This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2018) |
The administrative divisions of Rhode Island are the areas into which the U.S. state of Rhode Island is divided for political and administrative purposes.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2018) |
The administrative divisions of Rhode Island are the areas into which the U.S. state of Rhode Island is divided for political and administrative purposes.
While Rhode Island is subdivided geographically into five counties, county government was abolished in the state in 1842. Since that time, counties in Rhode Island have had no associated governmental structures. [1] All local government in the state is vested in its 39 municipalities. Counties are still generally used as both geographic regions and also as judicial districts.
The primary political subdivisions of Rhode Island are its cities and towns. New England towns are conceptually similar to civil townships in states where civil townships exist. However, they differ primarily in that New England towns are full-fledged municipal corporations. In Rhode Island, as in most of New England, the laws regulating municipal authority are very broadly construed. Thus, Rhode Island towns have the form, if not the substance, of home rule, with powers comparable to those that a city in other states would normally have.
Rhode Island state law does not distinguish between a city and a town. Cities are simply municipalities that acquired their charter through a special act of the Rhode Island General Assembly. In practice, however, all eight of Rhode Island's incorporated cities have at least 20,000 people. Any municipality (whether a city or a town) is free to adopt whatever form of government they choose.
In addition, cities and towns in Rhode Island also perform functions commonly assigned to counties in other states.
With a few exceptions, the city and town governments of Rhode Island are generally responsible for education management within their jurisdiction. Twenty-nine of the thirty-nine cities/towns manage their own school systems from pre-kindergarten to high school. One city, Central Falls, is governed by a board appointed by the state board of regents. Two towns, Glocester and Foster, manage schools only through elementary school. The other seven towns, which are more rural, have joined to form regional school districts to manage their entire school system, namely, Bristol-Warren, Exeter-West Greenwich, and Charlestown-Richmond-Hopkinton. For the purposes of managing their common middle school and high school, the Foster-Glocester Regional School District has also been established.
The Rhode Island General Assembly consists of a Senate and a House of Representatives. The state is divided into thirty-eight senatorial districts and seventy- five representative districts. Both sets of districts are set up such that each is roughly equal in population.
Rhode Island is divided into four judicial districts that correspond to county groupings of towns, with the exception of Bristol County, which is part of the jurisdiction associated with Providence County.
Rhode Island has 91 special-purpose districts that have been established throughout the state for various purposes. Most such districts in the state, including fire, water, lighting, street maintenance, garbage removal, and utility districts are established by a special act of the General Assembly. There are also two county-wide water authorities (Bristol and Kent). The cities of Providence and East Providence also have urban development commissions. The Capital Center Commission in Providence manages parking, transportation, and streetscaping in downtown Providence. The East Providence Special Development District Commission manages development in the waterfront area of the city.
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French comté denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count (earl) or a viscount. Literal equivalents in other languages, derived from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including comté, contea, contado, comtat, condado, Grafschaft, graafschap, and zhupa in Slavic languages; terms equivalent to 'commune' or 'community' are now often instead used.
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in five countries: Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, and the United States. An equivalent term, shire town, is used in the U.S. state of Vermont and in several other English-speaking jurisdictions.
In the United States, a county or county equivalent is an administrative or political subdivision of a U.S. state or other territories of the United States which consists of a geographic area with specific boundaries and usually some level of governmental authority. The term "county" is used in 48 states, while Louisiana and Alaska have functionally equivalent subdivisions called parishes and boroughs, respectively. The specific governmental powers of counties vary widely between the states, with many providing some level of services to civil townships, municipalities, and unincorporated areas. Certain municipalities are in multiple counties; New York City is uniquely partitioned into five counties, referred to at the city government level as boroughs. Some municipalities have been consolidated with their county government to form consolidated city-counties, or have been legally separated from counties altogether to form independent cities. Conversely, those counties in Connecticut, Rhode Island, eight of Massachusetts's 14 counties, and Alaska's Unorganized Borough have no government power, existing only as geographic distinctions.

Providence County is the most populous county in the U.S. state of Rhode Island. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 660,741, or 60.2% of the state's population. Providence County contains the city of Providence, the state capital of Rhode Island and the county's most populous city, with an estimated 190,934 residents in 2020. Providence County is included in the Providence-Warwick, RI-MA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which in turn constitutes a portion of the greater Boston-Worcester-Providence, MA-RI-NH-CT Combined Statistical Area. As of 2010, the center of population in Rhode Island is located in Providence County, in the city of Cranston.

Burrillville is a town in Providence County, Rhode Island, United States. The population was 16,158 at the 2020 census.
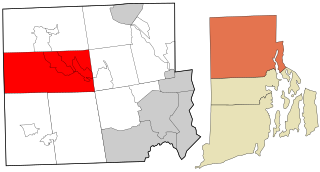
Glocester is a town in Providence County, Rhode Island, United States. The population was 9,974 as of the 2020 census. The villages of Chepachet and Harmony are in Glocester. Putnam Pike runs west through the town center of Glocester into Putnam, Connecticut.

Richmond is a town in Washington County, Rhode Island. The population was 8,020 at the 2020 census. It contains the villages of Alton, Arcadia, Barberville, Carolina, Hillsdale, Kenyon, Shannock, Tug Hollow, Usquepaug, Wood River Junction, Woodville, and Wyoming. Students in Richmond are part of the Chariho Regional School District.

A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.
A civil township is a widely used unit of local government in the United States that is subordinate to a county, most often in the northern and midwestern parts of the country. The term town is used in New England, New York, as well as Wisconsin to refer to the equivalent of the civil township in these states; Minnesota uses "town" officially but often uses it and "township" interchangeably. Specific responsibilities and the degree of autonomy vary in each state. Civil townships are distinct from survey townships, but in states that have both, the boundaries often coincide and may completely geographically subdivide a county. The U.S. Census Bureau classifies civil townships as minor civil divisions. Currently, there are 20 states with civil townships.

Ponaganset High School is a school of the Foster-Glocester School District, located in Glocester, Rhode Island in Providence County. The majority of high school students live in the rural towns of Glocester and Foster, Rhode Island. This is a public high school, known for its music program, AP and honors classes, as well as its CTE approved pathways; plant systems, animal systems, materials and manufacturing, pre-engineering, music technology, music performance, and pending programs: computer science and information technology, and biomedicine. The school's athletic teams are named the "Chieftains," and the FIRST Robotics Competition team is called "5112, The Gongoliers." The principal as of 2012 was Renee Palazzo.

Most U.S. states and territories have at least two tiers of local government: counties and municipalities. Louisiana uses the term parish and Alaska uses the term borough for what the U.S. Census Bureau terms county equivalents in those states. Civil townships or towns are used as subdivisions of a county in 20 states, mostly in the Northeast and Midwest.

The town is the basic unit of local government and local division of state authority in the six New England states. Most other U.S. states lack a direct counterpart to the New England town. New England towns overlay the entire area of a state, similar to civil townships in other states where they exist, but they are fully functioning municipal corporations, possessing powers similar to cities and counties in other states. New Jersey's system of equally powerful townships, boroughs, towns, and cities is the system which is most similar to that of New England. New England towns are often governed by a town meeting, an assembly of eligible town residents. The great majority of municipal corporations in New England are based on the town model; there, statutory forms based on the concept of a compact populated place are uncommon, though elsewhere in the U.S. they are prevalent. County government in New England states is typically weak at best, and in some states nonexistent. Connecticut, for example, has no county governments, nor does Rhode Island. Both of those states retain counties only as geographic subdivisions with no governmental authority, while Massachusetts has abolished eight of fourteen county governments so far. Counties serve mostly as dividing lines for the states' judicial systems and some other state services in the southern New England states, while providing varying services in the more sparsely populated three northern New England states.

The Government of Colorado is organized into three branches: the executive branch of the Governor, the legislative branch of the General Assembly, and the judicial branch of the Supreme Court and lower courts. This government was created by the Constitution of the State of Colorado, and allows for direct participation of the electorate by initiative, referendum, recall and ratification.
Connecticut shares with the five other New England states a governmental structure known as the New England town. From 1666 to 1960, Connecticut had a system of county governments, which each had limited powers given to it by the General Assembly. They were abolished by Public Act 152 in 1960. Connecticut also had a system of sheriffs' offices until October 2000, when those were also abolished.
The administrative divisions of Virginia are the areas into which the Commonwealth of Virginia, a U.S. state, is divided for political and administrative purposes. Some are local governments; others are not. However, all local governments are political subdivisions of the state.

The government of Indiana is established and regulated by the Constitution of Indiana. The state-level government consists of three branches: the judicial branch, the legislative branch, and the executive branch. The three branches share power and jointly govern the state of Indiana. County and local governments are also constitutional bodies with limited authority to levy taxes, pass legislation, and create and maintain local public infrastructure.
Local government in New Jersey is composed of counties and municipalities. Local jurisdictions in New Jersey differ from those in some other states because every square foot of the state is part of exactly one municipality; each of the 564 municipalities is in exactly one county; and each of the 21 counties has more than one municipality. New Jersey has no independent cities, or consolidated city-counties.
The Rhode Island Superior Court is the state trial court of general jurisdiction in Rhode Island.

The 2016 United States presidential election in Rhode Island took place on November 8, 2016, as part of the 2016 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Rhode Island voters chose four electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote.