NCSA Mosaic is a discontinued web browser, one of the first to be widely available. It was instrumental in popularizing the World Wide Web and the general Internet by integrating multimedia such as text and graphics. It was named for its support of multiple Internet protocols, such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol, File Transfer Protocol, Network News Transfer Protocol, and Gopher. Its intuitive interface, reliability, personal computer support, and simple installation all contributed to its popularity within the web. Mosaic is the first browser to display images inline with text instead of in a separate window. It is often described as the first graphical web browser, though it was preceded by WorldWideWeb, the lesser-known Erwise, and ViolaWWW.

The National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) is a state-federal partnership to develop and deploy national-scale computer infrastructure that advances research, science and engineering based in the United States. NCSA operates as a unit of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and provides high-performance computing resources to researchers across the country. Support for NCSA comes from the National Science Foundation, the state of Illinois, the University of Illinois, business and industry partners, and other federal agencies.

Scientific visualization is an interdisciplinary branch of science concerned with the visualization of scientific phenomena. It is also considered a subset of computer graphics, a branch of computer science. The purpose of scientific visualization is to graphically illustrate scientific data to enable scientists to understand, illustrate, and glean insight from their data. Research into how people read and misread various types of visualizations is helping to determine what types and features of visualizations are most understandable and effective in conveying information.

Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) is a set of file formats designed to store and organize large amounts of data. Originally developed at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications, it is supported by The HDF Group, a non-profit corporation whose mission is to ensure continued development of HDF5 technologies and the continued accessibility of data stored in HDF.
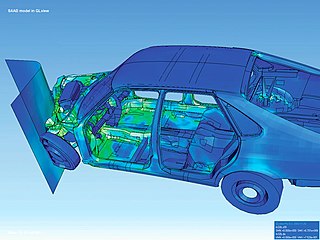
Visualization or visualisation is any technique for creating images, diagrams, or animations to communicate a message. Visualization through visual imagery has been an effective way to communicate both abstract and concrete ideas since the dawn of humanity. Examples from history include cave paintings, Egyptian hieroglyphs, Greek geometry, and Leonardo da Vinci's revolutionary methods of technical drawing for engineering and scientific purposes.

The San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) is an organized research unit of the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). SDSC is located at the UCSD campus' Eleanor Roosevelt College east end, immediately north the Hopkins Parking Structure.
Access Grid is a collection of resources and technologies that enables large format audio and video based collaboration between groups of people in different locations. The Access Grid is an ensemble of resources, including multimedia large-format displays, presentation and interactive environments, and interfaces with grid computing middleware and visualization environments. In simple terms, it is advanced videoconferencing using big displays and with multiple simultaneous camera feeds at each node (site). The technology was invented at Argonne National Laboratory, Chicago.
Michael Thomas Heath is a retired computer scientist who specializes in scientific computing. He is the director of the Center for the Simulation of Advanced Rockets, a Department of Energy-sponsored computing center at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, and the former Fulton Watson Copp Professor of Computer Science at UIUC. Heath was inducted as member of the European Academy of Sciences in 2002, a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery in 2000, and a Fellow of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics in 2010. He also received the 2009 Taylor L. Booth Education Award from IEEE. He became an emeritus professor in 2012.
Donna J. Cox is an American artist and scientist, Michael Aiken Endowed Chair; Professor of Art + Design; Director, Advanced Visualization Lab at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC); Director, Visualization and Experimental Technologies at National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA); and Director, edream. She is a recognized pioneer in computer art and scientific visualization, specifically cinematic scientific visualization.

The NASA Advanced Supercomputing (NAS) Division is located at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field in the heart of Silicon Valley in Mountain View, California. It has been the major supercomputing and modeling and simulation resource for NASA missions in aerodynamics, space exploration, studies in weather patterns and ocean currents, and space shuttle and aircraft design and development for almost forty years.

Fernanda Bertini Viégas is a Brazilian scientist and designer, whose work focuses on the social, collaborative and artistic aspects of information visualization.
The Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center (PSC) is a high performance computing and networking center founded in 1986 and one of the original five NSF Supercomputing Centers. PSC is a joint effort of Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States.
The Molecularium Project is an informal science education project of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. The Project introduces young audiences to the world of atoms and molecules using character driven stories, immersive animation, interactive games and activities, and state of the art molecular visualizations. Rensselaer's three principal scientist and educators behind the project are Linda Schadler, Richard W. Siegel, and Shekhar Garde. The Molecularium Project began as an outreach project of Rensselaer's Nanoscale Science and Engineering Center. To realize the productions, the scientists employed the creative team Nanotoon Entertainment, led by writer and director V. Owen Bush, and writer/producer Kurt Przybilla. The Molecularium Project is funded by Rensselaer, the National Science Foundation, and New York State.
Edward Seidel is an American academic administrator and scientist serving as the president of the University of Wyoming since July 1, 2020. He previously served as the Vice President for Economic Development and Innovation for the University of Illinois System, as well as a Founder Professor in the Department of Physics and a professor in the Department of Astronomy at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He was the director of the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at Illinois from 2014 to 2017.
Kevin Franklin, EdD was born in Virginia, where he received degrees in Psychology and Education from Old Dominion University. He holds a Doctorate of Education in Organization and Leadership from the University of San Francisco. Formerly Executive Director of the University of California system-wide Humanities Research Institute (UCHRI) and a Deputy Director of the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC), Franklin was appointed as Executive Director of the Institute for Computing in Humanities, Arts, and Social Science, (I-CHASS), Research Professor, Education Policy, Organization and Leadership, Adjunct Associate Professor, African American Studies, and Senior Research Scientist for the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois in July 2007. In addition Franklin was appointed Associate Director for the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) in 2014.

Pleiades is a petascale supercomputer housed at the NASA Advanced Supercomputing (NAS) facility at NASA's Ames Research Center located at Moffett Field near Mountain View, California. It is maintained by NASA and partners Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Intel.

Hubble is a 2010 American documentary film about Space Shuttle missions to repair and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. It is narrated by the actor Leonardo DiCaprio.

Mauro Martino is an Italian artist, designer and researcher. He is the founder and director of the Visual Artificial Intelligence Lab at IBM Research, and Professor of Practice at Northeastern University. He graduated from Polytechnic University of Milan, and was a research affiliate with the Senseable City Lab at MIT. Mauro was formerly an Assistant Research Professor at Northeastern University working with Albert-Laszlo Barabasi at Center for Complex Network Research and with David Lazer and Fellows at The Institute for Quantitative Social Science (IQSS) at Harvard University.
Nadieh Bremer is a data scientist and data visualization designer. She is based out of a small town outside of Amsterdam.

Cinematic scientific visualization (CSV) is the visual presentation of scientific data in a way that is typically associated with non-scientific filmmaking techniques including cinematography, lighting, and composition. Cinematic scientific visualizations are often created for purposes of science communication to the general public, e.g. through museum exhibits and documentary films. CSV is considered a subfield of scientific visualization, although the creation methods and visual outputs differ due to CSV's heavy emphasis on aesthetics and design.












