
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by a government. Coins often have images, numerals, or text on them. The faces of coins or medals are sometimes called the obverse and the reverse, referring to the front and back sides, respectively. The obverse of a coin is commonly called heads, because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse is known as tails.

Sterling is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling. In British English, its most common nickname is "quid."

Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction during the Republic, in the third century BC, through Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, denomination, and composition. A persistent feature was the inflationary debasement and replacement of coins over the centuries. Notable examples of this followed the reforms of Diocletian. This trend continued with Byzantine currency.
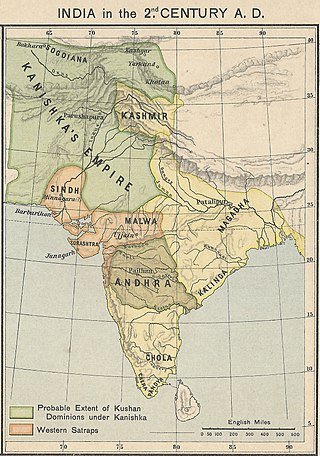
The Kushan Empire was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath, near Varanasi, where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great.

Silbannacus was an obscure Roman emperor or usurper during the Crisis of the Third Century. Silbannacus is not mentioned in any contemporary documents and his existence was forgotten until the 20th century, when two coins bearing his name were discovered, the first in the 1930s and the second in the 1980s. His unusual name suggests that he might have been of Gallic descent.

A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus Martes within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on the species; it is valued by animal trappers for the fur trade. Martens are slender, agile animals, adapted to living in the taiga, which inhabit coniferous and northern deciduous forests across the Northern Hemisphere.

The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India. This kingdom was in existence from c. 200 BC to the beginning of the common era.

Anthimachus I Theos was believed to have been an illegitimate son of Euthydemus, and one of the Greco-Bactrian kings, generally dated from around 185 BC to 170 BC.

Nicias was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in the Paropamisade. Most of his relatively few coins have been found in northern Pakistan, indicating that he ruled a smaller principate around the lower Kabul valley. He was possibly a relative of Menander I.

Indo-Scythians were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the northwestern Indian subcontinent, precisely into the modern-day South Asian regions of Afghanistan, Pakistan and northern India. The migrations persisted from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th century CE.

The Kingdom of Kuninda was an ancient central Himalayan kingdom documented from around the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century, located in the southern areas of modern Himachal Pradesh and far western areas of Uttarakhand in northern India and Doti Gadwall in Nepal.

The Satavahanas, also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late second century BCE and lasted until the early third century CE, although some assign the beginning of their rule to as early as the 3rd century BCE based on the Puranas, but uncorroborated by archaeological evidence. The Satavahana kingdom mainly comprised the present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Maharashtra. At different times, their rule extended to parts of modern Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka. The dynasty had different capital cities at different times, including Pratishthana (Paithan) and Amaravati (Dharanikota).

Panchala was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain. During Late Vedic times, it was one of the most powerful states of ancient India, closely allied with the Kuru Kingdom. By the c. 5th century BCE, it had become an oligarchic confederacy, considered one of the solasa (sixteen) mahajanapadas of the Indian subcontinent. After being absorbed into the Mauryan Empire, Panchala regained its independence until it was annexed by the Gupta Empire in the 4th century CE.
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India, between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana (Andhra) who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the "Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE.
Mytilos or Mytilus was an Illyrian king who reigned in southern Illyria, around the hinterland of Dyrrhachion and Apollonia. He was the successor of Monunios, and probably his son. Mytilus is mentioned by Pompeius Trogus and Frontinus reporting the events of the military conflict between the Illyrians and the Epirotes under Alexander II, son of Pyrrhus. From around 270 BC Mytilus minted in Dyrrhachion his own bronze coins bearing the king's name and the symbol of the city.

The Kingdom of Aksum, also known as the Kingdom of Axum, the City-State of Axum, or the Aksumite Empire, was centered in East Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in what is now Eritrea and Northern Ethiopia, and spanning Djibouti and Sudan, it extended at its height into much of Southern Arabia during the reign of Kaleb, King of Axum.
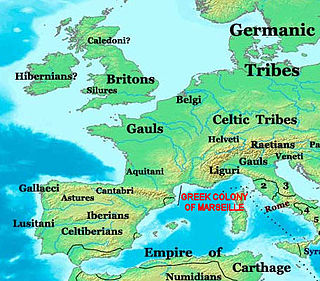
The Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul have a significant history of settlement, trade, cultural influence, and armed conflict in the Celtic territory of Gaul, starting from the 6th century BC during the Greek Archaic period. Following the founding of the major trading post of Massalia in 600 BC by the Phocaeans at present day Marseille, Massalians had a complex history of interaction with peoples of the region. Large Greek colonies also existed west of the Rhône, particularly at Agde and Béziers, the latter of which both predates, and was larger than, the Marseille colony.

Illyrian coinage which began in the 6th century BC continued up to the 1st century of Roman rule. It was the southern Illyrians who minted the first coins followed by the northern Illyrian during the Roman era. Illyrian coins have also been found in other areas apart from Illyria, such ancient Macedonia, Italy, Greece, Asia Minor and Egypt.

The Alchon Huns, also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana, and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. They were first mentioned as being located in Paropamisus, and later expanded south-east, into the Punjab and Central India, as far as Eran and Kausambi. The Alchon invasion of the Indian subcontinent eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India.

Qianlong Tongbao is an inscription used on cash coins produced under the reign of the Qianlong Emperor of the Qing dynasty. Initially the Qianlong Tongbao cash coins were equal to its predecessors in their weight and quality but as expensive military expenditures such as the Ten Great Campaigns began to take their financial toll on the government of the Qing dynasty the quality of these cash coins started to steadily decrease. The weight of the Qianlong Tongbao was changed several times and tin was added to their alloy to both reduce costs and to prevent people from melting down the coins to make utensils. As the intrinsic value of these coins was higher than their nominal value many provincial mints started reporting annual losses and were forced to close down, meanwhile the copper content of the coinage continued to be lowered while the copper mines of China were depleting. The Qianlong era also saw the conquest of Xinjiang and the introduction of cash coins to this new region of the Qing Empire.
![Coin of Yuezhi ruler Agesiles (20-1BC). Greek legend: "AR[?]EILE[?]" (Arseiles) YUEZHI. Arseiles. Late 1st century BCE.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/06/YUEZHI._Arseiles._Late_1st_century_BCE.jpg/350px-YUEZHI._Arseiles._Late_1st_century_BCE.jpg)

















