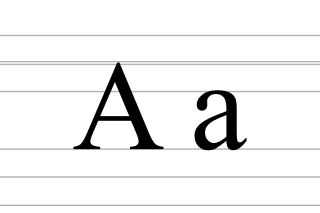
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is a, plural aes.

An alphabet is a standard set of letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from another in a given language. Not all writing systems represent language in this way: a syllabary assigns symbols to spoken syllables, while logographies assign symbols to words, morphemes, or other semantic units.
An abjad, also abgad, is a writing system in which only consonants are represented, leaving the vowel sounds to be inferred by the reader. This contrasts with alphabets, which provide graphemes for both consonants and vowels. The term was introduced in 1990 by Peter T. Daniels. Other terms for the same concept include partial phonemic script, segmentally linear defective phonographic script, consonantary, consonant writing, and consonantal alphabet.

The ancient Aramaic alphabet was used to write the Aramaic languages spoken by ancient Aramean pre-Christian tribes throughout the Fertile Crescent. It was also adopted by other peoples as their own alphabet when empires and their subjects underwent linguistic Aramaization during a language shift for governing purposes — a precursor to Arabization centuries later — including among the Assyrians and Babylonians who permanently replaced their Akkadian language and its cuneiform script with Aramaic and its script, and among Jews, but not Samaritans, who adopted the Aramaic language as their vernacular and started using the Aramaic alphabet, which they call "Square Script", even for writing Hebrew, displacing the former Paleo-Hebrew alphabet. The modern Hebrew alphabet derives from the Aramaic alphabet, in contrast to the modern Samaritan alphabet, which derives from Paleo-Hebrew.
Digamma or wau is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. It originally stood for the sound but it has remained in use principally as a Greek numeral for 6. Whereas it was originally called waw or wau, its most common appellation in classical Greek is digamma; as a numeral, it was called episēmon during the Byzantine era and is now known as stigma after the Byzantine ligature combining σ-τ as ϛ.
Epsilon is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a mid front unrounded vowel IPA:[e̞] or IPA:[ɛ̝]. In the system of Greek numerals it also has the value five. It was derived from the Phoenician letter He . Letters that arose from epsilon include the Roman E, Ë and Ɛ, and Cyrillic Е, È, Ё, Є and Э. The name of the letter was originally εἶ, but it was later changed to ἒ ψιλόν in the Middle Ages to distinguish the letter from the digraph αι, a former diphthong that had come to be pronounced the same as epsilon.
The Hebrew alphabet, known variously by scholars as the Ktav Ashuri, Jewish script, square script and block script, is an abjad script used in the writing of the Hebrew language and other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, Judeo-Arabic, and Judeo-Persian. In modern Hebrew, vowels are increasingly introduced. It is also used informally in Israel to write Levantine Arabic, especially among Druze. It is an offshoot of the Imperial Aramaic alphabet, which flourished during the Achaemenid Empire and which itself derives from the Phoenician alphabet.

The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered excepting several letters splitting—i.e. ⟨J⟩ from ⟨I⟩, and ⟨U⟩ from ⟨V⟩—additions such as ⟨W⟩, and extensions such as letters with diacritics, it forms the Latin script that is used to write most languages of modern Europe, Africa, America and Oceania. Its basic modern inventory is standardised as the ISO basic Latin alphabet.

S, or for lowercase, s, is the nineteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and other latin alphabets worldwide. Its name in English is ess, plural esses.
The Coptic alphabet is the script used for writing the Coptic language, the most recent development of Egyptian. The repertoire of glyphs is based on the uncial Greek alphabet, augmented by letters borrowed from the Egyptian Demotic. It was the first alphabetic script used for the Egyptian language. There are several Coptic alphabets, as the script varies greatly among the various dialects and eras of the Coptic language.
The Phoenician alphabet is an abjad used across the Mediterranean civilization of Phoenicia for most of the 1st millennium BC. It was one of the first alphabets, and attested in Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. In the history of writing systems, the Phoenician script also marked the first to have a fixed writing direction—while previous systems were multi-directional, Phoenician was written horizontally, from right to left. It developed directly from the Proto-Sinaitic script used during the Late Bronze Age, which was derived in turn from Egyptian hieroglyphs.
Omicron is the fifteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. This letter is derived from the Phoenician letter ayin: . In classical Greek, omicron represented the close-mid back rounded vowel IPA:[o] in contrast to omega which represented the open-mid back rounded vowel IPA:[ɔː] and the digraph ου which represented the long close-mid back rounded vowel IPA:[oː]. In modern Greek, both omicron and omega represent the mid back rounded vowel IPA:[o̞] or IPA:[ɔ̝]. Letters that arose from omicron include Roman O and Cyrillic O|Ю (Cyrillic)|Ю. The word literally means "little O" as opposed to "great O". In the system of Greek numerals, omicron has a value of 70.

The Ugaritic writing system is a cuneiform abjad with syllabic elements used from around either 1400 BCE or 1300 BCE for Ugaritic, an extinct Northwest Semitic language. It was discovered in Ugarit, modern Ras Shamra, Syria, in 1928. It has 30 letters. Other languages, particularly Hurrian, were occasionally written in the Ugaritic script in the area around Ugarit, although not elsewhere.

San (Ϻ) was an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. Its shape was similar to modern M or Mu, or to a modern Greek Sigma (Σ) turned sideways, and it was used as an alternative to Sigma to denote the sound. Unlike Sigma, whose position in the alphabet is between Rho and Tau, San appeared between Pi and Qoppa in alphabetic order. In addition to denoting this separate archaic character, the name San was also used as an alternative name to denote the standard letter Sigma.
Sigma is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used as an operator for summation. When used at the end of a letter-case word, the final form (ς) is used. In Ὀδυσσεύς (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end. The Latin letter S derives from sigma while the Cyrillic letter Es derives from a lunate form of this letter.
The history of the alphabet goes back to the consonantal writing system used to write Semitic languages in the Levant during the 2nd millennium BC. Nearly all alphabetic scripts used throughout the world today ultimately go back to this Semitic script. Its origins can be traced to the Proto-Sinaitic script that represented the language of Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in Egypt. Unskilled in the complex hieroglyphic system used to write the Egyptian language, which required a large number of pictograms, they selected a small number of those commonly seen in their surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values, of their own Canaanite language. This script was partly influenced by the older Egyptian hieratic, a cursive script related to Egyptian hieroglyphs. The Semitic alphabet became the ancestor of multiple writing systems across the Middle East, Europe, northern Africa, and South Asia, mainly through Phoenician and the closely related Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, and later Aramaic and the Nabatean—derived from the Aramaic alphabet and developed into the Arabic alphabet—five closely related members of the Semitic family of scripts that were in use during the early 1st millennium BC.
Geʽez is a script used as an abugida (alphasyllabary) for several Afro-Asiatic and Nilo-Saharan languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It originated as an abjad and was first used to write the Geʽez language, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Eritrean Catholic Church, the Ethiopian Catholic Church, and Haymanot Judaism of the Beta Israel Jewish community in Ethiopia. In the languages Amharic and Tigrinya, the script is often called fidäl (ፊደል), meaning "script" or "letter". Under the Unicode Standard and ISO 15924, it is defined as Ethiopic text.

The history of the Greek alphabet starts with the adoption of Phoenician letter forms in the 9th–8th centuries BC during early Archaic Greece and continues to the present day. The Greek alphabet was developed during the Iron Age, centuries after the loss of Linear B, the syllabic script that was used for writing Mycenaean Greek until the Late Bronze Age collapse and Greek Dark Age. This article concentrates on the development of the alphabet before the modern codification of the standard Greek alphabet.
Heta is a conventional name for the historical Greek alphabet letter Eta (Η) and several of its variants, when used in their original function of denoting the consonant.

Many local variants of the Greek alphabet were employed in ancient Greece during the archaic and early classical periods, until around 400 BC, when they were replaced by the classical 24-letter alphabet that is the standard today. All forms of the Greek alphabet were originally based on the shared inventory of the 22 symbols of the Phoenician alphabet, with the exception of the letter Samekh, whose Greek counterpart Xi (Ξ) was used only in a sub-group of Greek alphabets, and with the common addition of Upsilon (Υ) for the vowel. The local, so-called epichoric, alphabets differed in many ways: in the use of the consonant symbols Χ, Φ and Ψ; in the use of the innovative long vowel letters, in the absence or presence of Η in its original consonant function ; in the use or non-use of certain archaic letters ; and in many details of the individual shapes of each letter. The system now familiar as the standard 24-letter Greek alphabet was originally the regional variant of the Ionian cities in Anatolia. It was officially adopted in Athens in 403 BC and in most of the rest of the Greek world by the middle of the 4th century BC.