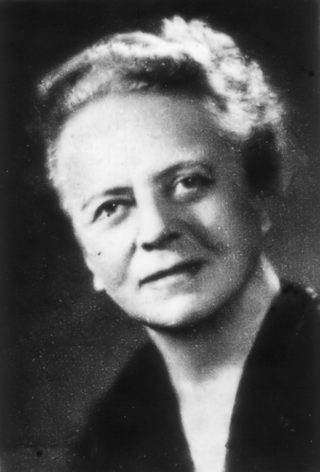Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, was a New Zealand physicist who was a pioneering researcher in both atomic and nuclear physics. Rutherford has been described as "the father of nuclear physics", the greatest experimentalist "since Michael Faraday," and "one of the greatest scientists of all time." In 1908, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for his investigations into the disintegration of the elements, and the chemistry of radioactive substances." He was the first Oceanian Nobel laureate, and the first to perform the awarded work in Canada.

The Ig Nobel Prize is a satiric prize awarded annually since 1991 to celebrate ten unusual or trivial achievements in scientific research. Its aim is to "honor achievements that first make people laugh, and then make them think." The name of the award is a pun on the Nobel Prize, which it parodies, and on the word ignoble.

Lise Meitner was an Austrian-Swedish physicist who was one of those responsible for the discovery of the element protactinium and nuclear fission. While working on radioactivity at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute of Chemistry in Berlin, she discovered the radioactive isotope protactinium-231 in 1917. In 1938, Meitner and her nephew, the physicist Otto Robert Frisch, discovered nuclear fission. She was praised by Albert Einstein as the "German Marie Curie".

Otto Hahn was a German chemist who was a pioneer in the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry. He is referred to as the father of nuclear chemistry and father of nuclear fission. Hahn and Lise Meitner discovered radioactive isotopes of radium, thorium, protactinium and uranium. He also discovered the phenomena of atomic recoil and nuclear isomerism, and pioneered rubidium–strontium dating. In 1938, Hahn, Lise Meitner and Fritz Strassmann discovered nuclear fission, for which Hahn received the 1944 Nobel Prize for Chemistry. Nuclear fission was the basis for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.

Irène Joliot-Curie was a French chemist, physicist and politician, the elder daughter of Pierre Curie and Marie Skłodowska–Curie, and the wife of Frédéric Joliot-Curie. Jointly with her husband, Joliot-Curie was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1935 for their discovery of induced radioactivity, making them the second-ever married couple to win the Nobel Prize, while adding to the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes. This made the Curies the family with the most Nobel laureates to date. She was also one of the first three women to be a member of a French government, becoming undersecretary for Scientific Research under the Popular Front in 1936. Both children of the Joliot-Curies, Hélène and Pierre, are also prominent scientists.

Edwin Mattison McMillan was an American physicist credited with being the first-ever to produce a transuranium element, neptunium. For this, he shared the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Glenn Seaborg.
Corentin Louis Kervran was a French scientist. Kervran was born in Quimper, Finistère (Brittany), and received a degree as an engineer in 1925. In World War II he was part of the French Resistance.

Sir Michael Victor Berry,, is a mathematical physicist at the University of Bristol, England.

Emilio Gino Segrè was an Italian and later naturalized American physicist and Nobel laureate, who discovered the elements technetium and astatine, and the antiproton, a subatomic antiparticle, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1959 along with Owen Chamberlain.

George Charles de Hevesy was a Hungarian radiochemist and Nobel Prize in Chemistry laureate, recognized in 1943 for his key role in the development of radioactive tracers to study chemical processes such as in the metabolism of animals. He also co-discovered the element hafnium.

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis of the various branches of chemistry. Examples include the discovery of fire, extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.
Since the first award in 1901, conferment of the Nobel Prize has occasionally engendered criticism and controversy. After his death in 1896, the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel established that an annual prize be awarded for service to humanity in the fields of physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, literature, and peace. Similarly, the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel is awarded along with the Nobel Prizes.
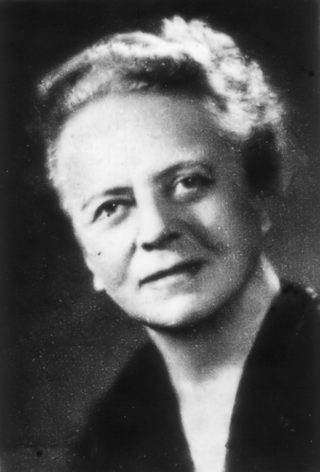
Ida Noddack, néeTacke, was a German chemist and physicist. In 1934 she was the first to mention the idea later named nuclear fission. With her husband Walter Noddack, and Otto Berg, she discovered element 75, rhenium. She was nominated three times for the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.

William Esco Moerner is an American physical chemist and chemical physicist with current work in the biophysics and imaging of single molecules. He is credited with achieving the first optical detection and spectroscopy of a single molecule in condensed phases, along with his postdoc, Lothar Kador. Optical study of single molecules has subsequently become a widely used single-molecule experiment in chemistry, physics and biology. In 2014, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.

This timeline of chemistry lists important works, discoveries, ideas, inventions, and experiments that significantly changed humanity's understanding of the modern science known as chemistry, defined as the scientific study of the composition of matter and of its interactions.
The B2FH paper was a landmark scientific paper on the origin of the chemical elements. The paper's title is Synthesis of the Elements in Stars, but it became known as B2FH from the initials of its authors: Margaret Burbidge, Geoffrey Burbidge, William A. Fowler, and Fred Hoyle. It was written from 1955 to 1956 at the University of Cambridge and Caltech, then published in Reviews of Modern Physics in 1957.

Sir Andre Konstantin Geim is a Russian-born Dutch-British physicist working in England in the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Manchester.
Particle accelerators in popular culture appear in popular science books, fictional literature, feature films, TV series and other media which include particle accelerators as part of their content. Particle physics, fictional or scientific, is an inherent part of this topic.

Nuclear fission was discovered in December 1938 by chemists Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann and physicists Lise Meitner and Otto Robert Frisch. Fission is a nuclear reaction or radioactive decay process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller, lighter nuclei and often other particles. The fission process often produces gamma rays and releases a very large amount of energy, even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay. Scientists already knew about alpha decay and beta decay, but fission assumed great importance because the discovery that a nuclear chain reaction was possible led to the development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons. Hahn was awarded the 1944 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of nuclear fission.