Related Research Articles

Boniface, OSB was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of the church in Germany and was made bishop of Mainz by Pope Gregory III. He was martyred in Frisia in 754, along with 52 others, and his remains were returned to Fulda, where they rest in a sarcophagus which remains a site of Christian pilgrimage.

Austrasia was a territory which formed the north-eastern section of the Kingdom of the Franks from the 6th to 8th centuries, ruled by the Frankish Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties during the Early Middle Ages. It was centred on the Meuse, Middle Rhine, and the Moselle rivers, and was the original territory of the Franks, including both the so-called Salian Franks and Ripuarian Franks, which Clovis I, King of the Franks (481–511) conquered after first taking control of the bordering part of Roman Gaul, which is sometimes described in this period as Neustria.

Hildegard, was a Frankish queen consort who was the second wife of Charlemagne and mother of Louis the Pious. Little is known about her life because like all other women related to Charlemagne, she became notable only from a political background with records on her parentage, wedding, death and role as a mother.

Sankt Wendel is a town in northeastern Saarland. It is situated on the river Blies 36 km northeast of Saarbrücken, the capital of Saarland, and is named after Saint Wendelin of Trier. According to a survey by the German Association for Housing, Town Planning and Land Use Regulation, St. Wendel is known to be one of the wealthiest regions in Germany, behind Starnberg in Bavaria.
Wideric was a Frankish nobleman and the count of the Bidgau and held the rights of a count within the city of Trier. He received also the advocacy of the Abbey of Saint Rumbold at Mechelen from King Charles the Simple of West Francia. From 915 or 916, he was the count palatine of Lotharingia. He was the founder of the House of Ardennes.

Ernst Adolf Alfred Oskar Adalbert von Dobschütz was a German theologian, textual critic, author of numerous books and professor at the University of Halle, the University of Breslau, and the University of Strasbourg. He also lectured in the United States and Sweden.
Sigfried was count in the Ardennes, and is known in European historiography as founder and first ruler of the Castle of Luxembourg in 963 AD, and ancestor and predecessor of the future counts and dukes of Luxembourg. He was also an advocate of the abbeys of St. Maximin in Trier and Saint Willibrord in Echternach.

The Electorate of Trier was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the end of the 9th to the early 19th century. It was the temporal possession of the prince-archbishop of Trier who was, ex officio, a prince-elector of the empire. The other ecclesiastical electors were the electors of Cologne and Mainz.

Longuyon is a commune in the Meurthe-et-Moselle department in the Grand Est region of north-eastern France. The inhabitants are called Longuyonnais.

The Catholic Archdiocese of Luxembourg is an archdiocese of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, comprising the entire Grand Duchy. The diocese was founded in 1870, and it became an archdiocese in 1988. The seat of the archdiocese is the Cathedral of Notre Dame in the city of Luxembourg, and since 2011 the archbishop is Jean-Claude Hollerich.

Elisabeth of Schönau was a German Benedictine visionary. She was an abbess at the Schönau Abbey in the Duchy of Nassau, and reportedly experienced numerous religious visions, for which she became widely sought after by many powerful men as far away as France and England.

Cunibert, Cunipert, or Kunibert was the ninth bishop of Cologne, from 623 to his death. Contemporary sources mention him between 627 and 643.

Trier in Rhineland-Palatinate, whose history dates to the Roman Empire, is the oldest city in Germany. Traditionally it was known in English by its French name of Treves.
Vollmersbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Herrstein-Rhaunen, whose seat is in Herrstein.

Rückweiler is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Baumholder, whose seat is in the like-named town.

Saint Poppo was a knight of noble descent who turned to a monastic life after experiencing a spiritual conversion. He became one of the best known abbots of Stavelot and was one of the first recorded Flemish pilgrims to the Holy Land. Liturgically, he is commemorated on the 25th of January.

Paulus of Verdun (576-648) was a bishop of Verdun in the Lorraine region of France from 630 until his death in 647 or 648.
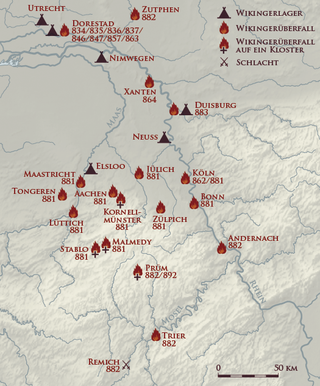
The Viking raids in the Rhineland were part of a series of invasions of Francia by the Vikings that took place during the final decades of the 9th century. From the Rhineland, which can be regarded as the nucleus of Frankish culture, the Franks had previously conquered almost the whole of Central Europe and established a great empire.

Diefflen is a district of Dillingen/Saar in the district of Saarlouis (Saarland) and has about 4700 inhabitants. It is located on the lower Prims, a tributary of the Saar. Since its foundation in the High Middle Ages Diefflen was historically linked to the villages of the former "Hochgericht Nalbacher Tal". This association was broken when Diefflen was incorporated into the city of Dillingen/Saar in 1969.
Eugen Ewig was a German historian who researched the history of the early Middle Ages. He taught as a professor of history at the University of Mainz and the University of Bonn. In the second half of the 20th century, he was considered the foremost expert on the Merovingian dynasty.