Related Research Articles

Riyadh is the capital of Saudi Arabia and the largest city on the Arabian Peninsula. Located in the center of the an-Nafud desert, on the eastern part of the Najd plateau, the city sits at an average of 600 metres (2,000 ft) above sea level, and receives around 5 million tourists each year, making it the forty-ninth most visited city in the world and the 6th in the Middle East. Riyadh had a population of 7.6 million people in 2019, making it the most populous city in Saudi Arabia, 3rd most populous in the Middle East, and 38th most populous in Asia.

The Safavid dynasty was one of the most significant ruling dynasties of Iran from 1501 to 1736. The Safavid dynasty had its origin in the Safavid order of Sufism, which was established in the city of Ardabil in the Iranian Azerbaijan region. It was an Iranian dynasty of Kurdish origin, but during their rule they intermarried with Turkoman, Georgian, Circassian, and Pontic Greek dignitaries. From their base in Ardabil, the Safavids established control over parts of Greater Iran and reasserted the Iranian identity of the region, thus becoming the first native dynasty since the Sasanian Empire to establish a national state officially known as Iran.

The Hashemites, also House of Hashim, are the royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Hejaz (1916–1925), Syria (1920) and Iraq (1921–1958). The family had ruled the city of Mecca continuously from the 10th century, frequently as vassals of outside powers, and were given the thrones of the Hejaz, Syria, Iraq and Jordan following their World War I alliance with the British Empire; this arrangement became known as the "Sharifian solution".

The House of Saud is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1744–1818), and his brothers, though the ruling faction of the family is primarily led by the descendants of Ibn Saud, the modern founder of Saudi Arabia. The most influential position of the royal family is the King of Saudi Arabia. The family in total is estimated to comprise some 15,000 members, however the majority of power, influence and wealth is possessed by a group of about 2,000 of them.
Sharif (also transliterated Shareef, Sherif, shreef Shareef, Alsharif, Alshareef, or Chérif is a traditional Arabic title. The origin of the word is an adjective meaning "noble", "highborn". The feminine singular is sharifa or shareefa . The masculine plural is Ashraf.

Safi-ad-din Ardabili was a Kurdish poet, mystic, teacher and Sufi master. He was the son-in-law and spiritual heir of the Sufi master Zahed Gilani, whose order—the Zahediyeh—he reformed and renamed the Safaviyya, which he led from 1301 to 1334.

The House of Khalifa is the ruling family of the Kingdom of Bahrain. The Al Khalifas profess Sunni Islam and belong to the Utub tribe that migrated from Central Arabia to Kuwait, then ruled all of Qatar more specifically al zubarah which they built and ruled over before settling in Bahrain in the early 17th century. The Utub tribe is part of the larger Anizah tribal confederation. The current head of the family is Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa, who became the Emir of Bahrain in 1999 and proclaimed himself King of Bahrain in 2002, in fact becoming a constitutional monarch.

The Idrisids were an Arab Muslim Dynasty in Morocco, ruling from 788 to 974. Named after the founder Idris I, the great grandchild of Hasan ibn Ali, the Idrisids are considered to be the founders of the first Moroccan state. The Idrisid dynasty was an Alid dynasty—that is, descendants of Ali ibn Abi Talib.

Alid dynasties of northern Iran or Alavids. In the 9th–14th centuries, the northern Iranian regions of Tabaristan, Daylam and Gilan, sandwiched between the Caspian Sea and the Alborz range, came under the rule of a number of Arab Alid dynasties, espousing the Zaydi branch of Shia Islam.

The Sulaymani branch of Tayyibi Isma'ilism is an Islamic community, of which around 70 thousand members reside in Yemen, while a few thousands of Sulaymani Bohras can be found in India. The Sulaymanis are headed by a da'i al-mutlaq from the Makrami family.

Bohtan was a medieval Kurdish principality in the Ottoman Empire centered on the town of Jazirah ibn 'Omar in southeastern Anatolia. Bohtanis were an ancient and prominent branch of the Kurds that claimed descent from the Islamic General and Sahaba Khalid ibn al-Walid. Some minor branches followed Yazidism but Sunni Islam predominated in the 14th century.
Shi‘a Islam, also known as Shi‘ite Islam or Shi‘ism, is the second largest branch of Islam after Sunni Islam. Shias adhere to the teachings of Muhammad and the religious guidance of his family or his descendants known as Shia Imams. Muhammad's bloodline continues only through his daughter Fatima Zahra and cousin Ali who alongside Muhammad's grandsons comprise the Ahl al-Bayt. Thus, Shias consider Muhammad's descendants as the true source of guidance. Shia Islam, like Sunni Islam, has at times been divided into many branches; however, only three of these currently have a significant number of followers, and each of them has a separate trajectory.
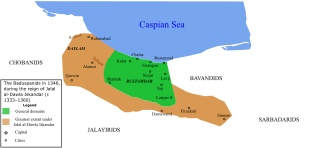
The Baduspanids or Badusbanids were a local dynasty of Tabaristan which ruled over Ruyan/Rustamdar. The dynasty was established in 665, and ended in 1598 when the Safavids invaded their domains.
Jalal al-Dawla Iskandar was the ruler (ustandar) of the Baduspanids from 1333 to 1360. Under his rule, the kingdom reached its zenith. Taking advantage of the collapse of the Mongol Ilkhanate in 1335, he expanded his rule into the southern Alborz, ruling an area stretching from Qazvin to Simnan. In 1346, he founded the town of Kojur and conquered the region of Daylam. In 1360, he was mortally wounded by his bodyguard during a ruckus at a drinking party. He died three days later, and was succeeded by his brother Fakhr al-Dawla Shah-Ghazi.
Abu Abd Allah al-Sheikh Muhammad ibn Yahya was the first Wattasid Sultan of Morocco and King of Fez between 1472 and 1504.
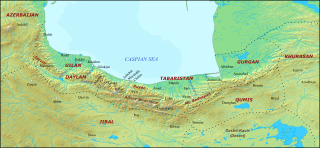
Ruyan, later known as Rustamdar (رستمدار), was the name of a mountainous district that encompassed the western part of Tabaristan/Mazandaran, a region on the Caspian coast of northern Iran.
Hasankeyf Emirate was a Kurdish emirate centered around Hasankeyf and ruled by descendants of the Ayyubid dynasty until its dissolution in 1524. They considered their emirate as the last remnant of the Ayyubid state. The rulers were called melik and continued to lead the emirate from 1232 to 1524 despite invasions and different sovereigns.
Kayumarth I was the ruler (ustandar) of the Baduspanids from 1394 to 1453, with a three-year interruption. An active expansionist ruler, his kingdom experienced a resurgence during his long reign, which included the reconquest of Rustamdar. He was often at odds with his suzerain, the Timurid ruler Shah Rukh. After his death, a dynastic struggle followed, which resulted in his kingdom being split up by his sons Iskandar IV and Ka'us II, in Kojur and Nur respectively.
Shahriyar III ibn Jamshid was the Baduspanid ruler of Ruyan and Rustamdar from 937 to 949. He belonged to a distant branch of the family, descended from Afridun ibn Karan. After a period of instability and dynastic struggles, Shahriyar emerged victorious and took over the throne, thus establishing a new line known as the Shahriyarids, succeeding the previous Afridunids. The new line notably wielded the pre-Islamic title of ustandar, originally an administrative title of provincial governors under the Sasanian Empire.
Ostandar or Ustandar was an administrative title wielded by provincial governors under the Sasanian Empire. They governed the royal lands, known as the ostan. The title was later assumed by the Baduspanids of Ruyan, starting with Shahriyar III ibn Jamshid.