
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating exposures to toxins and toxicants. The relationship between dose and its effects on the exposed organism is of high significance in toxicology. Factors that influence chemical toxicity include the dosage, duration of exposure, route of exposure, species, age, sex, and environment. Toxicologists are experts on poisons and poisoning. There is a movement for evidence-based toxicology as part of the larger movement towards evidence-based practices. Toxicology is currently contributing to the field of cancer research, since some toxins can be used as drugs for killing tumor cells. One prime example of this is ribosome-inactivating proteins, tested in the treatment of leukemia.

Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution, patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
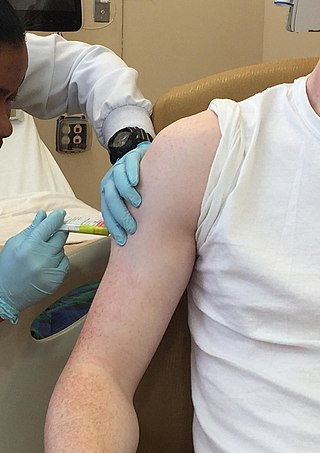
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted.
A cohort study is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort, performing a cross-section at intervals through time. It is a type of panel study where the individuals in the panel share a common characteristic.

Sir Austin Bradford Hill was an English epidemiologist who pioneered the modern randomised clinical trial and, together with Richard Doll, demonstrated the connection between cigarette smoking and lung cancer. Hill is widely known for pioneering the "Bradford Hill" criteria for determining a causal association.

Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center is a cancer research and treatment center located in Buffalo, New York. Founded by surgeon Roswell Park in 1898, the center was the first in the United States to specifically focus on cancer research. The center is usually called Roswell Park in short. The center, which conducts clinical research on cancer as well as the development new drugs, provides advanced treatment for all forms of adult and pediatric cancer, and serves as a member of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center is as of 2019, the only upstate New York facility to hold the National Cancer Institute designation of "comprehensive cancer center".
Medical statistics deals with applications of statistics to medicine and the health sciences, including epidemiology, public health, forensic medicine, and clinical research. Medical statistics has been a recognized branch of statistics in the United Kingdom for more than 40 years, but the term has not come into general use in North America, where the wider term 'biostatistics' is more commonly used. However, "biostatistics" more commonly connotes all applications of statistics to biology. Medical statistics is a subdiscipline of statistics.
It is the science of summarizing, collecting, presenting and interpreting data in medical practice, and using them to estimate the magnitude of associations and test hypotheses. It has a central role in medical investigations. It not only provides a way of organizing information on a wider and more formal basis than relying on the exchange of anecdotes and personal experience, but also takes into account the intrinsic variation inherent in most biological processes.
A glossary of terms used in clinical research.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to clinical research:

Centrum is an American brand of multivitamins produced by Haleon. It was previously owned by Pfizer and GSK.

JoAnn Elisabeth Manson is an American physician and professor known for her pioneering research, public leadership, and advocacy in the fields of epidemiology and women's health.
David M. Eddy is an American physician, mathematician, and healthcare analyst who has done seminal work in mathematical modeling of diseases, clinical practice guidelines, and evidence-based medicine. Four highlights of his career have been summarized by the Institute of Medicine of the National Academy of Sciences: "more than 25 years ago, Eddy wrote the seminal paper on the role of guidelines in medical decision-making, the first Markov model applied to clinical problems, and the original criteria for coverage decisions; he was the first to use and publish the term 'evidence-based'."
The discipline of evidence-based toxicology (EBT) strives to transparently, consistently, and objectively assess available scientific evidence in order to answer questions in toxicology, the study of the adverse effects of chemical, physical, or biological agents on living organisms and the environment, including the prevention and amelioration of such effects. EBT has the potential to address concerns in the toxicological community about the limitations of current approaches to assessing the state of the science. These include concerns related to transparency in decision making, synthesis of different types of evidence, and the assessment of bias and credibility. Evidence-based toxicology has its roots in the larger movement towards evidence-based practices.
Marvin Zelen was Professor Emeritus of Biostatistics in the Department of Biostatistics at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (HSPH), and Lemuel Shattuck Research Professor of Statistical Science. During the 1980s, Zelen chaired HSPH's Department of Biostatistics. Among colleagues in the field of statistics, he was widely known as a leader who shaped the discipline of biostatistics. He "transformed clinical trial research into a statistically sophisticated branch of medical research."
Susan S. Ellenberg is an American statistician specializing in the design of clinical trials and in the safety of medical products. She is a professor of biostatistics, medical ethics and health policy in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. She was the 1993 president of the Society for Clinical Trials and the 1999 President of the Eastern North American Region of the International Biometric Society.

Bhramar Mukherjee is an Indian-American biostatistician, data scientist, professor and researcher. She is currently serving as the inaugural Senior Associate Dean of Public Health Data Science and Data Equity at the Yale School of Public Health from August 1, 2024. She is also appointed as Anna MR Lauder Professor of Biostatistics, Professor of Epidemiology with secondary appointment as Professor of Statistics and Data Science at Yale University.

Lori Elizabeth Dodd is an American mathematical statistician specializing in clinical trials methodology, statistical analysis of genomic data, design of clinical trials using biomarkers and imaging modalities, and statistical methods for analyzing biomarkers. She is a statistician in the biostatistics research branch at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Threshold dose is the minimum dose of drug that triggers minimal detectable biological effect in an animal. At extremely low doses, biological responses are absent for some of the drugs. The increase in dose above threshold dose induces an increase in the percentage of biological responses. Several benchmarks have been established to describe the effects of a particular dose of drug in a particular species, such as NOEL(no-observed-effect-level), NOAEL(no-observed-adverse-effect-level) and LOAEL(lowest-observed-adverse-effect-level). They are established by reviewing the available studies and animal studies. The application of threshold dose in risk assessment safeguards the participants in human clinical trials and evaluates the risks of chronic exposure to certain substances. However, the nature of animal studies also limits the applicability of experimental results in the human population and its significance in evaluating potential risk of certain substances. In toxicology, there are some other safety factors including LD50, LC50 and EC50.








