Related Research Articles

A logic analyzer is an electronic instrument that captures and displays multiple logic signals from a digital system or digital circuit. A logic analyzer may convert the captured data into timing diagrams, protocol decodes, state machine traces, opcodes, or may correlate opcodes with source-level software. Logic analyzers have advanced triggering capabilities, and are useful when a user needs to see the timing relationships between many signals in a digital system.

IEEE 488, also known as HP-IB and generically as GPIB, is a short-range digital communications 8-bit parallel multi-master interface bus specification developed by Hewlett-Packard. It subsequently became the subject of several standards.

Agilent Technologies, Inc. is a global company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, that provides instruments, software, services, and consumables for laboratories. Agilent was established in 1999 as a spin-off from Hewlett-Packard. The resulting IPO of Agilent stock was the largest in the history of Silicon Valley at the time. From 1999 to 2014, the company produced optics, semiconductors, EDA software and test and measurement equipment for electronics; that division was spun off to form Keysight. Since then, the company has continued to expand into pharmaceutical, diagnostics & clinical, and academia & government (research) markets.

Electronic test equipment is used to create signals and capture responses from electronic devices under test (DUTs). In this way, the proper operation of the DUT can be proven or faults in the device can be traced. Use of electronic test equipment is essential to any serious work on electronics systems.
LAN eXtensions for Instrumentation (LXI) is a standard which defines the communication protocols for instrumentation and data acquisition systems using Ethernet.
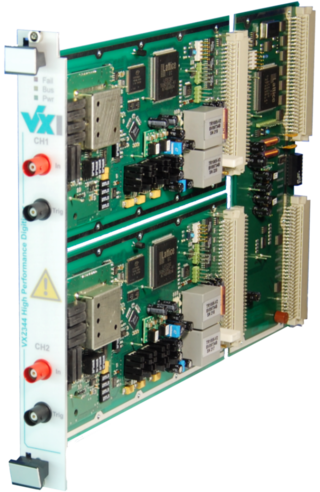
VME eXtensions for instrumentation bus refers to standards for automated test based upon VMEbus. VXI defines additional bus lines for timing and triggering as well as mechanical requirements and standard protocols for configuration, message-based communication, multi-chassis extension, and other features. In 2004, the 2eVME extension was added to the VXI bus specification, giving it a maximum data rate of 160 MB/s.

Automatic test equipment or automated test equipment (ATE) is any apparatus that performs tests on a device, known as the device under test (DUT), equipment under test (EUT) or unit under test (UUT), using automation to quickly perform measurements and evaluate the test results. An ATE can be a simple computer-controlled digital multimeter, or a complicated system containing dozens of complex test instruments capable of automatically testing and diagnosing faults in sophisticated electronic packaged parts or on wafer testing, including system on chips and integrated circuits.
SPIE is an international not-for-profit professional society for optics and photonics technology, founded in 1955. It organizes technical conferences, trade exhibitions, and continuing education programs for researchers and developers in the light-based fields of physics, including: optics, photonics, and imaging engineering. The society publishes peer-reviewed scientific journals, conference proceedings, monographs, tutorial texts, field guides, and reference volumes in print and online. SPIE is especially well-known for Photonics West, one of the laser and photonics industry's largest combined conferences and tradeshows which is held annually in San Francisco. SPIE also participates as partners in leading educational initiatives, and in 2020, for example, provided more than $5.8 million in support of optics education and outreach programs around the world.
Keysight VEE is a graphical dataflow programming software development environment from Keysight Technologies for automated test, measurement, data analysis and reporting. VEE originally stood for Visual Engineering Environment and developed by HP designated as HP VEE; it has since been officially renamed to Keysight VEE. Keysight VEE has been widely used in various industries, serving the entire stage of a product lifecycle, from design, validation to manufacturing. It is optimized in instrument control and automation with test and measurement devices such as data acquisition instruments like digital voltmeters and oscilloscopes, and source devices like signal generators and programmable power supplies.
Virtual instrument software architecture (VISA) is a widely used application programming interface (API) in the test and measurement (T&M) industry for communicating with instruments from a computer. VISA is an industry standard implemented by several T&M companies, such as, Anritsu, Bustec, Keysight Technologies, Kikusui, National Instruments, Rohde & Schwarz, and Tektronix.

PCI eXtensions for Instrumentation (PXI) is one of several modular electronic instrumentation platforms in current use. These platforms are used as a basis for building electronic test equipment, automation systems, and modular laboratory instruments.

A network analyzer is an instrument that measures the network parameters of electrical networks. Today, network analyzers commonly measure s–parameters because reflection and transmission of electrical networks are easy to measure at high frequencies, but there are other network parameter sets such as y-parameters, z-parameters, and h-parameters. Network analyzers are often used to characterize two-port networks such as amplifiers and filters, but they can be used on networks with an arbitrary number of ports.
VI Technology was a privately owned company based in Austin, Texas, that provided enterprise test solutions and services. These solutions ranged from benchtop test systems to enterprise-wide test solutions. VI Technology's main product, Arendar, was used by engineering teams in design, characterization, validation, and manufacturing. Working together with key partners, Microsoft and National Instruments, VI Technology had worked with companies from the semiconductor, communications, high-tech electronics, defense, biomedical, and automotive industries. VI Technology original corporate headquarters was located in Austin, Texas, with branch locations in Dallas, Texas, and Mountain View, California.
IEEE 1451 is a set of smart transducer interface standards developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Instrumentation and Measurement Society's Sensor Technology Technical Committee describing a set of open, common, network-independent communication interfaces for connecting transducers to microprocessors, instrumentation systems, and control/field networks. One of the key elements of these standards is the definition of Transducer electronic data sheets (TEDS) for each transducer. The TEDS is a memory device attached to the transducer, which stores transducer identification, calibration, correction data, and manufacturer-related information. The goal of the IEEE 1451 family of standards is to allow the access of transducer data through a common set of interfaces whether the transducers are connected to systems or networks via a wired or wireless means.

VTI Instruments Corporation sells precision instrumentation for electronic signal distribution, data acquisition and monitoring. The company's products are used to automate the functional testing of complex electronic systems as well as to monitor and record data that characterizes the physical integrity of aircraft, engines, and other large structures.
An instrument driver, in the context of test and measurement (T&M) application development, is a set of software routines that simplifies remote instrument control. Instrument drivers are specified by the IVI Foundation and define an I/O abstraction layer using the virtual instrument software architecture (VISA). The VISA hardware abstraction layer provides an interface-independent communication channel to T&M instruments. Furthermore, the instrument drivers encapsulate the Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments (SCPI) commands, which are an ASCII-based set of commands for reading and writing instrument settings and measurement data. This standard allows an abstract way of using various programming languages to program remote-control applications instead of using SCPI commands. An instrument driver usually has a well-defined API.

Aeroflex Inc. was an American company which produced test equipment, RF and microwave integrated circuits, components and systems used for wireless communications. Its headquarters were located in Plainview, New York. In May 2014, Aeroflex was acquired by the UK aerospace company Cobham for $1.46 billion.

Modular crate electronics are a general type of electronics and support infrastructure commonly used for trigger electronics and data acquisition in particle detectors. These types of electronics are common in such detectors because all the electronic pathways are made by discrete physical cables connecting together logic blocks on the fronts of modules. This allows circuits to be designed, built, tested, and deployed very quickly as an experiment is being put together. Then the modules can all be removed and used again when the experiment is done.
Keysight Technologies, Inc., or Keysight, is an American company that manufactures electronics test and measurement equipment and software. The name is a blend of key and insight. The company was formed as a spin-off of Agilent Technologies, which inherited and rebranded the test and measurement product lines developed and produced from the late 1960s to the turn of the millennium by Hewlett-Packard's Test & Measurement division.
References
- ↑ "AXIe Products | AXIe modular systems, including chassis and measurement modules". Keysight Technologies.
- ↑ Rick Nelson (November 11, 2009). "AXIe instrument standard emerges, but don't worry (archived at 22nd of February 2012)". Blog. Test and Measurement World. Archived from the original on February 22, 2012. Retrieved May 27, 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ Aeroflex, Inc. (June 2009). "Annual Report (Form 10K)". US Securities and Exchange Commission. Retrieved May 27, 2013.
- ↑ "Aeroflex, Agilent Technologies, and Test Evolution Propose New AXIe Test Standard" (PDF). News release. November 10, 2009. Retrieved May 27, 2013.
- ↑ Bill Schweber (November 10, 2009). "Three companies form AXIe test standard consortium". EE Times. Retrieved May 27, 2013.
- ↑ "AXIe Consortium" . Retrieved May 11, 2020.
- ↑ "AXIe Consortium and Multiple Companies Announce Optical Communication Standard for Instrumentation Systems" (PDF). AXIe Consortium. May 11, 2020.