Related Research Articles

The Coptic Orthodox Church, also known as the Coptic Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian church based in Egypt, servicing Africa and the Middle East. The head of the church and the See of Alexandria is the Pope of Alexandria on the Holy Apostolic See of Saint Mark, who also carries the title of Father of fathers, Shepherd of Shepherds, Ecumenical Judge and the thirteenth among the Apostles. The See of Alexandria is titular, and today the Coptic Pope presides from Saint Mark's Coptic Orthodox Cathedral in the Abbassia District in Cairo. The church follows the Coptic Rite for its liturgy, prayer and devotional patrimony. With approximately 25 million members worldwide, it is the country's largest Christian denomination.

The history of Islam concerns the political, social, economic, military, and cultural developments of the Islamic civilization. Most historians believe that Islam originated in Mecca and Medina at the start of the 7th century CE. Muslims regard Islam as a return to the original faith of the Abrahamic prophets, such as Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, David, Solomon, and Jesus, with the submission (Islām) to the will of God.

The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital.
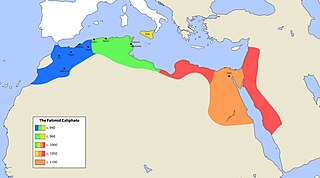
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shia caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dynasty of Arab origin, trace their ancestry to Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband ‘Ali b. Abi Talib, the first Shi‘ite imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma‘ili communities, but also in many other Muslim lands, including Persia and the adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Tunisia and established the city of "al-Mahdiyya". The Ismaili dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast of Africa and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included – in addition to Egypt – varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hijaz.
Shura can for example take the form of a council or a referendum. The Quran encourages Muslims to decide their affairs in consultation with each other.

The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church is the largest of the Oriental Orthodox Churches. One of the few Christian churches in sub-Saharan Africa originating before European colonization of the continent, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church dates back centuries, and has a current membership of about 36 million people, the majority of whom live in Ethiopia. It is a founding member of the World Council of Churches. The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church is in communion with the other Oriental Orthodox churches.

The Al-Azhar University is a public university in Cairo, Egypt. Associated with Al-Azhar Mosque in Islamic Cairo, it is Egypt's oldest degree-granting university – and the world's second oldest degree granting university – and is renowned as the most prestigious university for Islamic learning. In addition to higher education, Al-Azhar oversees a national network of schools with approximately two million students. As of 1996, over 4,000 teaching institutes in Egypt were affiliated with the university.

Following the Islamic conquest in 639, Lower Egypt was ruled at first by governors acting in the name of the Rashidun Caliphs and then the Umayyad Caliphs in Damascus, but in 747 the Umayyads were overthrown. Throughout the Islamic rule, Askar was named the capital and housed the ruling administration. The conquest led to two separate provinces all under one ruler: Upper and Lower Egypt. These two very distinct regions would be heavily governed by the military and followed the demands handed down by the governor of Egypt and imposed by the heads of their communities.

Kairouan, also spelled Al Qayrawān or Kairwan, is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by the Umayyads around 670, in the period of Caliph Mu'awiya ; this is when it became an important centre for Sunni Islamic scholarship and Quranic learning, attracting Muslims from various parts of the world, next only to Mecca, Medina and Jerusalem. The Mosque of Uqba is situated in the city.
Pope Cyril II of Alexandria, 67th Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark.
Cyril III, known as Cyril ibn Laqlaq, was the 75th Coptic Pope and Patriarch of Alexandria.
Pope John V of Alexandria, 72nd Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark. He was initially a monk in the Monastery of Saint John the Dwarf in Scetes. He was enthroned as a Pope of Alexandria on the second day of Pi Kogi Enavot, 863 A.M..
Abuna is the honorific title used for any bishop of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church as well as of the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church. It was historically used solely for the head of the Coptic Orthodox Church in Ethiopia during the more than 1000 years when the Coptic Patriarchate of Alexandria appointed only one bishop at a time to serve its Ethiopian flock. When referred to without a name following, it is Abun, and if a name follows, it becomes Abuna.

Al-Ahbash, also known as the Association of Islamic Charitable Projects is a neo-traditionalist Sufi religious movement which was founded in the mid-1980s. The group follow the teachings of Ethiopian scholar Abdullah al-Harari. Due to the group's origins and activity in Lebanon, the Ahbash have been described as the "activist expression of Lebanese Sufism."
Ethiopian ecclesiastical titles refers to the offices of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, a hierarchical organization. Some of the more important offices are unique to it.

Abuna Basilios was an Ethiopian-born first Archbishop or Abuna, and later the first Patriarch, of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church.

Al-Azhar Mosque, known in Egypt simply as al-Azhar, is a mosque in Cairo, Egypt in the historic Islamic core of the city. Commissioned by Jawhar al-Siqilli shortly after Cairo was established as the new capital of the Fatimid Caliphate in 970, it was the first mosque established in a city that eventually earned the nickname "the City of a Thousand Minarets". Its name is usually thought to derive from az-Zahrāʾ, a title given to Fatimah, the daughter of Muhammad.

Orthodox Tewahedo is the common and historical name of the Oriental Orthodox church in the former Ethiopian Empire, that would later become the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo and Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo churches. Until 1959, the Orthodox Tewahedo were administratively part of the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria. The church was granted autocephaly and its own patriarch that year by Pope Cyril VI of Alexandria. Following Eritrean independence from Ethiopia in 1993, the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church became autocephalous through Pope Shenouda III of Alexandria and it officially separated from what is now the distinct Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church.
Abuna Yohannes was an Abuna, or head of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church in the 14th century, during the reign of Emperor Amda Seyon. He was accused of simony by a group of Ethiopian clergy at the Royal Court.
Bartalomewos of Ethiopia was an Abuna, or head of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church from 1398/99 to sometime after 1434; he succeeded Abuna Salama II. His tenure was a period marked by a series of doctrinal disputes in the Church, and at one point Bartalomewos was accused of denying the threefold nature of the Holy Trinity. Emperor Yishaq appointed a committee to investigate this serious charge, whose members included graduates of the school at Istifanos Monastery in Lake Hayq.