| Look up ageing , aged , aging , or oldness in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Aging is the effect of time on a person.
Contents
Aging or ageing may also refer to:
| Look up ageing , aged , aging , or oldness in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Aging is the effect of time on a person.
Aging or ageing may also refer to:
Dynamics or dynamic may refer to:
Spin or spinning may refer to:
Age or AGE may refer to:

Spandex, Lycra, or elastane is a synthetic fiber known for its exceptional elasticity. It is a polyether-polyurea copolymer that was invented in 1958 by chemist Joseph Shivers at DuPont's Benger Laboratory in Waynesboro, Virginia, US.
Source may refer to:
CDP may refer to:

Barolo is a red Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita (DOCG) wine produced in the northern Italian region of Piedmont. It is made from the nebbiolo grape and is often described as one of Italy's greatest wines.
Stabilizer, stabiliser, stabilisation or stabilization may refer to:
Convergence may refer to:
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption and wear characteristics of those materials.
A port is a facility for receiving ships and transferring cargo.
Share may refer to:
Conduit may refer to:
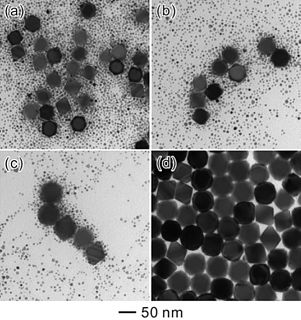
Ostwald ripening is a phenomenon observed in solid solutions or liquid sols that describes the change of an inhomogeneous structure over time, i.e., small crystals or sol particles dissolve, and redeposit onto larger crystals or sol particles.
Lustre or Luster may refer to:
A blend is a mixture of two or more different things or substances; e.g., a product of a mixer or blender.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.
Wrinkle-resistant or permanent press or durable press is a finishing method for textiles that avoids creases and wrinkles and provides a better appearance for the articles. Most cellulosic fabrics and blends of cellulosic rich fabrics tend to crease or wrinkle. A durable press finish makes them dimensionally stable and crease free. The finishing includes chemical finishing as well as mechanical finishing. Wrinkle-resistant finishes were developed in the early 20th century, as a way to deal with fabrics derived from cotton, rayon, and linen, which were found to wrinkle easily and retain the wrinkles. These treatments have a lasting effect on the fabric. Synthetics like polyester, nylon, acrylic and olefin, have a natural resistance to wrinkles and a greater stability since they do not absorb water as efficiently.

Aging or ageing, in the context of food or beverages, is the leaving of a product over an extended period of time to aid in improving the flavor of the product. Aging can be done under a number of conditions, and for a number of reasons including stronger umami flavors and tenderness.

Ageing is a kind of after treatment process for certain printed textile materials in which the goods are exposed to warm and moist atmosphere. Steaming is an evolved way to obtain the intended results. The objectives of the ageing process include the developing and fixing of the mordants and colors.