Related Research Articles
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to linguistics:
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Typically data is collected in text corpora, using either rule-based, statistical or neural-based approaches in machine learning and deep learning.
Template:Short description Group of words Template:Unreferenced section date=May 2023
In the study of language, description or descriptive linguistics is the work of objectively analyzing and describing how language is actually used by a speech community.
Cognitive linguistics is an interdisciplinary branch of linguistics, combining knowledge and research from cognitive science, cognitive psychology, neuropsychology and linguistics. Models and theoretical accounts of cognitive linguistics are considered as psychologically real, and research in cognitive linguistics aims to help understand cognition in general and is seen as a road into the human mind.
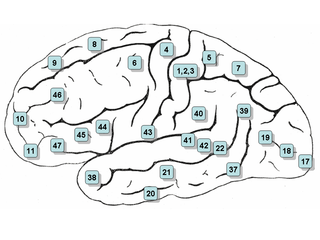
Neurolinguistics is the study of neural mechanisms in the human brain that control the comprehension, production, and acquisition of language. As an interdisciplinary field, neurolinguistics draws methods and theories from fields such as neuroscience, linguistics, cognitive science, communication disorders and neuropsychology. Researchers are drawn to the field from a variety of backgrounds, bringing along a variety of experimental techniques as well as widely varying theoretical perspectives. Much work in neurolinguistics is informed by models in psycholinguistics and theoretical linguistics, and is focused on investigating how the brain can implement the processes that theoretical and psycholinguistics propose are necessary in producing and comprehending language. Neurolinguists study the physiological mechanisms by which the brain processes information related to language, and evaluate linguistic and psycholinguistic theories, using aphasiology, brain imaging, electrophysiology, and computer modeling.

Zellig Sabbettai Harris was an influential American linguist, mathematical syntactician, and methodologist of science. Originally a Semiticist, he is best known for his work in structural linguistics and discourse analysis and for the discovery of transformational structure in language. These developments from the first 10 years of his career were published within the first 25. His contributions in the subsequent 35 years of his career include transfer grammar, string analysis, elementary sentence-differences, algebraic structures in language, operator grammar, sublanguage grammar, a theory of linguistic information, and a principled account of the nature and origin of language.
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is the process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar. The term parsing comes from Latin pars (orationis), meaning part.

Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists, tend to share certain working assumptions such as the competence–performance distinction and the notion that some domain-specific aspects of grammar are partly innate in humans. These assumptions are rejected in non-generative approaches such as usage-based models of language. Generative linguistics includes work in core areas such as syntax, semantics, phonology, psycholinguistics, and language acquisition, with additional extensions to topics including biolinguistics and music cognition.
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general principles and specific parameters that for particular languages are either turned on or off. For example, the position of heads in phrases is determined by a parameter. Whether a language is head-initial or head-final is regarded as a parameter which is either on or off for particular languages. Principles and parameters was largely formulated by the linguists Noam Chomsky and Howard Lasnik. Many linguists have worked within this framework, and for a period of time it was considered the dominant form of mainstream generative linguistics.

Syntactic Structures is an important work in linguistics by American linguist Noam Chomsky, originally published in 1957. A short monograph of about a hundred pages, it is recognized as one of the most significant and influential linguistic studies of the 20th century. It contains the now-famous sentence "Colorless green ideas sleep furiously", which Chomsky offered as an example of a grammatically correct sentence that has no discernible meaning, thus arguing for the independence of syntax from semantics.
In linguistics, linguistic competence is the system of unconscious knowledge that one knows when they know a language. It is distinguished from linguistic performance, which includes all other factors that allow one to use one's language in practice.
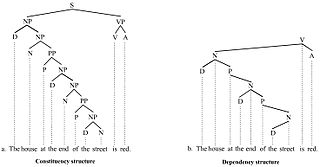
In linguistics, a treebank is a parsed text corpus that annotates syntactic or semantic sentence structure. The construction of parsed corpora in the early 1990s revolutionized computational linguistics, which benefitted from large-scale empirical data.
Artificial grammar learning (AGL) is a paradigm of study within cognitive psychology and linguistics. Its goal is to investigate the processes that underlie human language learning by testing subjects' ability to learn a made-up grammar in a laboratory setting. It was developed to evaluate the processes of human language learning but has also been utilized to study implicit learning in a more general sense. The area of interest is typically the subjects' ability to detect patterns and statistical regularities during a training phase and then use their new knowledge of those patterns in a testing phase. The testing phase can either use the symbols or sounds used in the training phase or transfer the patterns to another set of symbols or sounds as surface structure.
The term linguistic performance was used by Noam Chomsky in 1960 to describe "the actual use of language in concrete situations". It is used to describe both the production, sometimes called parole, as well as the comprehension of language. Performance is defined in opposition to "competence"; the latter describes the mental knowledge that a speaker or listener has of language.
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the goal of which is to formulate rules that define well-formed, grammatical sentences. These rules of grammaticality also provide explanations of ill-formed, ungrammatical sentences.
A stochastic grammar is a grammar framework with a probabilistic notion of grammaticality:
Indirect memory tests assess the retention of information without direct reference to the source of information. Participants are given tasks designed to elicit knowledge that was acquired incidentally or unconsciously and is evident when performance shows greater inclination towards items initially presented than new items. Performance on indirect tests may reflect contributions of implicit memory, the effects of priming, a preference to respond to previously experienced stimuli over novel stimuli. Types of indirect memory tests include the implicit association test, the lexical decision task, the word stem completion task, artificial grammar learning, word fragment completion, and the serial reaction time task.

Aspects of the Theory of Syntax is a book on linguistics written by American linguist Noam Chomsky, first published in 1965. In Aspects, Chomsky presented a deeper, more extensive reformulation of transformational generative grammar (TGG), a new kind of syntactic theory that he had introduced in the 1950s with the publication of his first book, Syntactic Structures. Aspects is widely considered to be the foundational document and a proper book-length articulation of Chomskyan theoretical framework of linguistics. It presented Chomsky's epistemological assumptions with a view to establishing linguistic theory-making as a formal discipline comparable to physical sciences, i.e. a domain of inquiry well-defined in its nature and scope. From a philosophical perspective, it directed mainstream linguistic research away from behaviorism, constructivism, empiricism and structuralism and towards mentalism, nativism, rationalism and generativism, respectively, taking as its main object of study the abstract, inner workings of the human mind related to language acquisition and production.
In linguistics, the term near-native speakers is used to describe speakers who have achieved "levels of proficiency that cannot be distinguished from native levels in everyday spoken communication and only become apparent through detailed linguistic analyses" (p. 484) in their second language or foreign languages. Analysis of native and near-native speakers indicates that they differ in their underlying grammar and intuition, meaning that they do not interpret grammatical contrasts the same way. However, this divergence typically does not impact a near-native speaker's regular usage of the language.
References
- ↑ Weskott, T. & Fanselow, G. (2011):On the informativity of different measures of linguistic acceptability. In: Language, 87(2), 249-273.