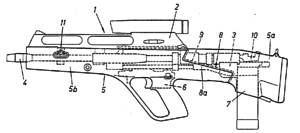
The SA80 is a British family of 5.56×45mm NATO service weapons used by the British Army. The L85 Rifle variant has been the standard issue service rifle of the British Armed Forces since 1987, replacing the L1A1 Self-Loading Rifle. The prototypes were created in 1976, with production of the A1 variant starting in 1985 and ending in 1994. The A2 variant came to be as the result of a significant upgrade in the early 2000s by Heckler & Koch and remains in service as of 2024. The A3 variant was first issued in 2018 with several new improvements.

A bullpup firearm is one with its firing grip located in front of the breech of the weapon, instead of behind it. This creates a weapon with a shorter overall length for a given barrel length, and one that is often lighter, more compact, concealable and more maneuverable than a conventionally configured firearm. Where it is desirable for troops to be issued a more compact weapon, the use of a bullpup configuration allows for barrel length to be retained, thus preserving muzzle velocity, range and ballistic effectiveness.

A flechette is a pointed, fin-stabilized steel projectile. The name comes from French fléchette, meaning "little arrow" or "dart", and sometimes retains the acute accent in English: fléchette. They have been used as ballistic weapons since World War I. Delivery systems and methods of launching flechettes vary, from a single shot, to thousands in a single explosive round. The use of flechettes as antipersonnel weapons has been controversial.

The .50 BMG, also known as 12.7×99mm NATO, and designated as the 50 Browning by the C.I.P., is a .50 in (12.7 mm) caliber cartridge developed for the M2 Browning heavy machine gun in the late 1910s, entering official service in 1921. Under STANAG 4383, it is a standard service cartridge for NATO forces. The cartridge itself has been made in many variants: multiple generations of regular ball, tracer, armor-piercing (AP), incendiary, and saboted sub-caliber rounds. The rounds intended for machine guns are made into a continuous ammunition belt using metallic links.

The Steyr AUG is an Austrian bullpup assault rifle chambered for the 5.56×45mm NATO intermediate cartridge, designed in the 1960s by Steyr-Daimler-Puch, and now manufactured by Steyr Arms GmbH & Co KG.

A needlegun, also known as a needler, flechette gun or fletcher, is a firearm that fires small, sometimes fin-stabilized, metal darts or flechettes. Theoretically, the advantages of a needlegun over conventional projectile firearms are in its compact size, high rate of fire, and extreme muzzle velocity. The needle presents less frontal area than a bullet, producing less drag and thus more effective range than a wider projectile of the same mass and velocity. There have been experiments to make guided flechettes that can home in on targets.

The Heckler & Koch G11 is a non-production prototype assault rifle developed from the late 1960s–1980s by Gesellschaft für Hülsenlose Gewehrsysteme (GSHG), a conglomeration of companies headed by firearm manufacturer Heckler & Koch, Dynamit Nobel, and Hensoldt Wetzlar. The rifle is noted for its use of caseless ammunition.

A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.

The Steyr IWS 2000 is an Austrian single-shot bolt-action anti-materiel rifle produced by Steyr Mannlicher. IWS stands for Infantry Weapon System. Unlike other anti-tank rifle designs, it has a smoothbore barrel. This facilitates higher projectile velocities and allows a longer barrel service life, but the lack of gyroscopic spin-stabilization requires the projectile to have aerodynamic stabilizing fins instead. The IWS is chambered in a 15.2×169 mm armor-piercing fin-stabilized discarding-sabot cartridge, and is the first man-portable rifle to use this type of ammunition.
The Special Purpose Individual Weapon (SPIW) was a long-running United States Army program to develop, in part, a flechette-firing "rifle", though other concepts were also involved. The concepts continued to be tested under the Future Rifle Program and again in the 1980s under the Advanced Combat Rifle program, but neither program resulted in a system useful enough to warrant replacing the M16.
The Advanced Combat Rifle (ACR) was a United States Army program, started in 1986, to find a replacement for the M16 assault rifle. Under the stress of battle the average soldier with an M16 may shoot a target at 45 meters, but hit probability is reduced to one out of ten shots on target by 220 meters. Because of this, the ACR program was initiated in the late 1980s to create a weapon that could double the hit probability. The ACR program was preceded by older programs such as the Special Purpose Individual Weapon. The program ended in 1990 after an expenditure of approximately US$300 million.
The Advanced Individual Combat Weapon (AICW) was an Australian prototype combination assault rifle and grenade launcher developed as a technology demonstrator. The AICW combined a standard 5.56 mm assault rifle based on the successful F88 Austeyr with a superposed load grenade launcher developed by Metal Storm.

The Heckler & Koch HK CAWS is a prototype automatic shotgun—designed as a combat shotgun—co-produced by Heckler & Koch and Winchester/Olin during the 1980s. It was Heckler & Koch's entry into the U.S military's Close Assault Weapon System program.
Steyr Arms is a firearms manufacturer based in Sankt Peter in der Au, Austria. Originally part of Steyr-Daimler-Puch, it became independent when the conglomerate was broken up in 1989. Prior to 1 January 2019, the company was named Steyr Mannlicher AG. In April 2024, the company was acquired by Czech holding RSBC, which owns also Slovenian gun maker Arex Arms.

The ASM-DT is a Russian prototype folding-stock underwater firearm. It emerged in the 1990s.
The LAPA FA-03 was a bullpup assault rifle designed in Brazil by the company LAPA, and developed by its owner, Nelmo Suzano (1930-2013). The acronym FA-03 stands for "Fuzil de Assalto Modelo 03".
The Lightweight Small Arms Technologies (LSAT) program is funded by the U.S. Joint Service Small Arms Program, with the goal of significantly reducing the weight of small arms and their ammunition. Following a series of military programs to investigate advances in small arms, the LSAT program is the US military's latest project to replace existing US small arms. Tactical concepts and the research from the previous small arms programs indicates that lightening small arms is the first significant step towards increasing soldiers' lethality and survivability.

Polymer-cased ammunition (PCA) is firearm ammunition (cartridge) with casings made from synthetic polymer instead of the typical metallic casing. PCA is considered a new alternative that potentially reduces production cost and weight for long guns and handguns.
The STG-556 is a Steyr AUG clone formerly manufactured by Microtech Small Arms Research (MSAR). It was available in civilian and military/law enforcement (select-fire) variants.
The AAI ACR was a prototype flechette-firing assault rifle built for the US Army's Advanced Combat Rifle program of 1989/90. Although the AAI design proved effective, as did most of the weapons submitted, the entire ACR program ended with none of the entrants achieving performance 100% better than the M16A2, the baseline for a successful ACR weapon.