distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with support . The two parameters are:
In finance, the duration of a financial asset that consists of fixed cash flows, such as a bond, is the weighted average of the times until those fixed cash flows are received. When the price of an asset is considered as a function of yield, duration also measures the price sensitivity to yield, the rate of change of price with respect to yield, or the percentage change in price for a parallel shift in yields.
The System Average Interruption Duration Index (SAIDI) is commonly used as a reliability index by electric power utilities. SAIDI is the average outage duration for each customer served, and is calculated as:
The System Average Interruption Frequency Index (SAIFI) is commonly used as a reliability index by electric power utilities. SAIFI is the average number of interruptions that a customer would experience, and is calculated as
The Customer Average Interruption Duration Index (CAIDI) is a reliability index commonly used by electric power utilities. It is related to SAIDI and SAIFI, and is calculated as
An index of qualitative variation (IQV) is a measure of statistical dispersion in nominal distributions. Examples include the variation ratio or the information entropy.
An outage management system (OMS) is a computer system used by operators of electric distribution systems to assist in restoration of power.
The constellation model is a probabilistic, generative model for category-level object recognition in computer vision. Like other part-based models, the constellation model attempts to represent an object class by a set of N parts under mutual geometric constraints. Because it considers the geometric relationship between different parts, the constellation model differs significantly from appearance-only, or "bag-of-words" representation models, which explicitly disregard the location of image features.
The Momentary Average Interruption Frequency Index (MAIFI) is a reliability index used by electric power utilities. MAIFI is the average number of momentary interruptions that a customer would experience during a given period. Electric power utilities may define momentary interruptions differently, with some considering a momentary interruption to be an outage of less than 1 minute in duration while others may consider a momentary interruption to be an outage of less than 5 minutes in duration.
The Customer Average Interruption Frequency Index (CAIFI) is a popular reliability index used in the reliability analysis of an electric power system. It is designed to show trends in customers interrupted and helps to show the number of customers affected out of the whole customer base.

In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time if these events occur with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event. It can also be used for the number of events in other types of intervals than time, and in dimension greater than 1.
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, the M/M/c queue is a multi-server queueing model. In Kendall's notation it describes a system where arrivals form a single queue and are governed by a Poisson process, there are c servers, and job service times are exponentially distributed. It is a generalisation of the M/M/1 queue which considers only a single server. The model with infinitely many servers is the M/M/∞ queue.
The Confirmed Line Item Performance (CLIP) is one of the diagnostic metrics for perfect order fulfillment which defines the supply chain delivery reliability measurement between facilities within a supply chain.
Krippendorff's alpha coefficient, named after academic Klaus Krippendorff, is a statistical measure of the agreement achieved when coding a set of units of analysis. Since the 1970s, alpha has been used in content analysis where textual units are categorized by trained readers, in counseling and survey research where experts code open-ended interview data into analyzable terms, in psychological testing where alternative tests of the same phenomena need to be compared, or in observational studies where unstructured happenings are recorded for subsequent analysis.
The Average Service Availability Index (ASAI) is a reliability index commonly used by electric power utilities. ASAI is calculated as
The Average Service Unavailability Index (ASUI) is a reliability index commonly used by electric power utilities. It is calculated as
Evaluation measures for an information retrieval (IR) system assess how well an index, search engine, or database returns results from a collection of resources that satisfy a user's query. They are therefore fundamental to the success of information systems and digital platforms.
Reliability index is an attempt to quantitatively assess the reliability of a system using a single numerical value. The set of reliability indices varies depending on the field of engineering, multiple different indices may be used to characterize a single system. In the simple case of an object that cannot be used or repaired once it fails, a useful index is the mean time to failure representing an expectation of the object's service lifetime. Another cross-disciplinary index is forced outage rate (FOR), a probability that a particular type of a device is out of order. Reliability indices are extensively used in the modern electricity regulation.









