Related Research Articles

The Dutch West India Company or WIC was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors, formally known as GWC. Among its founders were Reynier Pauw, Willem Usselincx (1567–1647), and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was granted a charter for a trade monopoly in the Dutch West Indies by the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands and given jurisdiction over Dutch participation in the Atlantic slave trade, Brazil, the Caribbean, and North America.

The Dutch began their colonisation of the Guianas, the coastal region between the Orinoco and Amazon rivers in South America, in the late 16th century. The Dutch originally claimed all of Guiana but—following attempts to sell it first to Bavaria and then to Hanau and the loss of sections to Portugal, Britain, and France—the section actually settled and controlled by the Netherlands became known as Dutch Guiana.
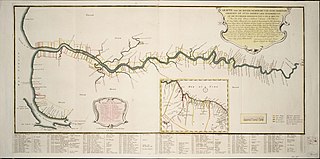
Demerara is a historical region in the Guianas, on the north coast of South America, now part of the country of Guyana. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1745 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Essequibo in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana until 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Demerara River, and its main settlement was Georgetown.

Cuffy, also known as Kofi Badu, also spelled as Coffy, Cuffy, Kofi, or Koffi, was an Akan man who was captured in his native West Africa and stolen for slavery to work on the plantations of the Dutch colony of Berbice in present-day Guyana. In 1763, he led a major slave revolt of more than 3,800 slaves against the colonial regime. Today, he is a national hero in Guyana.

Arguin is an island off the western coast of Mauritania in the Bay of Arguin. It is approximately 6 km × 2 km in size, with extensive and dangerous reefs around it. The island is now part of the Banc d'Arguin National Park.

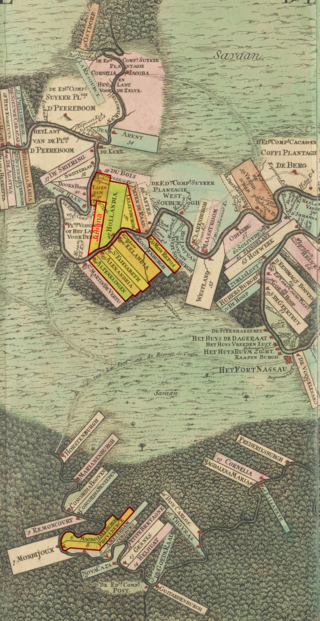
Berbice is a region along the Berbice River in Guyana, which was between 1627 and 1792 a colony of the Dutch West India Company and between 1792 and 1815 a colony of the Dutch state. After having been ceded to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in the latter year, it was merged with Demerara-Essequibo to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. It became a county of British Guiana in 1838 till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana.

Essequibo was a Dutch colony in the Guianas and later a county on the Essequibo River in the Guiana region on the north coast of South America. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1616 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Demerara in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Essequibo River.

Dutch Brazil, also known as New Holland, was a colony of the Dutch Republic in the northeastern portion of modern-day Brazil, controlled from 1630 to 1654 during Dutch colonization of the Americas. The main cities of the colony were the capital Mauritsstad, Frederikstadt, Nieuw Amsterdam (Natal), Saint Louis, São Cristóvão, Fort Schoonenborch (Fortaleza), Sirinhaém, and Olinda.

The Colony of Demerara-Essequibo was created on 28 April 1812, when the British combined the colonies of Demerara and Essequibo into the colony of Demerara-Essequibo. They were officially ceded to Britain on 13 August 1814. On 20 November 1815 the agreement was ratified by the Netherlands. On 21 July 1831 Demerara-Esequibo united with Berbice as British Guiana.
The Berbice Rebellion was a slave rebellion in Guyana that began on 23 February 1763 and lasted to December, with leaders including Coffij. The first major slave revolt in South America, it is seen as a major event in Guyana's anti-colonial struggles, and when Guyana became a republic in 1970 the state declared 23 February as a day to commemorate the start of the Berbice slave revolt.
Jan van Ryen was a 17th-century Dutch privateer, explorer, and colonist. He was granted a commission by the Dutch West Indies Company and active against the Spanish in the West Indies during the 1620s. He and Claude Prevost attempted to establish Dutch colonies in Guyana, although they both failed with most Dutch colonists being killed by natives in 1627. However, Zeelandian merchant Abraham van Peere was able to found a successful colony in the area shortly after.

The Cassard expedition was a sea voyage by French Navy captain Jacques Cassard in 1712, during the War of the Spanish Succession. Targeting English, Dutch, and Portuguese possessions, he raided and ransomed the colonies of Cape Verde, Sint Eustatius, and Curaçao—factories, depots, and seasoning camps used in the Atlantic slave trade. He also raided and ransomed Montserrat, Antigua, Surinam, Berbice, and Essequibo—wealthy sugar-producing colonies in the Caribbean whose economies were based on the exploitation of slave labor.

Fort Nassau was the capital of the Dutch colony of Berbice, in present-day Guyana. It was situated on the Berbice River approximately 88 kilometres upstream from New Amsterdam.
The Society of Berbice was founded on 24 October 1720 by the owners of the colony of Berbice currently in Guyana. These owners had acquired the colony from the French on 24 October 1714, who in turn had occupied the colony which was previously a hereditary fief in the possession of the Van Peere family.

Pomeroon is the name of a former Dutch plantation colony on the Pomeroon River in the Guyana region on the north coast of South America. After early colonization attempts in the late 16th century were attacked by Spaniards and local Indians, the original inhabitants fled the interior of Guyana, founding the colony of Essequibo around Fort Kyk-Over-Al shortly after. A second, and more serious attempt at colonization started in 1650, but was ultimately unsuccessful, as French privateers destroyed the colony in 1689. In the late 18th century, a third attempt of colonization was started, this time under the jurisdiction of the Essequibo colony.

Suriname was a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands between 1954 and 1975. The country had full autonomy, except in areas of defence and foreign policy, and participated on a basis of equality with the Netherlands Antilles and the Netherlands itself in the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The country became fully independent as the Republic of Suriname on 25 November 1975.

Surinam, also unofficially known as Dutch Guiana, was a Dutch plantation colony in the Guianas, bordered by the equally Dutch colony of Berbice to the west, and the French colony of Cayenne to the east. It later bordered British Guiana from 1831 to 1966.

Laurens Storm van's Gravesande was a Dutch governor of the colonies of Essequibo and Demerara from 1743 to 1772. He turned Demerara in a successful plantation colony, and the borders of Guyana are mainly based on his expeditions into the interior. He is also noted for his treatment of the Amerindians.
Borsselen is an island in the Demerara River of Guyana, and was the capital of Demerara between 1755 and 1782.
Wolfert Simon van Hoogenheim was a Dutch States Army officer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of Berbice from 1760 to 1764. During his tenure as governor, the Berbice Rebellion took place.
References
- van Groesen, Michiel (2019). Imagining the Americas in Print. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-34803-5 . Retrieved 2024-10-07.
- Hartsinck, J.J. (1770), Beschryving van Guiana, of de wilde kust in Zuid-America, Amsterdam: Gerrit Tielenburg