The M16 rifle is a family of assault rifles adapted from the ArmaLite AR-15 rifle for the United States military. The original M16 rifle was a 5.56×45mm automatic rifle with a 20-round magazine.

The 5.56×45mm NATO is a rimless bottlenecked centerfire intermediate cartridge family developed in the late 1970s in Belgium by FN Herstal. It consists of the SS109, L110, and SS111 cartridges. On 28 October 1980, under STANAG 4172, it was standardized as the second standard service rifle cartridge for NATO forces as well as many non-NATO countries. Though they are not identical, the 5.56×45mm NATO cartridge family was derived from and is dimensionally similar to the .223 Remington cartridge designed by Remington Arms in the early 1960s.

A flechette or flèchette is a pointed, fin-stabilized steel projectile. The name comes from French flèchette, meaning "little arrow" or "dart", and sometimes retains the grave accent in English: flèchette. They have been used as ballistic weapons since World War I. Delivery systems and methods of launching flechettes vary, from a single shot, to thousands in a single explosive round. The use of flechettes as antipersonnel weapons has been controversial.

A needlegun, also known as a needler, flechette gun or fletcher, is a firearm that fires small, sometimes fin-stabilized, metal darts or flechettes. Theoretically, the advantages of a needlegun over conventional projectile firearms are in its compact size, high rate of fire, and extreme muzzle velocity. The needle presents less frontal area than a bullet, producing less drag and thus more effective range than a wider projectile of the same mass and velocity. There have been experiments to make guided flechettes that can home in on targets.

The Heckler & Koch G11 is a non-production prototype assault rifle developed from the late 1960s to the 1980s by Gesellschaft für Hülsenlose Gewehrsysteme (GSHG), a conglomeration of companies headed by firearm manufacturer Heckler & Koch, Dynamit Nobel, and Hensoldt Wetzlar. The rifle is noted for its use of caseless ammunition.

A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.

The Steyr IWS 2000 is an Austrian single-shot bolt-action anti-materiel rifle produced by Steyr Mannlicher. IWS stands for Infantry Weapon System. Unlike other anti-tank rifle designs, it has a smoothbore barrel. This facilitates higher projectile velocities and allows a longer barrel service life, but the lack of gyroscopic spin-stabilization requires the projectile to have aerodynamic stabilizing fins instead. The IWS is chambered in a 15.2×169 mm armor-piercing fin-stabilized discarding-sabot cartridge, and is the first man-portable rifle to use this type of ammunition.
The Special Purpose Individual Weapon (SPIW) was a long-running United States Army program to develop, in part, a flechette-firing "rifle", though other concepts were also involved. The concepts continued to be tested under the Future Rifle Program and again in the 1980s under the Advanced Combat Rifle program, but neither program resulted in a system useful enough to warrant replacing the M16.

The Steyr ACR was a prototype flechette-firing assault rifle built for the US Army's Advanced Combat Rifle program of 1989/90. Although the Steyr design proved effective, as did most of the weapons submitted, the entire ACR program ended with none of the entrants achieving performance 100% better than the M16A2, the baseline for a successful ACR weapon.

The 6.8mm Remington Special Purpose Cartridge is a rimless bottlenecked intermediate rifle cartridge that was developed by Remington Arms in collaboration with members of the U.S. Army Marksmanship Unit and United States Special Operations Command to possibly replace the 5.56 NATO cartridge in short barreled rifles (SBR) and carbines. Based on the .30 Remington cartridge, it is midway between the 5.56×45mm NATO and 7.62×51mm NATO in bore diameter. It uses the same diameter bullet as the .270 Winchester hunting cartridge.

The two most common assault rifles in the world are the Soviet AK-47 and the American M16. These Cold War-era rifles have been used in conflicts both large and small since the 1960s. They are used by military, police, security forces, revolutionaries, terrorists, criminals, and civilians alike and will most likely continue to be used for decades to come. As a result, they have been the subject of countless comparisons and endless debate.

The Heckler & Koch HK CAWS is a prototype automatic shotgun—designed as a combat shotgun—co-produced by Heckler & Koch and Winchester/Olin during the 1980s. It was Heckler & Koch's entry into the U.S. military's Close Assault Weapon System program.

The Colt ACR was Colt's entry in the U.S. DoD Advanced Combat Rifle program, which concluded with the result that none of the entrants achieved enough of an improvement over the M16 to be worth the cost.
The 5.8×42mm / DBP87 is a military bottlenecked intermediate cartridge developed in the People's Republic of China. There is limited information on this cartridge, although the People's Liberation Army claims that it is superior to the 5.56×45mm NATO and Soviet 5.45×39mm cartridges.
The Lightweight Small Arms Technologies (LSAT) program is funded by the U.S. Joint Service Small Arms Program, with the goal of significantly reducing the weight of small arms and their ammunition. Following a series of military programs to investigate advances in small arms, the LSAT program is the US military's latest project to replace existing US small arms. Tactical concepts and the research from the previous small arms programs indicates that lightening small arms is the first significant step towards increasing soldiers' lethality and survivability.

An underwater firearm is a firearm designed for use underwater. Underwater firearms or needleguns usually fire flechettes or spear-like bolts instead of standard bullets. These may be fired by pressurised gas.

The 7.62×51mm NATO is a rimless, straight walled, bottlenecked, centerfire rifle cartridge. It is a standard for small arms among NATO countries.
Military use of combat shotguns through the 20th century has created a need for ammunition maximizing the combat effectiveness of such weapons within the limitations of international law. 12-gauge has been widely accepted as an appropriate bore diameter to provide an effective number of projectiles within an acceptable recoil. Early 12-gauge popularity for sporting purposes produced a large number of repeating firearms designs readily adaptable to military purposes.
The AAI CAWS is a prototype automatic shotgun—designed as a combat shotgun— produced by the AAI Corporation during the 1980s. It was AAI's entry into the U.S military's Close Assault Weapon System program.
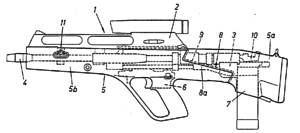
The AAI ACR was a prototype flechette-firing assault rifle built for the US Army's Advanced Combat Rifle program of 1989/90. Although the AAI design proved effective, as did most of the weapons submitted, the entire ACR program ended with none of the entrants achieving performance 100% better than the M16A2, the baseline for a successful ACR weapon.