Related Research Articles

Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services.
In food safety, the concept of substantial equivalence holds that the safety of a new food, particularly one that has been genetically modified (GM), may be assessed by comparing it with a similar traditional food that has proven safe in normal use over time. It was first formulated as a food safety policy in 1993, by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).

Genetically modified crops are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of Agrobacterium for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. In most cases, the aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. Examples in food crops include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, reduction of spoilage, resistance to chemical treatments, or improving the nutrient profile of the crop. Examples in non-food crops include production of pharmaceutical agents, biofuels, and other industrially useful goods, as well as for bioremediation.

Marc, Baron Van Montagu is a Belgian molecular biologist. He was full professor and director of the Laboratory of Genetics at the faculty of Sciences at Ghent University (Belgium) and scientific director of the genetics department of the Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB). Together with Jozef Schell he founded the biotech company Plant Genetic Systems Inc. (Belgium) in 1982, of which he was scientific director and member of the board of directors. Van Montagu was also involved in founding the biotech company CropDesign, of which he was a board member from 1998 to 2004. He is president of the Public Research and Regulation Initiative (PRRI).

The International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA) is a non-profit international organization that shares agricultural biotechnology, focusing on genetic engineering.

Sartorius AG is an international pharmaceutical and laboratory equipment supplier, covering the segments of Bioprocess Solutions and Lab Products & Services. In September 2021, Sartorius has been admitted to the DAX, Germany's largest stock market index. As a leading partner to the biopharmaceutical research and industry, Sartorius supports its customers in the development and production of biotech drugs and vaccines - from the initial idea in the laboratory to commercial production. Sartorius conducts its operating business in the two divisions Bioprocess Solutions and Lab Products&Services. The divisions bundle their respective businesses according to the same application areas and customer groups. The divisions share some of the infrastructure and central services.

UF Innovate | Accelerate @ Sid Martin Biotech is located in Alachua, Florida, in Progress Park. The program's mission is to foster the growth of bioscience startup companies that have some relationship to the university. The Incubator works with companies in all product areas relating to the life sciences, biomedical research, medicine, and chemical sciences.
China has seen double-digit growth in its biotechnology industry and has gone from being one of the slowest to one of the fastest nations in the adoption of new biotechnologies. The biotech sector is seen in China and internationally as a core area of national scientific and economic development. The main national biotech body in the country is the China National Center for Biotechnology Development. The CNCBD is an organization established on November 3, 1983, under the Ministry of Science and Technology with the approval of the State Council. CNCBD is the sole national center to coordinate and implement the national S&T program in Biotechnology and Health.
Richard Gilmore is President/CEO of GIC Trade, Inc., an international agribusiness company with partner offices in Beijing, São Paulo, Quito, Moscow, and Tel Aviv. He is also Founder and Chairman of the Global Food Safety Forum (GFSF), a non-profit industry organization focused on educational and training activities in Asia with offices in the People's Republic of China (PRC) and Vietnam. A trade economist and businessman with a Ph.D. from the Graduate Institute of International Studies in Geneva, where he was a Fulbright Fellow, Gilmore served as Trustee for Bayer CropSciences, Syngenta Corporation, and Agrium, Inc. He is currently Trustee in the U.S. and Canada for Nutrien. He also served as Special External Advisor to the White House/USAID for the Private Sector/Global Food Security and Managing Director of the Global Food Safety Forum (GFSF) in Beijing. Gilmore developed two agro-carbon instruments: Commodity Plus Carbon (CPC)and GIC Ag Carbon Intensity Index.
BB Biotech AG is a Swiss investment company in the field of biotechnology. Since 1993 it is listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange, since 1997 on the German TecDAX and from 2000 to 2023 on the Italian Borsa Italiana. The company invests mainly in the United States and Western Europe and is managed by Bellevue Asset Management, a division of Bellevue Group which accounts for approximately 40% of the Group's assets under management.
Religious views on genetically modified foods have been mixed, although as yet, no genetically modified foods have been designated as unacceptable by religious authorities.
Genes to Cells is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes original research on the molecular mechanisms of biological events. The journal has been published since 1996 by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Molecular Biology Society of Japan.

The regulation of genetic engineering varies widely by country. Countries such as the United States, Canada, Lebanon and Egypt use substantial equivalence as the starting point when assessing safety, while many countries such as those in the European Union, Brazil and China authorize GMO cultivation on a case-by-case basis. Many countries allow the import of GM food with authorization, but either do not allow its cultivation or have provisions for cultivation, but no GM products are yet produced. Most countries that do not allow for GMO cultivation do permit research. Most (85%) of the world's GMO crops are grown in the Americas. One of the key issues concerning regulators is whether GM products should be labeled. Labeling of GMO products in the marketplace is required in 64 countries. Labeling can be mandatory up to a threshold GM content level or voluntary. A study investigating voluntary labeling in South Africa found that 31% of products labeled as GMO-free had a GM content above 1.0%. In Canada and the US labeling of GM food is voluntary, while in Europe all food or feed which contains greater than 0.9% of approved GMOs must be labelled.
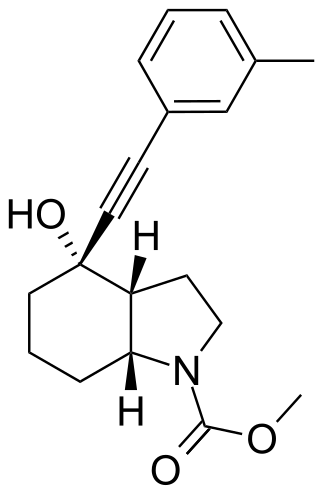
Mavoglurant (developmental code name AFQ-056) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of fragile X syndrome and other conditions. It exerts its effect as an antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5).

A genetically modified tree is a tree whose DNA has been modified using genetic engineering techniques. In most cases the aim is to introduce a novel trait to the plant which does not occur naturally within the species. Examples include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, and herbicide tolerance, or the alteration of lignin levels in order to reduce pulping costs.
Kevin M. Folta is a professor of the horticultural sciences department at the University of Florida. From 2007 to 2010 he helped lead the project to sequence the strawberry genome, and continues to research photomorphogenesis in plants and compounds responsible for flavor in strawberries. Folta has been active as a science communicator since 2002, especially relating to biotechnology. He has faced controversy over what his critics say are his industry connections. In 2017 he was elected as a fellow of the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry.
Biotechnology in India is a sunrise sector within the Indian economy. Agencies of the Government of India concerned with the biotechnology industry include the Department of Biotechnology and the proposed Biotechnology Regulatory Authority of India. As of 2022, the sector is valued at $80 billion. Biotechnology in India is in a growth phase and the sector is expected to be valued at $150 billion by 2025 and surpass $300 billion in value by 2030.
Banwari Lal is an Indian environmental and industrial biotechnologist and the director of the Environmental and Industrial Biotechnology Division at The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI). Known for the development of oilzapper technology, Dr. Lal is the chief executive officer of ONGC-TERI Biotech Limited, a collaborative venture between TERI and the Oil and Natural Gas Corporation since 2008. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences in 2004. He have many Indian and international joint patents with ONGC, DBT, IOCL, OIL INDIA and TERI.

The Plant Journal is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of plant science published by Wiley-Blackwell for the Society for Experimental Biology. It was established in 1991 and is currently edited by Katherine J. Denby. The journal is published twice per month.
The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of eukaryotic microbiology. The journal publishes research on protists, including lower algae and fungi.
References
- ↑ "AgBiotechNet". SciDev. Retrieved 2018-09-23.
- ↑ Nicholson, David (January 2001). "New business models: AgBiotechNet™, a case study". Learned Publishing. 14 (1): 55–59. doi: 10.1087/09531510125100287 . ISSN 0953-1513. S2CID 263148.
- ↑ Hemming, David (Winter 2004). "Staying on Top of Agbiotech -- An International Perspective". Issues in Science and Technology Librarianship (39). doi:10.5062/f4p26w2x.