Related Research Articles
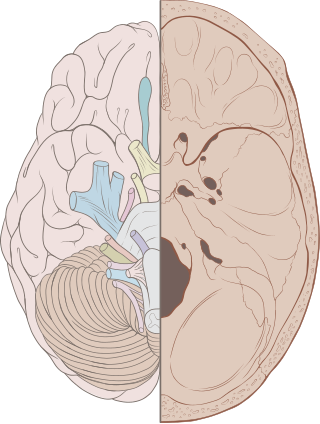
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain, of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing.

The ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna, one of the two long bones in the forearm. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

Panphobia, omniphobia, pantophobia, or panophobia is a vague and persistent dread of some unknown evil. Panphobia is not registered as a type of phobia in medical references.

Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition.

Polyneuropathy is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hands and feet and may progress to the arms and legs and sometimes to other parts of the body where it may affect the autonomic nervous system. It may be acute or chronic. A number of different disorders may cause polyneuropathy, including diabetes and some types of Guillain–Barré syndrome.
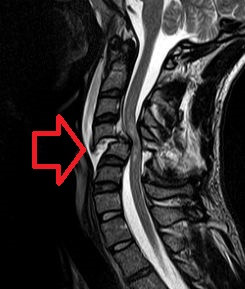
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.

A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to the subjacent vertebra to a degree less than a luxation (dislocation). Retrolistheses are most easily diagnosed on lateral x-ray views of the spine. Views where care has been taken to expose for a true lateral view without any rotation offer the best diagnostic quality.

A myotome is the group of muscles that a single spinal nerve innervates. Similarly a dermatome is an area of skin that a single nerve innervates with sensory fibers. Myotomes are separated by myosepta. In vertebrate embryonic development, a myotome is the part of a somite that develops into muscle.

Neuritis, from the Greek νεῦρον), is inflammation of a nerve or the general inflammation of the peripheral nervous system. Inflammation, and frequently concomitant demyelination, cause impaired transmission of neural signals and leads to aberrant nerve function. Neuritis is often conflated with neuropathy, a broad term describing any disease process which affects the peripheral nervous system. However, neuropathies may be due to either inflammatory or non-inflammatory causes, and the term encompasses any form of damage, degeneration, or dysfunction, while neuritis refers specifically to the inflammatory process.
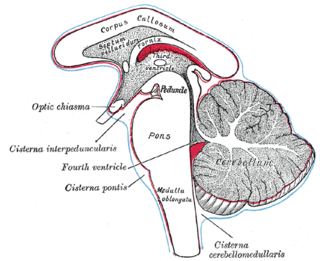
Duret haemorrhages are small linear areas of bleeding in the midbrain and upper pons of the brainstem. They are caused by a traumatic downward displacement of the brainstem.
Hypersalivation or hypersialosis is the excessive production of saliva. It has also been defined as increased amount of saliva in the mouth, which may also be caused by decreased clearance of saliva.
Dorland's is the brand name of a family of medical reference works in various media spanning printed books, CD-ROMs, and online content. The flagship products are Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary and Dorland's Pocket Medical Dictionary. The principal dictionary was first published in 1890 as the American Illustrated Medical Dictionary, including 770 pages. The pocket edition, called the American Pocket Medical Dictionary, was first published in 1898, consisting of just over 500 pages.
Focal neurologic signs also known as focal neurological deficits or focal CNS signs are impairments of nerve, spinal cord, or brain function that affects a specific region of the body, e.g. weakness in the left arm, the right leg, paresis, or plegia.
Graphesthesia is the ability to recognize writing on the skin purely by the sensation of touch. Its name derives from Greek graphē ("writing") and aisthēsis ("perception"). Graphesthesia tests combined cortical sensation; therefore, it is necessary that primary sensation be intact.
Hypohidrosis is a medical condition in which a person exhibits diminished sweating in response to appropriate stimuli. In contrast with hyperhidrosis, which is a socially troubling yet often benign condition, the consequences of untreated hypohidrosis include hyperthermia, heat stroke and death. An extreme case of hypohidrosis in which there is a complete absence of sweating and the skin is dry is termed anhidrosis. The condition is also known as adiaphoresis, ischidrosis, oligidria, oligohidrosis and sweating deficiency.
Traumatic brain injury can cause a variety of complications, health effects that are not TBI themselves but that result from it. The risk of complications increases with the severity of the trauma; however even mild traumatic brain injury can result in disabilities that interfere with social interactions, employment, and everyday living. TBI can cause a variety of problems including physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral complications.
Bruns apraxia, or frontal ataxia, is a gait apraxia found in patients with bilateral frontal lobe disorders. It is characterised by an inability to initiate the process of walking, despite the power and coordination of the legs being normal when tested in the seated or lying position. The gait is broad-based with short steps with a tendency to fall backwards. It was originally described in patients with frontal lobe tumours, but is now more commonly seen in patients with cerebrovascular disease.
The fields of Forel are areas in a deep part of the brain known as the diencephalon. They are below the thalamus and consist of three defined, white matter areas of the subthalamus. These three regions are also named "H fields":

This glossary of medical terms is a list of definitions about medicine, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.
The middle superior alveolar artery is an inconstant artery supplying the upper jaw. It is one of the three superior alveolar arteries. When present, it arises from the infraorbital artery and descends upon the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus, forming anastomotic arcades with the other two superior alveolar arteries of the same side before ending near the canine tooth. It contributes to the arterial supply to the upper/maxillary incisor and canine teeth.
References
Notes
- ↑ Dorland 2011, baragnosis
- ↑ Black 1995, pg. 14
- ↑ abarognosis, Drugs.com , retrieved 2013-03-21
- ↑ "abarognosis", The American Heritage® Stedman's Medical Dictionary , Houghton Mifflin , retrieved 2013-03-21
- ↑ Campbell 2012, pg. 554
Sources
- Black, Peter McLaren; Rossitch, Eugene (1995), "Neurological Diagnosis", Neurosurgery: An Introductory Text (Google eBook), Oxford University Press, ISBN 9780195044492 , retrieved 2013-02-21
- Buck, Carol J. (2013), "Section Index to Diseases and Injuries", 2013 ICD-9-CM for Physicians (Google preview), vol. 2 (Professional ed.), Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 9781455775033 , retrieved 2013-03-21
- Campbell, William W. (2012), "36: Sensory Localization", DeJong's The Neurologic Examination (Google eBook) (7th ed.), Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, ISBN 9781469817521 , retrieved 2013-03-21
- Dorland (2011), Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (Google eBook) (32nd ed.), Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 9781455709854 , retrieved 2013-03-21