
The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, Greece, and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. The word Acropolis is from the Greek words ἄκρον and πόλις. The term acropolis is generic and there are many other acropoleis in Greece. During ancient times the Acropolis of Athens was also more properly known as Cecropia, after the legendary serpent-man Cecrops, the supposed first Athenian king.

Pergamon or Pergamum, also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (Πέργαμος), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located 26 kilometres (16 mi) from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north side of the river Caicus and northwest of the modern city of Bergama, Turkey.

Selinunte was a rich and extensive ancient Greek city of Magna Graecia on the south-western coast of Sicily in Italy. It was situated between the valleys of the Cottone and Modione rivers. It now lies in the comune of Castelvetrano, between the frazioni of Triscina di Selinunte in the west and Marinella di Selinunte in the east.

Eleusinion, also called the City Eleusinion was a sanctuary on the lower part of the north slope of the Acropolis in Athens, Greece, dedicated to Demeter and Kore (Persephone). It was the central hub of Eleusinian Mysteries within Athens and the starting point for the annual procession to Eleusis, in the northwest of Attica. Religious activity is attested in the area from the 7th century BC and construction took place throughout late Archaic, Classical, Hellenistic, and Roman periods. The sanctuary was enclosed within the new city walls built after the Herulian sack of Athens in AD 267 and it remained in use until the late fourth century AD.

The Pnyx is a hill in central Athens, the capital of Greece. Beginning as early as 507 BC, the Athenians gathered on the Pnyx to host their popular assemblies, thus making the hill one of the earliest and most important sites in the creation of democracy.

The ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill known as the Agoraios Kolonos, also called Market Hill. The Agora's initial use was for a commercial, assembly, or residential gathering place.

The Stoa of Attalos was a stoa in the Agora of Athens, Greece. It was built by and named after King Attalos II of Pergamon, who ruled between 159 BC and 138 BC. The building was reconstructed from 1952 to 1956 by the American School of Classical Studies at Athens and currently houses the Museum of the Ancient Agora.

Brauron was one of the twelve cities of ancient Attica, but never mentioned as a deme, though it continued to exist down to the latest times. It was situated on or near the eastern coast of Attica, between Steiria and Halae Araphenides, near the river Erasinus. Brauron is celebrated on account of the worship of Artemis Brauronia, in whose honour a festival was celebrated in this place. This site includes the remains of a temple, a stoa, and a theatre, providing insights into the religious practices and social life of ancient Greece. It's significance as a religious and cultural site can be further understood through the exploration of its archeological remains and historical accounts.

Lycosura was a city in the ancient Parrhasia region of south Arcadia said by Pausanias to be the oldest city in the world, although there is no evidence for its existence before the fourth century BCE. Its current significance is chiefly associated with the sanctuary of the goddess Despoina, which contained a colossal sculptural group that Pausanias wrote was made by Damophon of Messene. This group comprises acrolithic-technique statues of Despoina and Demeter seated on a throne, with statues of Artemis and the Titan Anytos standing on either side of them – all in Pentelic marble. The dates of both the temple and the sculptural group have occasioned some dispute. Remains of a stoa, altars, and other structures have been found at the site as well. The Sanctuary of Despoina at Lycosoura is located 9 km WSW of Megalopolis, 6.9 km SSE of Mount Lykaion, and 160 km SW of Athens. There is a small museum at the archaeological site housing small finds as well as part of the cult group, while the remains of the cult statues of Despoina and Demeter are displayed at the National Archaeological Museum of Athens.

The South Stoa I of Athens was located on the south side of the Agora, in Athens, Greece, between the Heliaia and the Enneakrounos, a southeastern fountain house. It was built around 425–400 BC. The stoa was in use until c. 150 BC, when it was replaced by South Stoa II.

Termessos was a Pisidian city built at an altitude of more than 1000 metres at the south-west side of the mountain Solymos in the Taurus Mountains. It lies 17 kilometres to the north-west of Antalya. It was founded on a natural platform on top of Güllük Dağı, soaring to a height of 1,665 metres from among the surrounding travertine mountains of Antalya.

The Heraion of Perachora is a sanctuary of the goddess Hera situated in a small cove of the Corinthian gulf at the end of the Perachora peninsula. In addition to a temple of Hera of unusual construction and antiquity, the remains of a number of other structures have also been found, including an L-shaped stoa, a large cistern, dining rooms, and a second potential temple. The Sanctuary of Hera at Perachora is 14.2 kilometres (8.8 mi) north-northwest of Corinth and 75.9 kilometres (47.2 mi) west of Athens. Although there is debate between Argos, Megara and Corinth, the sanctuary was probably under the control of Corinth, as it faced the harbors of that powerful city across the Corinthian gulf. Cult activity at the site continued from perhaps the 9th century BCE to 146 BCE, when the Roman general Mummius sacked Corinth during the war with the Achaean League. In the Roman period, domestic structures were built on the site, indicating that the area was no longer a sanctuary. This site is significant for the study of the origins of Greek temple architecture and rural cults.

The Brauroneion was the sanctuary of Artemis Brauronia on the Athenian Acropolis, located in the southwest corner of the Acropolis plateau, between the Chalkotheke and the Propylaea in Greece. It was originally dedicated during the reign of Peisistratos. Artemis Brauronia, protector of women in pregnancy and childbirth, had her main sanctuary at Brauron, a demos on the east coast of Attica.

The city of Athens during the classical period of ancient Greece was the major urban centre of the notable polis (city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Isagoras. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC. The peak of Athenian hegemony was achieved in the 440s to 430s BC, known as the Age of Pericles.

The Acropolis of Rhodes is the acropolis, or upper town, of ancient Rhodes dating from the 5th century BC and located 3 kilometers SW from the centre of the modern city. Situated on Monte Smith overlooking the west coast of the island, the archaeological site includes some of the most important monuments in the ancient city, such as the Temple of Athena Polias and Zeus Polieus and the Temple of Apollo, below which are a stadium, an odeon and a gymnasium. Unlike other acropoleis, no walled citadel was built here.


The Sanctuary of Asclepius was a sanctuary in Epidaurus dedicated to Asclepius. Especially in the Classical and Hellenistic periods, it was the main holy site of Asclepius. The sanctuary at Epidaurus was the rival of such major cult sites as the Sanctuary of Zeus at Olympia and Apollo at Delphi. The temple was built in the early 4th century BC. If still in use by the 4th century AD, the temple would have been closed during the persecution of pagans in the late Roman Empire, when the Christian Emperors issued edicts prohibiting non-Christian worship. In 1988, the temple was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List because of its exceptional architecture and its importance in the development and spread of healing sanctuaries (asclepeion) throughout Classical Antiquity.

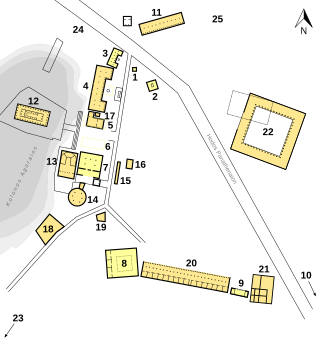
The Square Peristyle is the modern name for a structure on the east side of the Ancient Agora of Athens, which was among the largest peristyles built in Classical Grece. Construction began around 300 BC, but was abandoned ca. 285-275 BC, leaving the structure unfinished. It probably served as Athens' law courts at the beginning of the Hellenistic period, but fell out of use. In the early second century BC the building was demolished and the material was reused in South Stoa II, on the southern side of the Agora. The Stoa of Attalos was subsequently built over the top of its foundations.

























