
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac ; however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location.

Flushing is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished from blushing, since blushing is psychosomatic, milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or ears, and generally assumed to reflect emotional stress, such as embarrassment, anger, or romantic stimulation. Flushing is also a cardinal symptom of carcinoid syndrome—the syndrome that results from hormones being secreted into systemic circulation.

Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria. HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the CPOX gene, and is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, although homozygous individuals have been identified. Unlike acute intermittent porphyria, individuals with HCP can present with cutaneous findings similar to those found in porphyria cutanea tarda in addition to the acute attacks of abdominal pain, vomiting and neurological dysfunction characteristic of acute porphyrias. Like other porphyrias, attacks of HCP can be induced by certain drugs, environmental stressors or diet changes. Biochemical and molecular testing can be used to narrow down the diagnosis of a porphyria and identify the specific genetic defect. Overall, porphyrias are rare diseases. The combined incidence for all forms of the disease has been estimated at 1:20,000. The exact incidence of HCP is difficult to determine, due to its reduced penetrance.

The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals, from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a human — is usually divided into the thoracic segment, the abdominal segment, and the pelvic and perineal segments.

Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) affecting medium-sized muscular arteries, typically involving the arteries of the kidneys and other internal organs but generally sparing the lungs' circulation. Small aneurysms are strung like the beads of a rosary, therefore making this "rosary sign" an important diagnostic feature of the vasculitis. PAN is sometimes associated with infection by the hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. The condition may be present in infants.

Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesions, and itchy skin.

The iliohypogastric nerve is a nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus that supplies sensation to skin over the lateral gluteal and hypogastric regions and motor to the internal oblique muscles and transverse abdominal muscles.

The ilioinguinal nerve is a branch of the first lumbar nerve (L1). It separates from the first lumbar nerve along with the larger iliohypogastric nerve. It emerges from the lateral border of the psoas major just inferior to the iliohypogastric, and passes obliquely across the quadratus lumborum and iliacus. The ilioinguinal nerve then perforates the transversus abdominis near the anterior part of the iliac crest, and communicates with the iliohypogastric nerve between the transversus and the internal oblique muscle.

The anterior divisions of the seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, and eleventh thoracic intercostal nerves are continued anteriorly from the intercostal spaces into the abdominal wall; hence they are named thoraco-abdominal nerves.

Angiolipoma is a subcutaneous nodule with vascular structure, having all other features of a typical lipoma. They are commonly painful. Angiolipomas manifest as multiple painful subcutaneous nodules commonly on the upper limbs. The can occur sporadically, with a family history or after trauma. Angiolipomas can be seen on CT scans and MRI but are diagnosed based of histopathology. Total excision or liposuction is used to treat angiolipomas. They are more common in med and usually appear in third and second decades of life.
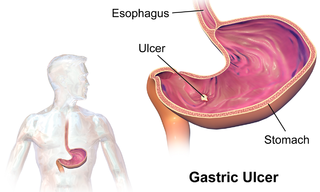
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing out of inflamed necrotic tissue." Common forms of ulcers recognized in medicine include:
Cutaneous endometriosis is characterized by the appearance of papules at the umbilicus or in lower abdominal scars after gynecologic surgery in middle-aged women. The size averages to 2 cm in diameter. Its colour ranges from blue to violet, brown or skin-coloured.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV) is inflammation of small blood vessels, usually accompanied by small lumps beneath the skin. The condition is also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis,
Urticarial vasculitis is a skin condition characterized by fixed urticarial lesions that appear histologically as a vasculitis.
Cobb syndrome is a rare congenital disorder characterized by visible skin lesions and spinal angiomas or arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). The skin lesions of Cobb syndrome typically are present as port wine stains or angiomas, but reports exist of angiokeratomas, angiolipomas, and lymphangioma circumscriptum. The intraspinal lesions may be angiomas or AVMs and occur at levels of the spinal cord corresponding to the affected skin dermatomes. They may in turn produce spinal cord dysfunction and weakness or paralysis.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:

Spiradenomas (SA) are rare, benign cutaneous adnexal tumors that may progress to become their malignant counterparts, i.e. spiradenocarcinomas (SAC). Cutaneous adnexal tumors are a group of skin tumors consisting of tissues that have differentiated towards one of the four primary adnexal structures found in normal skin: hair follicles, sebaceous sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and eccrine sweat glands. SA and SAC tumors were regarded as eccrine gland tumors and termed eccrine spiradenomas and eccrine spiradenocarcinomas, respectively. However, more recent studies have found them to be hair follicle tumors and commonly term them spiradenomas and spiradenocarcinomas, respectively. Further confusing the situation, SA-like and SAC-like tumors are also 1) manifestations of the inherited disorder, CYLD cutaneous syndrome (CCS), and 2) have repeatedly been confused with an entirely different tumor, adenoid cystic carcinomas of the salivary gland. Here, SA and SAC are strictly defined as sporadic hair follicle tumors that do not include the hereditary CCS spiradenomas and heridtary spiradenocarcinoms of CCS or the adenoid cystic carcinomas.

Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC) or Reed's syndrome is rare autosomal dominant disorder associated with benign smooth muscle tumors and an increased risk of renal cell carcinoma. It is characterised by multiple cutaneous leiomyomas and, in women, uterine leiomyomas. It predisposes individuals to renal cell cancer, an association denominated hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer. It is also associated with increased risk of uterine leiomyosarcoma. The syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fumarate hydratase gene, which leads to an accumulation of fumarate. The inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant and screening can typically begin in childhood.














