
Abacá (Spanish), Musa textilis, is a species of banana endemic to the Philippines. The plant grows to 13–22 feet (4.0–6.7 m), and averages about 12 feet (3.7 m). The plant, also known as Manila hemp, has great economic importance, being harvested for its fiber, also called Manila hemp, extracted from the leaf-stems.
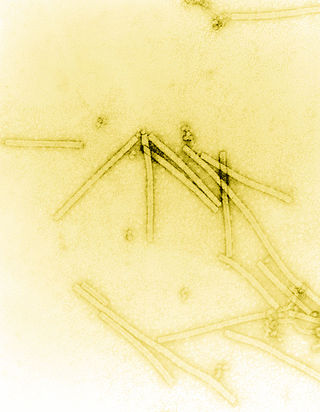
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus species in the genus Tobamovirus that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns, such as "mosaic"-like mottling and discoloration on the leaves. TMV was the first virus to be discovered. Although it was known from the late 19th century that a non-bacterial infectious disease was damaging tobacco crops, it was not until 1930 that the infectious agent was determined to be a virus. It is the first pathogen identified as a virus. The virus was crystallised by Wendell Meredith Stanley. It has a similar size to the largest synthetic molecule, known as PG5.
Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) is a member of the genus Caulimovirus, one of the six genera in the family Caulimoviridae, which are pararetroviruses that infect plants. Pararetroviruses replicate through reverse transcription just like retroviruses, but the viral particles contain DNA instead of RNA.

Plant viruses are viruses that have the potential to affect plants. Like all other viruses, plant viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that do not have the molecular machinery to replicate without a host. Plant viruses can be pathogenic to vascular plants.

Tobamovirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Virgaviridae. Many plants, including tobacco, potato, tomato, and squash, serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include: necrotic lesions on leaves. The name Tobamovirus comes from the host and symptoms of the first virus discovered.

Musa is one of three genera in the family Musaceae. The genus includes 83 species of flowering plants producing edible bananas and plantains. Though they grow as high as trees, banana and plantain plants are not woody and their apparent "stem" is made up of the bases of the huge leaf stalks. Thus, they are technically gigantic herbaceous plants.

Potyvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. Like begomoviruses, members of this genus may cause significant losses in agricultural, pastoral, horticultural, and ornamental crops. More than 200 species of aphids spread potyviruses, and most are from the subfamily Aphidinae. The genus contains 190 species and potyviruses account for about thirty percent of all currently known plant viruses.

A viroplasm, sometimes called "virus factory" or "virus inclusion", is an inclusion body in a cell where viral replication and assembly occurs. They may be thought of as viral factories in the cell. There are many viroplasms in one infected cell, where they appear dense to electron microscopy. Very little is understood about the mechanism of viroplasm formation.

Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV), also known as Lucerne mosaic virus or Potato calico virus, is a worldwide distributed phytopathogen that can lead to necrosis and yellow mosaics on a large variety of plant species, including commercially important crops. It is the only Alfamovirus of the family Bromoviridae. In 1931 Weimer J.L. was the first to report AMV in alfalfa. Transmission of the virus occurs mainly by some aphids, by seeds or by pollen to the seed.

Abacarus hystrix, the cereal rust mite or grain rust mite, belongs to the family Eriophyidae. They are extremely small with adults measuring up to 1 millimetre in length and only have four legs at the front of the body. Viewing by the human eye requires a 10 – 20X lens. The adult mites are usually yellow but also have been seen to be white or orange. The cereal rust mite was first found on Elymus repens, a very common perennial grass species. It has now been found on more than 60 grass species including oats, barley, wheat and ryegrass, found in Europe, North America, South Africa and Australia. Mites migrate primarily through wind movement and are usually found on the highest basal sections of the top two leaf blades. Abacarus hystrix produces up to twenty overlapping generations per year in South Australian perennial pastures, indicating that the species breeds quite rapidly. It has been noted that the cereal rust mite can cause losses in yield of up to 30-70%.
Banana bract mosaic virus (BBrMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Potyviridae.

Cymbidium mosaic virus (CymMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Alphaflexiviridae.

Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) is a plant pathogenic virus that occurs worldwide on species of field grown bell, hot and ornamental pepper species. It is caused by members of the plant virus genus Tobamovirus—otherwise known as the tobacco mosaic virus family. Tobamovirus are viruses that contain positive sense RNA genomes that infect plants. Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the cultivar. Typical symptoms include the chlorosis of leaves, stunting, and distorted and lumpy fruiting structures. The virus is spread by mechanical transmission and infected seeds. Avoidance is the best means of controlling the disease because once a plant is infected it cannot be treated. Only seeds that have been tested and treated for the pathogen should be planted.

Sugarcane mosaic virus (SCMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Potyviridae. The virus was first noticed in Puerto Rico in 1916 and spread rapidly throughout the southern United States in the early 1920s. SCMV is of great concern because of the high economic impact it has on sugarcane and maize.
Alternanthera mosaic virus (AltMV) is a plant pathogenic virus. AltMV belongs to the virus genus Potexvirus and the virus family Alphaflexiviridae.

Bamboo mosaic virus (BaMV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the genus Potexvirus and the family Alphaflexiviridae. BaMV is a filamentous, flexuous rod, 490 nm in length and 15 nm in width. The virus has been fully sequenced and it is 6366 nucleotides long.

Peregrinus maidis, commonly known as the corn planthopper, is a species of insect in the order Hemiptera and the family Delphacidae. It is widespread throughout most tropical and subtropical regions on earth, including southern North America, South America, Africa, Australia, Southeast Asia and China. P. maidis are a commercially important pest of maize and its relatives. In addition to physical plant damage, P. maidis is the vector for several species-specific maize viruses, including maize stripe virus, maize mosaic virus and the non-pathogenic Peregrinus maidis reovirus.
Abaca bunchy top virus (ABTV) is a pathogenic plant virus of the family Nanoviridae. ABTV has been isolated from both abacá (Musa textilis) and banana (Musa sp.). ABTV has many similarities to banana bunchy top virus (BBTV) but is both genetically and serologically distinct in that it lacks two open reading frames found in BBTV's genome. ATBV's genome contains six circular components, each of which are 1,000-1,500 base pairs in length.
Banana virus X (BVX) is a plant virus that infects members of the genus Musa. Its genome is about 2,900 nucleotides in length and contains five open reading frames that encode for a replication-associated protein, a movement-associated triple gene block and a capsid protein. A polyvalent degenerate oligonucleotide reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PDO-RT-PCR) assay has been developed to detect BVX nucleic acid in infected leaves. The virus was originally discovered in Guadeloupe.

Caulimovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. They are para-retroviruses with dsDNA and plants as their host. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: vein-clearing or banding mosaic.













